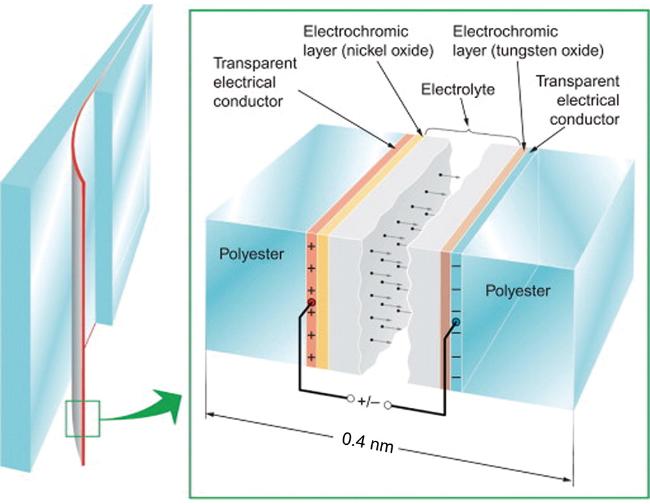
1 引言
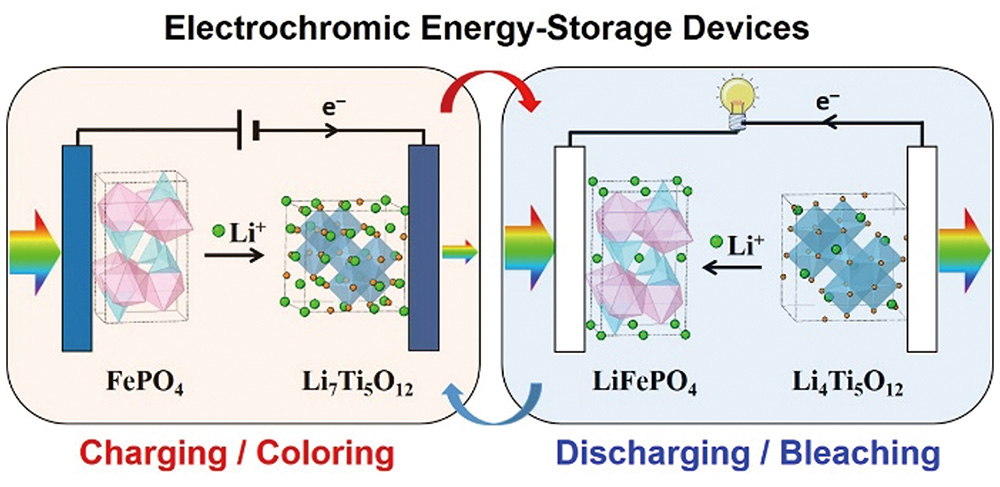
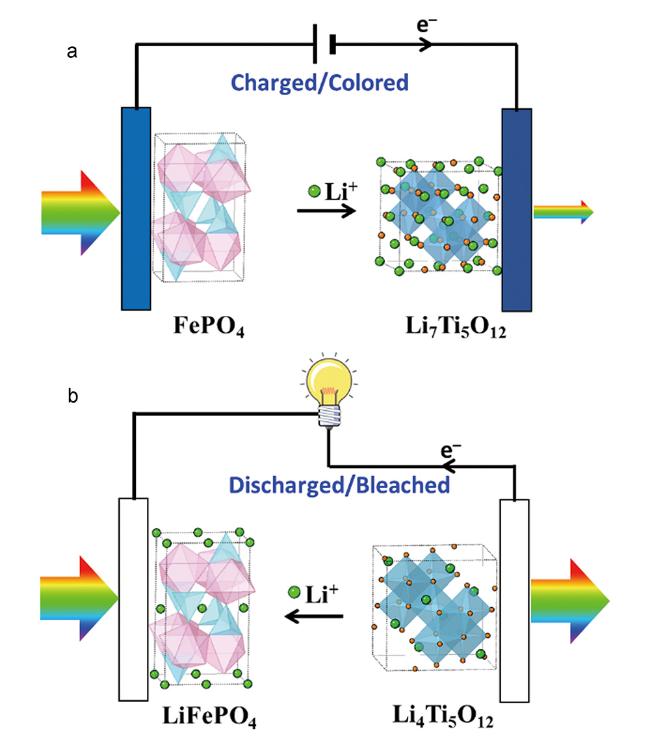
| $LiFePO_{4} - Li^{+} - e^{-} \longrightarrow FePO_{4}$ | (2) | |||
| 透明 | 着色 | |||
| $Li_{4}Ti_{5}O_{12} + 3Li^{+} + 3e^{-} \longrightarrow Li_{7}Ti_{5}O_{12}$ | (3) | |||
| 透明 | 着色 | |||
2 电致变色电池
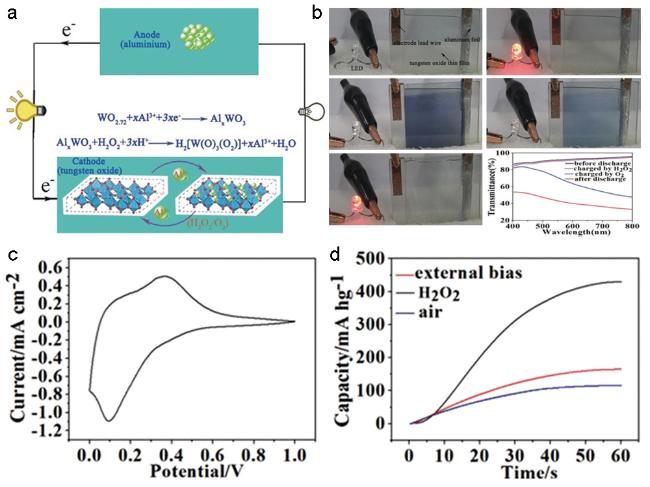
图3 (a) 铝/氧化钨电致变色电池的工作原理示意图;(b) 电致变色电池的颜色与荷电状态相关;(c) 电池的循环伏安曲线;(d) 不同条件充电(空气、加微量双氧水、外电路)后电池的放电曲线[6]Fig. 3 (a) The working mechanism of the Al-tungsten oxide electrochromic battery;(b) the state of charge of the Al-tungsten oxide electrochromic battery is associated with its transparency;(c) cyclic voltammetry(CV) curve of the two electrode Al-tungsten oxide battery in AlCl3(1 M aqueous) between 0~1.2 V;(d) the first discharge capacity and the specific accumulative discharge capacity of the recovered Al-tungsten oxide electrochromic battery recharged by oxygen and $H_{2}O_{2}$[6] |
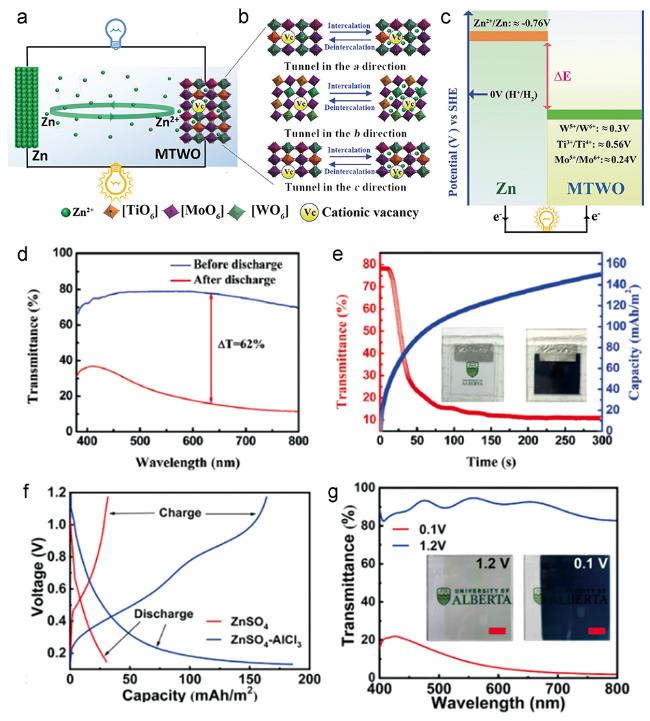
