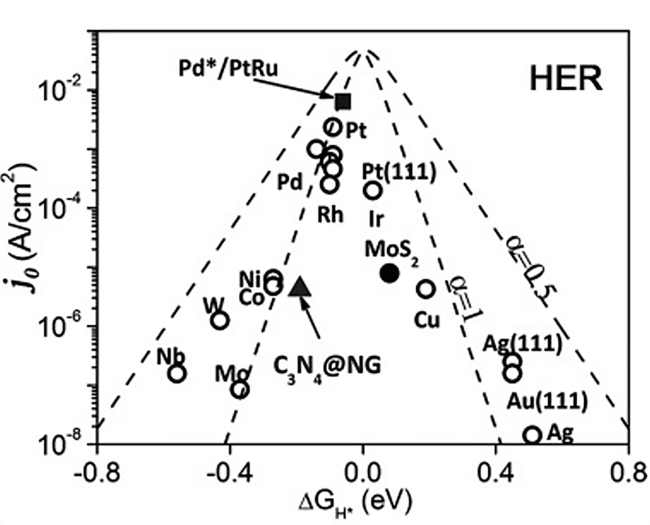
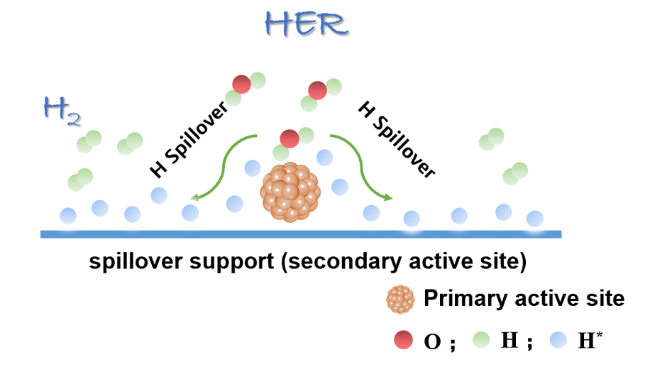
1 引言
2 氢溢流型电催化剂
2.1 金属氧化物
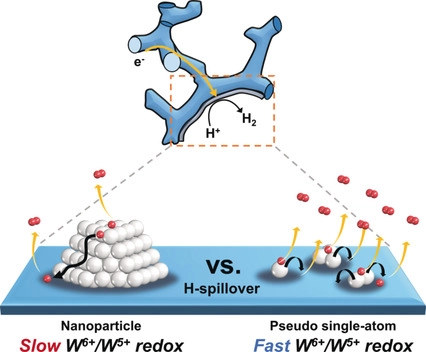
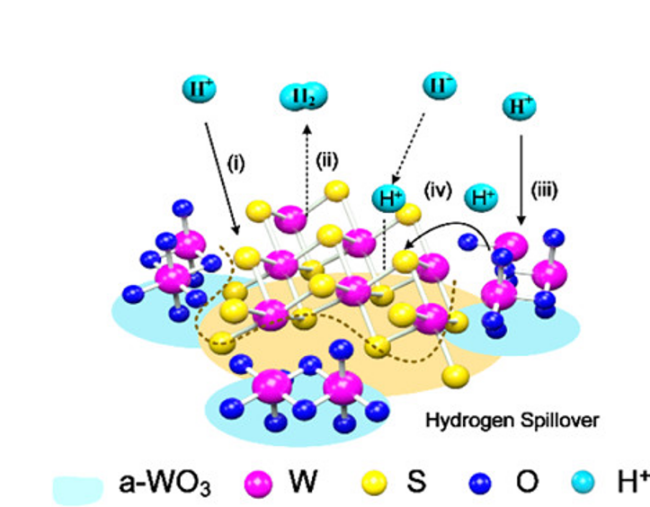
2.1.1 氧化钨
2.1.2 氧化钛
2.1.3 氧化镍
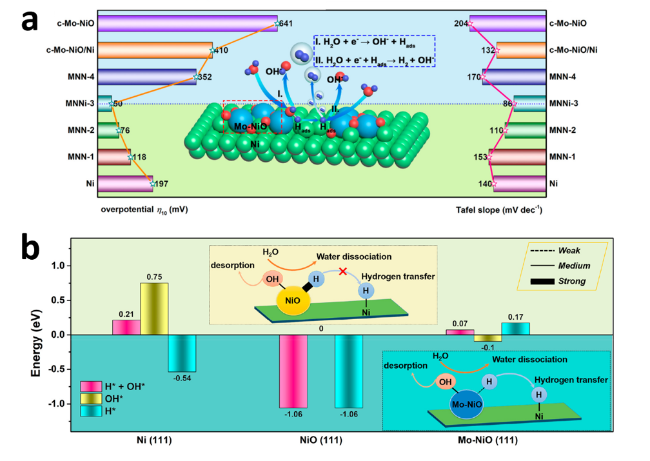
图5 (a) 电流密度为10 mA·cm-2时的过电位(左)和Tafel斜率(右), 插图为HER机理的示意图;(b)H*+OH*、OH*和H*在不同活性位点处的吸附能, 插图为NiO/Ni和Mo-NiO/Ni电化学反应中氢转移的化学示意图[45]Fig.5 (a) Overpotential )left) and Tafel slope (right) at a current density of 10 mA·cm-2, inset is a schematic representation of the HER mechanism; (b) Adsorption energy of H*+OH*, OH* and H* at different active sites, inset is a schematic representation of the chemistry of hydrogen transfer in NiO/Ni and Mo-NiO/Ni electrochemical reactions[45]. Copyright 2019, ACS Energy Lett. |
2.1.4 其他金属氧化物
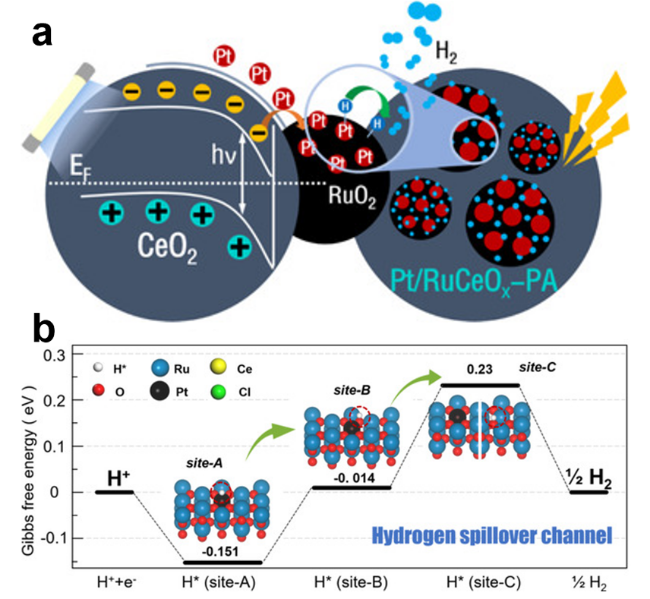
图7 (a) 光生电子通过RuO2与CeO2间异质界面转移并在RuO2上锚定Pt单原子示意图; (b) Pt/RuCeOx-PA上H*的转移路径[42]Fig.7 (a) Schematic diagram showing the photogenerated charge separation by an internal electric field at the RuO2/CeO2 