Fig. 7 Surface and interface engineering: (A) Schematic representation of CO2 conversion to formate mediated on a GC electrode in a liquid-phase electrolyzer and CO2RR mediated on a GDE modified by [EMIM]+ layer in a gas-phase electrolyzer. (B) Conformational and chemical characterization of pristine GC cathode and modified GC cathode obtained by immobilization of imidazolium cation by SEM and WCA. (C) On IM+EE/GDE cathode with 9 successive electrolysis at different current densities, respectively. (D) Variation of the average full-cell energy efficiency and EC of formate generation with applied current density on bare carbon GDE and IM+EE/GDE, respectively[12]. (E) Schematic diagram of the preparation process and the reaction mechanism of Si-Bi@C photocathode. SEM images of (F) SiNWs, (G) BiMOF and (H) Si-Bi@C800. (I) FE of Si-Bi@C1000 photocathode at different potentials (left). Chemical generation rate versus potential for Si, Si-Bi@C600, Si-Bi@C800 and Si-Bi@C1000 photocathodes (middle). Comparison of the catalytic performance of the Si-Bi@C800 photocathode with that of the reported photocathodes for the formation of formate from CO2 (right)[9].
Other figure/table from this article

 Fig. 1 Electrode configurations of Cu-based materials: (A) Catalytic mechanism of Cu electrode. (B) Scanning electron microscope images (SEM) of 0.5-UiO/Cu. (C) SEM and EDS elemental mapping of cross-section. (D) FE vs. potential of CO2RR and HER products[
Fig. 1 Electrode configurations of Cu-based materials: (A) Catalytic mechanism of Cu electrode. (B) Scanning electron microscope images (SEM) of 0.5-UiO/Cu. (C) SEM and EDS elemental mapping of cross-section. (D) FE vs. potential of CO2RR and HER products[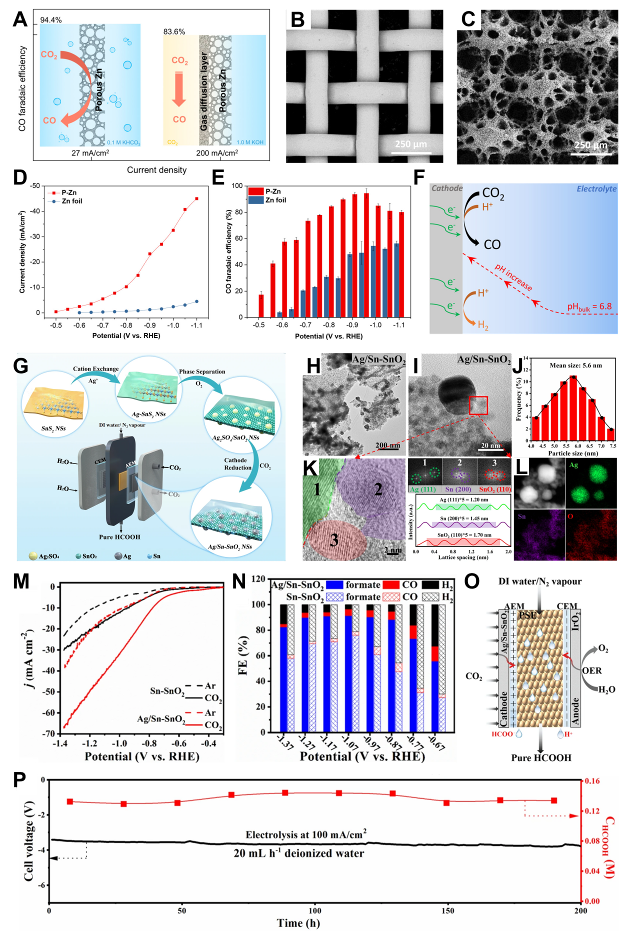 Fig. 2 Electrode configurations of Zn, Ag, and Sn-based materials: (A) Porous Zn electrode can convert CO2 to CO at -0.95 V (relative to the RHE electrode) with high FE (∼95%) and current density (27 mA cm−2). (B) SEM images of Cu lattice and (C) P-Zn. (D) Potential-dependent current densities of P-Zn and Zn foils. (E) FE of CO. (F) Schematic representation of the local pH effect in CO2RR[