图4 (a~c) ZIEB变色电池的结构示意图和工作机制;(d) ZIEB变色电池在放电前后的可见光-近红外光透过率;(e) ZIEB变色电池的透过率及容量随放电时间的变化曲线;(f) WO3正极在两种电解液中的恒电流充放电曲线;(g) 电池在0.1和1.2 V电压下的可见光-近红外光谱[16, 17]Fig. 4 (a~c) Structure and working mechanism for the ZIEB electrochromic battery;(d) visible-near infrared transmittance spectrum of the battery measured before and after discharging;(e) in situ self-coloring process of the ZIEB;(f) galvanostatic charge and discharge curves of the WO3 anode at 0.5 mA·cm-2 between 0.1 and 1.2 V;(g) visible near-infrared transmittance spectra of WO3 cathode measured at 0.1 and 1.2 V in 1 M $ZnSO_{4}-AlC_{3}$[16, 17] |
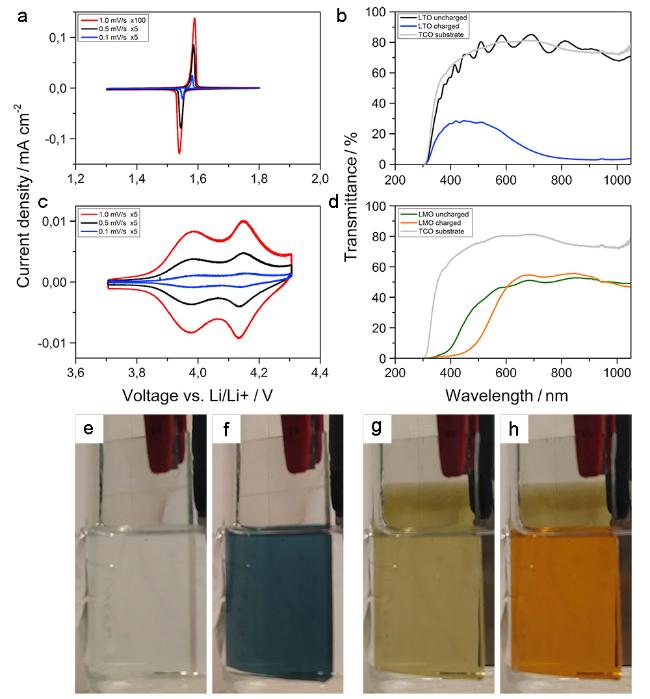
图5 (a) Li4Ti5O12和(c) LiMn2O4的循环伏安曲线;(b) Li4Ti5O12和(d) LiMn2O4在嵌锂和脱锂态的紫外可见近红外光谱;(e, f) Li4Ti5O12的褪色态和着色态照片;(g, h) LiMn2O4的褪色态和着色态照片[24]Fig. 5 CVs of Li4Ti5O12(a) and LiMn2O4(c) samples at various scan rates.(b) Transmittance spectra of a charged(blue) and discharged(black) Li4Ti5O12 transparent thin film electrode compared to the pure FTO-glass substrate(grey).