heterojunction and the incorporation of platinum atoms on RuCeOx; (b) Transfer path of H* on Pt/RuCeOx-PA. [42]. Copyright 2020, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. |
图8 (a) 二元组分催化剂体系的氢溢流示意图;(b) 具有原子级多催化位点单组分催化剂体系氢溢流示意图。红色、蓝色和灰色的球分别代表强H吸附、热中性H吸附和H2易脱附位点[63]Fig.8 (a) The conventional hydrogen spillover based binary-component catalysts system; (b) Hydrogen spillover one-component catalyst system with atomic-level multiple catalytic sites. The red, blue, and gray spheres represent strong H adsorption, thermoneutral H adsorption, and easy H2 desorption sites, respectively[63]. Copyright 2022, Nat. Commun. |
2.2 金属磷化物
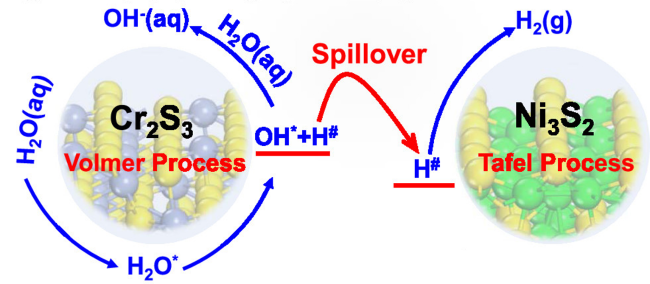
2.3 金属硫化物
3 结论与展望
表1 有无氢溢流效应的电催化剂析氢性能比较Table 1 The hydrogen-evolving performance comparison of electrocatalysts with and without hydrogen spillover effect |
| Sample | Electrolyte | Loading | Overpotential (10 mA·cm-2) | Tafel slope | Contrast sample | Overpotential (10 mA·cm-2) | Tafel slope | ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
