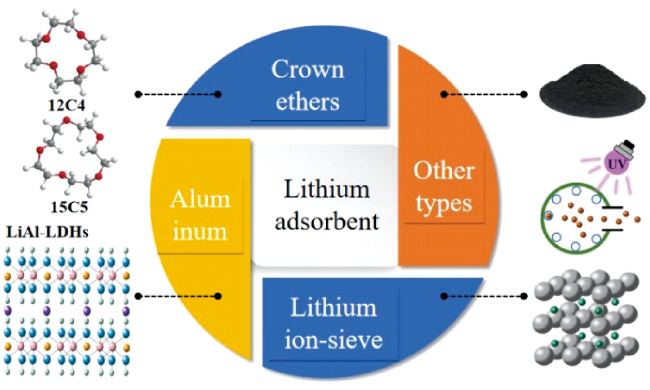
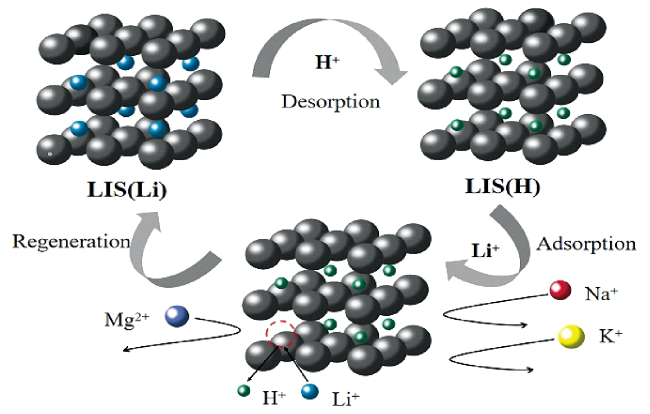
1 引言
2 冠醚类吸附剂
2.1 冠醚吸附剂的制备
2.2 选择性提锂性能
表1 冠醚配体复合吸附材料的性能Table 1 Performance of crown ether ligand composite adsorption materials |
| Crown ether ligands | Matrixes | Specific surface area (m2/g) | pH | Adsorption capacity (mg/g) | Selectivity α(Li/Na) | Cycling stability | ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
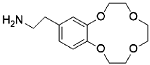 Aminoethylbenzo-12-crown-4 | Polymer nanosheets (PMBA-PMA) | / | 7 | 14.67 | / | 90% (Five cycles) | 30 |
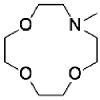 1-aza-12-crown-4 | mesoporous silica SBA-15 3-Aminopropyltriethoxy 4-ylsilane | 578 | 8 | 7.63 × 10-3 | / | / | 31 |
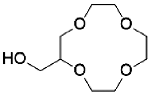 2- (hydroxymethyl) 12-crown-4 | graphene oxide chitosan polyvinyl alcohol | 101.5 | 7 | 168.50 | 2.51 | 88.31% (Five cycles) | 32 |
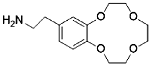 Aminoethylbenzo-12-crown-4 | Porous polymer substrate (PVBC) | / | 7 | 4.22 | 6.59 | 95.0% (Five cycles) | 35 |
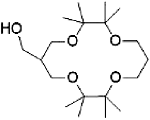 Octamethyl 14-crown-4 | methacrylate polymer | / | / | 3.05 | / | / | 36 |
1) 选择性系数α,也称分离因子,是表示某一单元分离操作或某一分离流程将两种物质分离的程度,其计算方法为 =Kd(Li+)/Kd(Me)。Me: K+、Na+、Ca2+、Mg2+。 2) Kd为吸附分配系数,是指一定温度达到反应平衡时,组分在固定相中的质量分数与流动相中的质量浓度之比,其大小反映离子在固液两相中的移动与分离能力。 |
2.3 选择性提锂机理
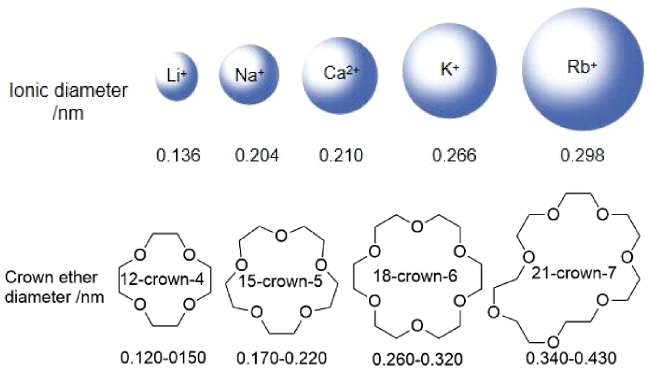
2.3.1 冠醚空穴尺寸与离子尺寸的匹配程度
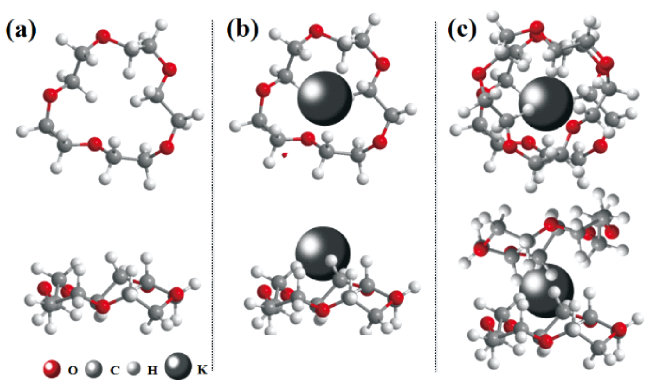
2.3.2 冠醚分子的柔软程度
2.3.3 供体杂原子以及取代基
3 铝基吸附剂
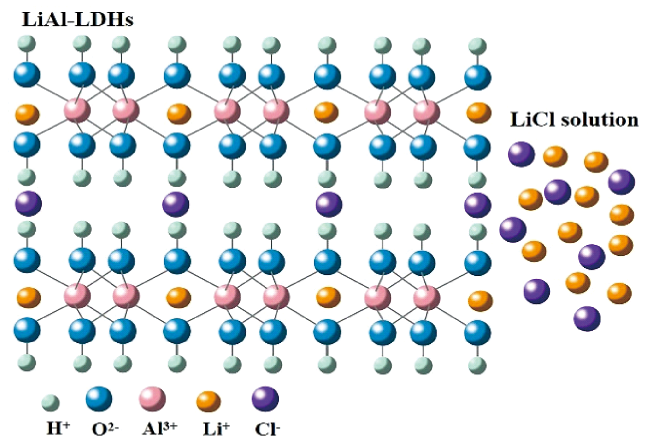
3.1 铝基吸附剂的制备
3.2 铝基吸附剂的选择性提锂机理
3.3 铝基吸附剂的选择性提锂性能
表2 三种金属基吸附剂性能比较Table 2 Performance comparison of three metal-based adsorbent |
| Performance | Al-based | Mn-based | Ti-based |
|---|---|---|---|
| Li+ Adsorption Capacity | √ | √√ | √√√ |
| Li+ Selectivity | √ | √√√ | √√ |