(d) Transmittance spectra of a charged(orange) and uncharged(green) LiMn2O4 electrode. Optical photographs of a Li4Ti5O12 thin film electrode in its colorless discharged(e) and dark-blue colored charged state(f). The LiMn2O4 electrode showed a green color in the uncharged state(g) changing to orange when being charged(h)[24] |
| (4) | ||
| PB | PW | |
| $[Fe^{III} Fe^{II}(CN)_{6}]^{-} \longrightarrow Fe^{III}\{[Fe^{III}(CN)_{6}]_{\frac{2}{3}}[Fe^{II}(CN)_{6}]_{\frac{1}{3}}\}^{\frac{1}{3}}+\frac{2}{3}e^{-}$ | (5) | |||
| PB | BG | |||
| (6) | ||||
| PB | PY | |||
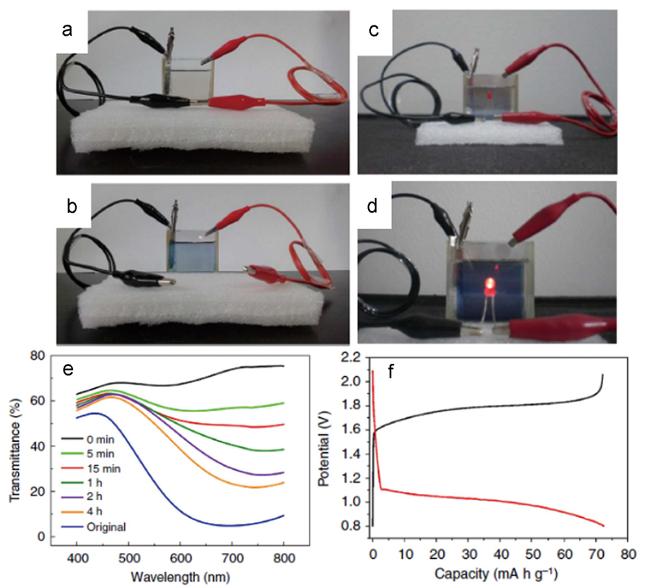
图6 (a) PB/Al变色电池短接时呈透明态;(b) 断开时自充电并着色;(c) 透明态时无法点亮LED灯;(d) 着色态(充电态)可点亮LED灯;(e) 器件随自充电时间延长的紫外可见光谱;(f) 电池在2000 mA·g-1电流密度下的充放电曲线[26]Fig. 6 (a) Optical photo of the bleached EC device, and(b) the EC device recovered for 1 h;(c) in bleached state with connected circuit showing no light from the LED;(d) in colored state with connected circuit powering a LED;(e) Transmittance spectra of the original self-powered PB/Al EC device(original curve) and the bleached device at various recovery times from 0, 5 min to 4 h;(f) galvanostatic discharge and charge curves of the PB/Al cell at a current density of 2000 mA·g-1 [26] |