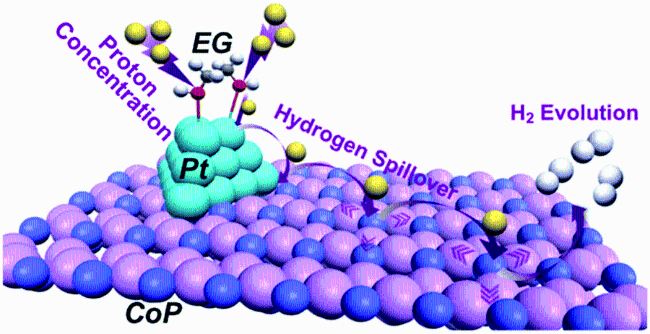
| EG-Pt/CoP | 0.5 M H2SO4 | 1.5 wt% | 21 | 42.5 | EG-CoP | 167 | 104.6 | 5 |
| LPWGA | 0.5 M H2SO4 | 0.81(ugPt·cm-2) | 42 | 30 | LPGA | 52 | - | 28 |
| PtCu/WO3@CF | 0.5 M H2SO4 | 0.0032(ugPt·cm-2) | 41 | 45.9 | WO3@CF | 182 | 101.49 | 33 |
| Ru-WO3-x/CP | 1.0 M PBS | 5.1 wt% | 19 | 41 | Ru/C | 86 | 78 | 35 |
| 1T-WS2/a-WO3 | 0.5 M H2SO4 | - | 212@100 mA·cm-2 | 102.2 | 1T-WS2 | 308@100 mA·cm-2 | 136.1 | 37 |
| WO3·2H2O/WS2 | 0.5 M H2SO4 | - | 152@100 mA·cm-2 | 54 | WO3·2H2O particles | 300@100mA·cm-2 | 148 | 38 |
| VO-rich Pt/TiO2 | 0.5 M H2SO4 | 0.4 wt% | 45.28 mA @100 mV | 34 | VO-deficient Pt/TiO2 | 2.71mA@100 mV | 52 | 41 |
| Mo-NiO/Ni | 1.0 M KOH | 16 wt% | 50 | 86 | Mo-NiO/Ni-4 | 354 | 170 | 45 |
| HOM-NiO/Cu | 1.0 M KOH | - | 33 | 51 | NiO/Cu | 106 | 120 | 53 |
| Pt/RuCeOxPA | 1.0 M KOH | 0.5wt% | 45 | 36 | Pt/RuCeOx-CA | 72 | 116 | 42 |
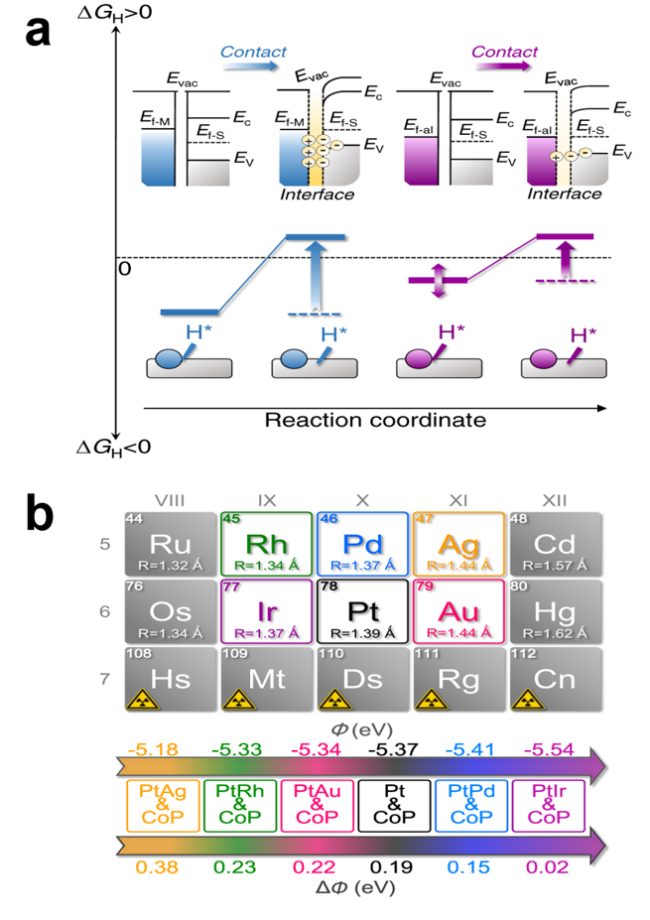
| Pt2Ir1/CoP | 0.5 M H2SO4 | 1.0 wt% | 7 | 25.2 | CoP | 150 | 108.1 | 65 |