| Technology Maturity | √√√ | √√ | √ |
| Stability and Regeneration Ability | √√√ | √ | √√ |
| Facile Operation Conditions | √√√ | √ | √√ |
| Environmental Safety | √√√ | √ | √√ |
| Low Preparation Cost | √√√ | √ | √√ |
表3 铝基吸附剂的合成方法与性能Table 3 Synthesis methods and properties of aluminum-based adsorbents |
| Adsorbent | Source | Method | Li+ adsorption capacity (mg/g) | pH | Selectivity (α) | Recovery rate | ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LiAl-LDHs | AlCl3·6H2O NaOH Na2CO3 | Reaction coupling separation technology | / | / | / | 96.07% | 55 |
| MLDH (Fe3O4 doped LiAl-LDHs) | FeCl3·6H2O AlCl3·6H2O LiCl·H2O NaOH FeCl2·4H2O | Sectional chemical co-precipitation method | 5.83 | 7 | α(Li/Mg)= 362.68 | / | 56 |
| Al(OH)3 | AlCl3·6H2O NaOH brine | co-precipitation method | / | 7.5 | / | 76.4% | 57 |
| LiOH/Al(OH)3 | NaOH anhydrous aluminum chloride anhydrous lithium | single step co-precipitation | 15.06 | 6~7 | / | / | 58 |
| Li/Al-LDHs | Al(OH)3 LiOH·H2O | hydrothermal method | / | / | α(Li/Na)= 47.80 | 91% | 59 |
4 锂离子筛吸附剂
4.1 离子筛吸附剂制备
4.1.1 Li-Mn-O系离子筛吸附剂制备
4.1.2 Li-Ti-O系离子筛吸附剂制备
4.2 锂离子嵌入/脱嵌机理
4.2.1 氧化还原机理
4.2.2 离子交换机理
4.2.3 复合机理
4.3 锂离子筛选择性提锂性能
4.4 成型锂离子筛吸附剂
表4 不同类型钛基离子筛合成方法与性能Table 4 Synthesis methods and properties of different titanium-based ion sieves |
| Precursor | Source | Method | Li+ adsorption Capacity (mg/g) | pH | Selectivity (α) | Cycling stability | ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Li4Ti5O12 | TTIP LiOH·H2O | solvothermal reaction | 35.5 | 13 | / | 92.5% (Five cycles) | 12 |
| Li4Ti5O12 | Ti3AlC2 LiOH | two-step hydrothermal method | 43.20 | 12.1 | α(Li/Mg) =269.00 | 93% (Twenty cycles) | 70 |
| Li4Ti5O12 | TiO2LiOH | Soft hydrothermal method | 39.43 | / | / | / | 81 |