3 电致变色超级电容器
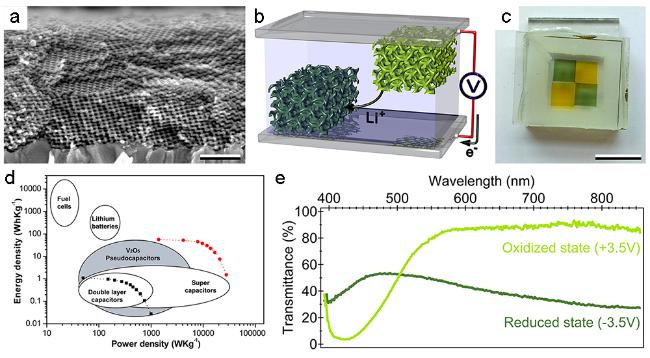
图7 (a) FTO玻璃上介孔V2O5薄膜的SEM照片;(b) V2O5电致变色超级电容器的结构示意图;(c) 实物照片;(d) 能量密度-功率密度对数关系图;(e) 电致变色光谱调制性能[34]Fig. 7 (a) Cross-sectional electronic micrograph of a mesoporous V2O5 thin film on a FTO substrate;(b) structure,(c) photograph,(d) Ragone plot and (e) optical transmittance spectra of the electrochromic supercapacitor[34] |
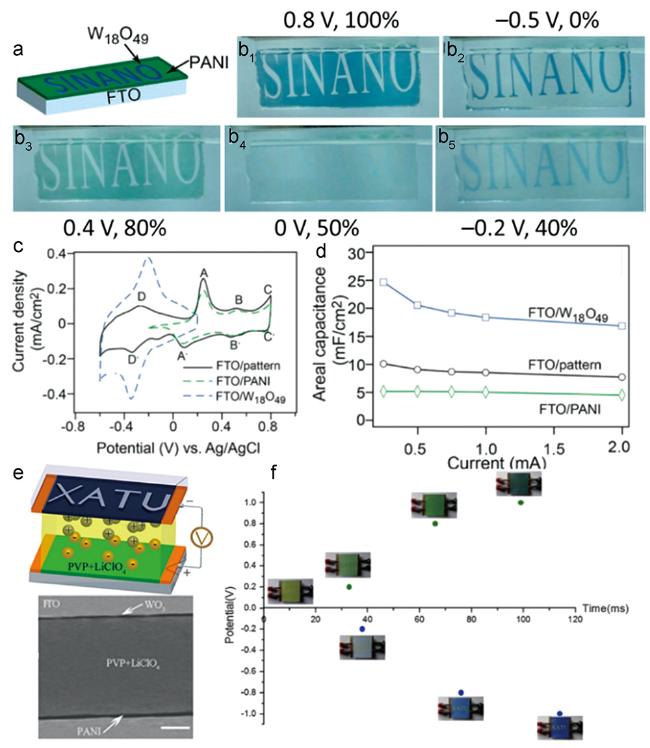
图8 (a) 在FTO玻璃上制备的W18O49和聚苯胺图案化复合电极示意图;(b1~5) 图案化复合电极在不同电压下的照片;(c) 图案化复合电极以及PANI和W18O49电极的循环伏安曲线;(d) 三种电极的面积比电容[35];(e) WO3/PANI电致变色超级电容器的结构;(f) WO3/PANI电致变色超级电容器颜色与电压关系[36]Fig. 8 (a) Schematic of a patterned supercapacitor electrode composed of W18O49 and PANI;(b1~5) Images of the supercapacitor electrode at several typical states;(c) CV curves of the PANI film, W18O49 nanowire film, and hybrid smart supercapacitor electrode;(d) areal capacitance values for the three