1 引言
2 水热炭化法制备手性碳点
2.1 基于手性传递策略的一步法
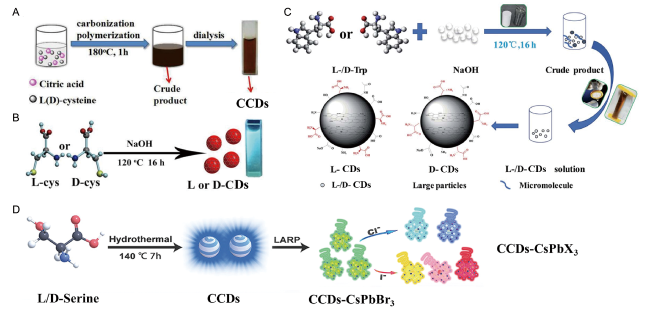
图1 (A) 以柠檬酸和L-/D-半胱氨酸一步法制备CCDs[46];(B) 以L-/D-半胱氨酸为手性源和碳源合成CCDs[29];(C)以L-/D-色氨酸为手性源和碳源合成CCDs[31];(D) 全彩色CPL发射的CCDs-CsPbX3的制备[59]Fig. 1 (A) Preparation of CCDs via one-step method of citric acid and L-/D-cysteine[46]; (B) Synthesis of CCDs using L-/D-Cysteine as chiral source and carbon source[29];(C)Synthesis of CCDs using L-/D-Tryptophon as chiral source and carbon source[31];(D) Schematic of the preparation procedure for full-color CPL CCDs-CsPbX3[59] |
表1 基于手性传递策略的一步法合成CCDsTable 1 One-step method based on chiral transfer strategy |
| Method | Chiral source | Carbon source | Other source | T(℃) | t(h) | EM(nm) | ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| One-step method | L-/D-glutamine | Citric acid | — | 140 | 16 | 450 | 45 |
| L-/D-cysteine | Citric acid | — | 180 | 1 | — | 46 | |
| L-/D-cysteine | — | NaOH | 120 | 16 | 460 | 29 | |
| L-aspartic acid | Citric acid | NaOH | 200 | 4 | 420 | 30 | |
| L-cysteine | Citric acid | — | 160 | 6 | 453 | 47 | |
| L-cysteine L-glutathione L-phenylglycine L-tryptophan | Citric acid+ ethylenediamine | — | 190 | 8 | 450 | 48 | |
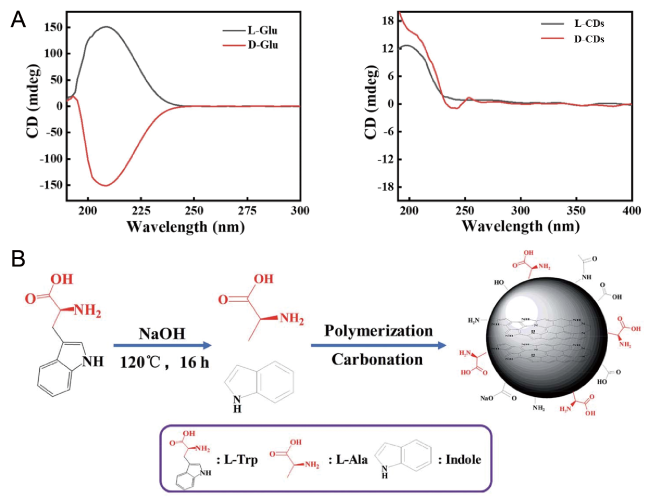
| L-/D-tryptophan | — | NaOH | 120 | 16 | 476 | 31,67 | |
| L-/D-tryptophan | o-Phenylenediamine | HCl+Ethanol -H2SO4 | 160 | 7 | 441 546 604 | 32 | |
| L-/D-cysteine | Urea | — | 180 | 1 | 450 | 49 | |
| L-/D-glutamic acid | Citric acid | — | 180 | 4 | 454/418 | 50 | |
| D-proline | Citric acid | — | 180 | 2 | 420 | 51 | |