| Li2TiO3 | C2H3LiO2·2H2O TiO2 | high-temperature calcination | 40.16 | 10 | α(Li/Mg) =5441.17 | 98% (Five cycles) | 87 |
| 3DM-Li4Ti5O12 | CH3COOLi C12H28O4Ti | hydrothermal method low temperature calcination method | 38.24 | / | α(Li/Mg) =30.00 | 80% (Six cycles) | 90 |
| Li2TiO3 | Ti(OBu)4 Li2CO3 | solid state reaction | 34.2 | 12 | α(Li/Na) =19.96 | 90.6% (Eight cycles) | 92 |
表5 不同类型锰基离子筛合成方法与性能Table 5 Synthesis methods and properties of different manganese ion sieves |
| Precursor | Source | Method | Li+ adsorption capacity | pH | Selectivity | Cycling stability | ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-D Li4Mn5O12 | MnSO4LiNO3 | hydrothermal method low-temperature solid-phase reaction | 6.62 mmol/g | / | α(Li/Mg) =599.12 | / | 66 |
| LiMg0.56Mn1.50O4 | MnCl2·4H2O Mg(NO3)2·6H2O LiOH | soft chemical method | 37.4 mg/g | 12 | / | 95% (Four cycles) | 89 |
| LiMxMn2-xO4(M=Mg,Cu and Zn) | Li2CO3 CuO ZnO MgCO3MnO | high-temperature calcination | / | / | / | / | 88 |
| Li1.6(Mn0.7Al0.3)1.6O4 | MnO2LiCl AlCl3 | hydrothermal method | 32.32 mg/L | / | / | 95% (Five cycles) | 91 |
| Li1.33Mn1.67O4 | Li2CO3MnCO3 | solid-phase synthesis method | 10.00 mg/g | / | / | / | 95 |
| Li1.6Mn1.6O4 | KMnO4LiOH | hydrothermal method Solid high temperature sintering method | 41 mg/g | / | C =474.46 | 85.37% (Five cycles) | 97 |
5 其他类型吸附剂
6 结论与展望
表6 冠醚、铝基、锂离子筛型以及其他类型吸附剂的优缺点总结Table 6 Summary of advantages and disadvantages of crown ether, aluminum based, lithium-ion sieve type, and other types of adsorbents |
| Performance | Crown ether | Alumina-based adsorbent | Lithium ion-sieve | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adsorption Capacity | ★★ | ★ | ★★★ | ★★ |
| Selectivity | ★★ | ★ | ★★★ | ★★ |
| Technology Maturity | ★ | ★★★ | ★★ | ★ |
| Stability and Regeneration | ★★ | ★★★ | ★ | ★★ |
| Cost | ★ | ★★★ | ★★ | ★ |