electrodes[35];(e) the structure of the WO3/PANI electrochromic supercapacitors; and(f) the relation between time and color of the device under different potential(-1 ~ 1 V)[36] |
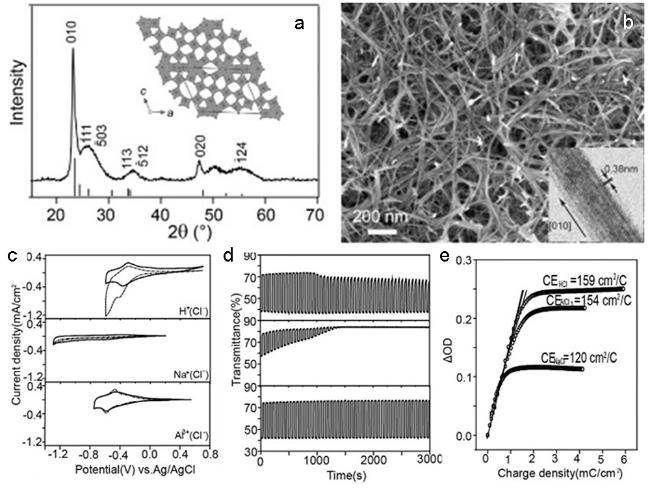
图9 (a) W18O49的结构和XRD;(b) W18O49纳米线的形貌;W18O49纳米线薄膜在1.0 M Al(ClO4)3、LiClO4、NaClO4的碳酸丙烯酯溶液中的性能; (c) 循环伏安曲线;(d) 在波长为660 nm的可见光处的透过率变化;(e) 电致变色效率[13]Fig. 9 (a) XRD and structure of W18O49 NW;(b) SEM and TEM(inset) images of W18O49 NW;(c) CV curves at a scan rate of 10 mV·s-1,(d) in situ transmittance variation curve between colored and bleached state, and(e) coloration efficiency of the W18O49 nanowires film in 1.0 M PC-Al(ClO4)3, PC-LiClO4, PC-NaClO4 [13] |
4 光驱动电致变色器件
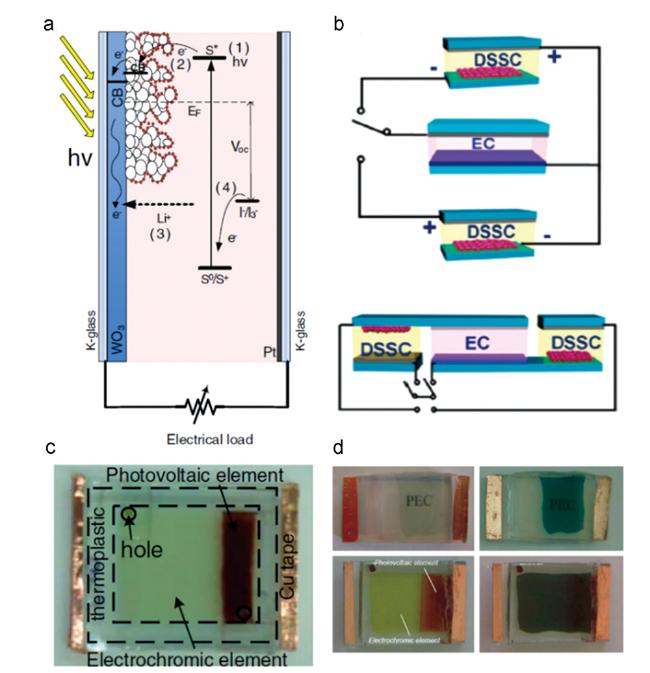
图10 (a) 光驱动电致变色器件原理示意图[44];(b) DSSC系统和电致变色器件的两种集成方式(Ⅰ型和Ⅱ型)[46];(c) 光驱动电致变色器件照片;(d) 光驱动电致变色器件变色效果[47]Fig. 10 (a)Schematic diagram of photochromic device driven by light[44];(b) two integration modes of DSSC system and electrochromic device(type Ⅰ and Ⅱ)[46];(c) photo of photochromic device driven by light;(d) photographs of photochromic device driven by light at different states[47] |