| L-/D-alanine | Citric acid | — | 160 | 4 | 400 | 66 | |
| L-cysteine | m-Phenylenediamine | — | 200 | 2 | 510 | 52 | |
| L-ascorbic acid L-cysteine+L-ascorbic acid | Ethylenediamine Ethylenediamine | — | 100 140 | 2 4 | 484 420 | 67 | |
| L-cysteine | Neutral red | Ethanol | 140 | 8 | 601/604 | 75 | |
| L-/D-tryptophan | OTD | H2SO4 | 160 | 8 | — | 69 | |
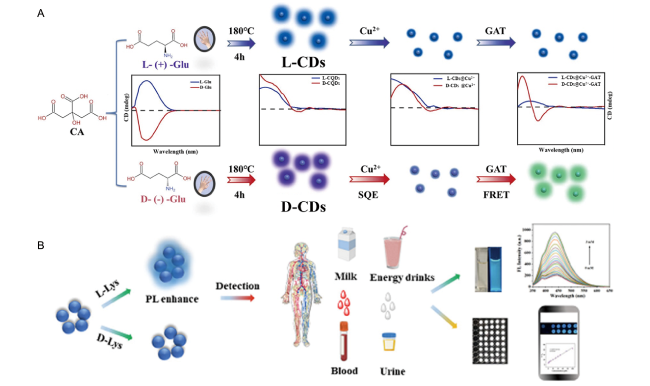
| L-/D-glutamic acid | Citric acid | NaOH | 180 | 10 | 407 | 34 | |
| D-(-)-fructose | Vine teas | NADES | 160 | 3 | 445 | 35 | |
| L-/D-cysteine | Citric acid | — | 180 | 1.5 | 442 | 54 | |
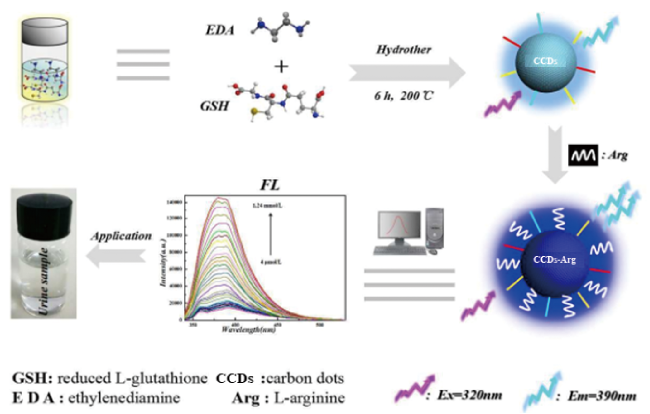
| L-glutathione | Ethylenediamine | — | 200 | 6 | 390 | 57 | |
| L-/D-lysine | Jeffamine® ED-900 | Ethylene glycol | 170 | 3 | 400~600 | 37 | |
| L-/D-lysine | Jeffamine® ED-900 | Ethylene glycol | 170 | 2 | 400~600 | 38 | |
| L-/D-cysteine | — | NaOH | 60 | 24 | 510 | 39 | |
| L-/D-cysteine | — | — | 80 | 48 | — | 55 | |
| L-/D-glutamic | Citric acid | Polyethyleneimine | 160 | 1 | 450 | 41 | |
| L-/D-cysteine | — | NaOH | 120 | 16 | 460 | 42 | |
| L-/D-cysteine | Citric acid | — | 160 | 6 | 445 | 58 | |
| L-/D-serine | — | — | 140 | 8 | 475 | 59 | |
| L-/D-cysteine L-/D-glutathione L-/D-threonine | Citric acid | — | 180 | 1.5 | 432 425 430 | 60 | |
| L-tyrosine | o-phenylenediamine | H2SO4 | 160 | 7 | 627 | 43 |
2.2 基于手性继承策略的两步法
表2 基于手性继承策略的两步法合成CCDsTable 2 Two-step method based on chiral inheritance strategy |
| Method | Chiral source | Carbon source | Other source | T(℃) | t(h) | EM(nm) | ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