Fig. 2 Electrode configurations of Zn, Ag, and Sn-based materials: (A) Porous Zn electrode can convert CO2 to CO at -0.95 V (relative to the RHE electrode) with high FE (∼95%) and current density (27 mA cm−2). (B) SEM images of Cu lattice and (C) P-Zn. (D) Potential-dependent current densities of P-Zn and Zn foils. (E) FE of CO. (F) Schematic representation of the local pH effect in CO2RR[ Fig. 4 Graphene and carbon nanotube thin-film electrode constructs: (A) Synthesis procedures of RGOL@PPS/CNT+RGO thin films. (B, C) SEM images of Cu2O nanocrystals on RGOL@PPS/CNT+RGO thin films at 15 s and (D, E) 90 s electrodeposition times. (F) Polarization curves of (PPS/CNT+RGO)-Cu2O, RGOL@PPS/CNT+RGO and PPS/CNT+RGO substrates with polarization curves[
Fig. 4 Graphene and carbon nanotube thin-film electrode constructs: (A) Synthesis procedures of RGOL@PPS/CNT+RGO thin films. (B, C) SEM images of Cu2O nanocrystals on RGOL@PPS/CNT+RGO thin films at 15 s and (D, E) 90 s electrodeposition times. (F) Polarization curves of (PPS/CNT+RGO)-Cu2O, RGOL@PPS/CNT+RGO and PPS/CNT+RGO substrates with polarization curves[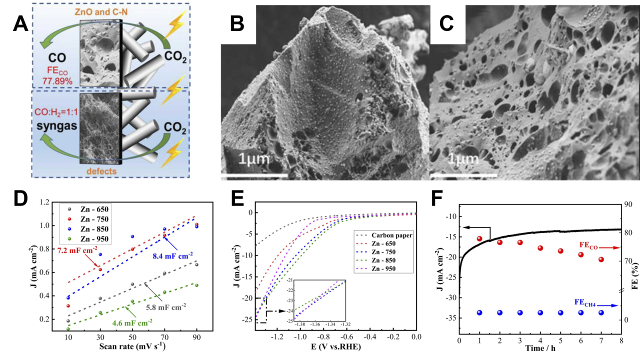 Fig. 5 Carbon aerogel versus carbon foam electrode constructs: (A) Schematic representation of the active sites of Zn-750 and Zn-950. (B) SEM images of Zn-650 and (C) Zn-750. (D) ECSA curves and (E) LSV curves of Zn-T. (F) FE stability of Zn-750 after 8 h of continuous operation at −1.0 V vs. RHE[
Fig. 5 Carbon aerogel versus carbon foam electrode constructs: (A) Schematic representation of the active sites of Zn-750 and Zn-950. (B) SEM images of Zn-650 and (C) Zn-750. (D) ECSA curves and (E) LSV curves of Zn-T. (F) FE stability of Zn-750 after 8 h of continuous operation at −1.0 V vs. RHE[ Fig. 6 Emerging structures with 3D printed electrodes: (A) 3D printed electrodes with different shapes and optimal 3Dp-PNCE catalytic electrodes. (B) TEM images of the optimal 3Dp-PNCE. (C) Comparison of current densities on 3Dp-CE, 3Dp-NCE, and 3Dp-PNCE. (D) CO2RR stability test of 3Dp-PNCE at −0.7 V[
Fig. 6 Emerging structures with 3D printed electrodes: (A) 3D printed electrodes with different shapes and optimal 3Dp-PNCE catalytic electrodes. (B) TEM images of the optimal 3Dp-PNCE. (C) Comparison of current densities on 3Dp-CE, 3Dp-NCE, and 3Dp-PNCE. (D) CO2RR stability test of 3Dp-PNCE at −0.7 V[