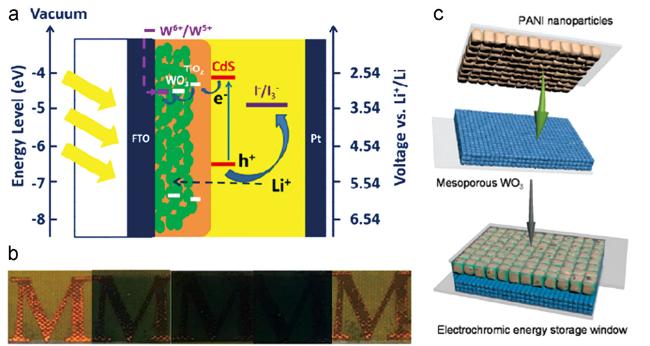
图11 (a) 光电致变色器件和锂离子电池集成器件的结构示意图;(b) 光电致变色器件和锂离子电池集成器件的电致变色效果[53];(c) 介孔结构WO3和PANI为电极组成的电致变色器件[55]Fig. 11 (a) Structure diagram of integrated photochromic and lithium-ion storage device;(b) electrochromic effect of photochromic device and lithium-ion battery integrated device[53];(c) mesoporous structured WO3 and PANI as electrodes for electrochromic devices[55] |
5 柔性变色储能器件
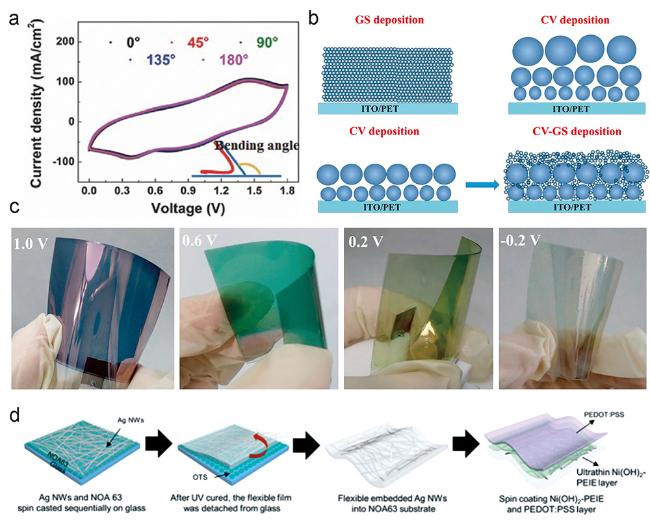
图12 (a) W18O49 NW/SCNTs复合电极在不同弯曲程度下的CV曲线;(b) CV和GS结合的方法制备纳米结构PANI示意图;(c) CV和GS结合法制备出柔韧性和电致变色效果较好的PANI薄膜[40];(d) 柔性透明超级电容器的制备流程示意图[62]Fig. 12 (a) CV curves of W18O49 NW/SCNTs composite electrodes under different bending degrees;(b) schematic diagram of nanostructured PANI prepared by combining CV and GS;(c) PANI film with good flexibility and electrochromic effect prepared by combining CV and GS[40];(d) schematic diagram of preparation process of flexible transparent supercapacitors[62] |