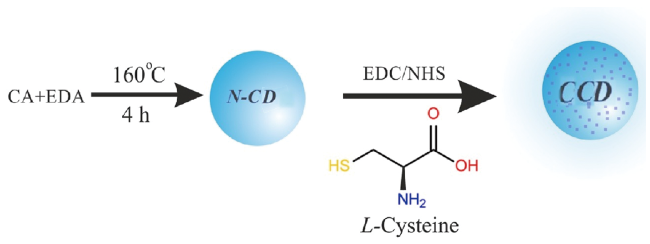
| Two-step method | L-/D-cysteine | Citric acid+ethylenediamine | — | 160 | 4 | 424 | 9 |
| L-/D-cysteine | Urea | — | 180 | 1 | 450 | 49 | |
| L-/D-cysteine | Citric acid+Urea | DMF | 180 | 6 | 625 | 33,68 | |
| L-/D-arginine/L-lysine | Citric acid+Urea | DMF | 160 | 6 | >600 | 44 | |
| L-/D-cysteine | Cane molasses | — | 160+120 | 24+2 | 400~440 | 61 |
3 制备因素对CCDs性质的影响
3.1 碳源的影响
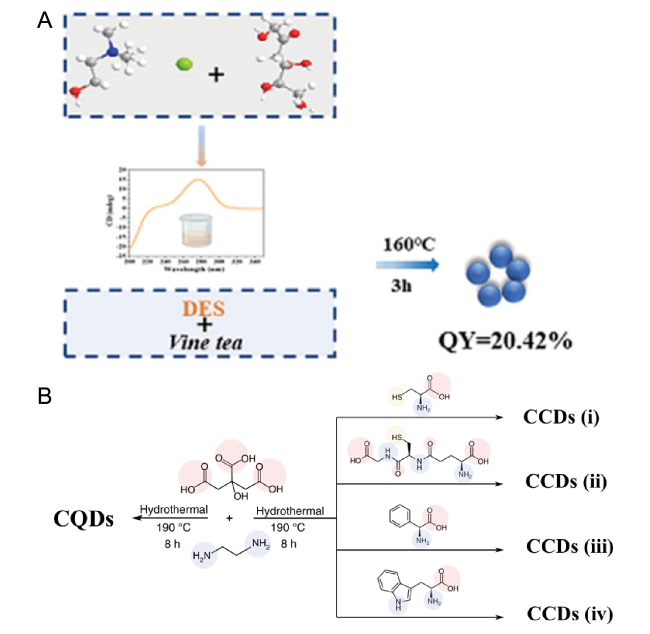
图4 (A) 以藤茶和NADES为原料合成CCDs[37];(B) 以柠檬酸和乙二胺与(ⅰ) L-半胱氨酸,(ⅱ) L-谷胱甘肽,(ⅲ) L-苯基甘氨酸,(ⅳ) 色氨酸四种手性前驱体为原料水热炭化合成CCDs[49]Fig. 4 (A) CCDs synthesized from vine tea and NADES as raw materials[37] (B) CCDs were synthesized by hydrothermal carbonization of citric acid and ethylenediamine with four chiral precursors of (ⅰ) L-cysteine, (ⅱ) L-glutathione, (ⅲ) L-phenylglycine, and (ⅳ) tryptophan[49] |
3.2 手性配体的影响
3.3 其他前驱体的影响
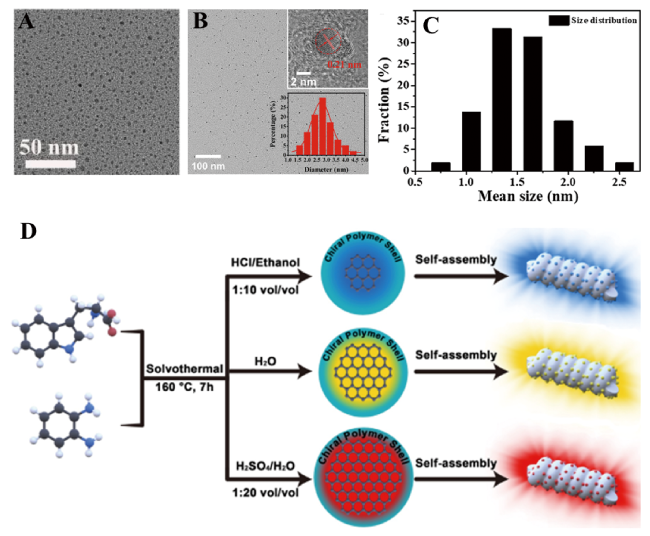
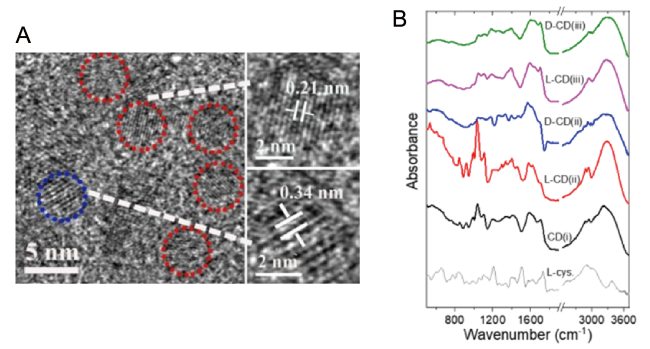
图5 (A~C) 以L-/D-半胱氨酸为原料合成CCDs的TEM图和尺寸分布图[29,40,42];(D) 多色CCDs的制备[32]Fig. 5 (A~C) TEM image and size distribution histograms of CCDs prepared by L-/D-cysteine[29,40,42]. (D) The preparation procedure for multicolor-emitting chiral carbon dots[32]. (Reprinted with permission from ref 42; Copyright (2023) American Chemical Society) |
3.4 水热炭化温度的影响
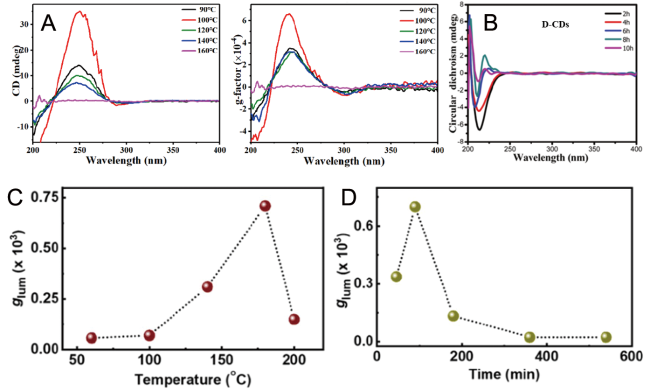
图6 (A) 不同温度下制备CCDs的CD光谱和glum光谱[67]; (B) 不同反应时间制备CCDs的CD光谱[51]; (C,D) 不同反应温度和时间制备CCDs的glum光谱[60]Fig. 6 (A) CD and glum spectra of CCDs prepared at different reaction temperatures[67]. (B) CD spectra of CCDs were prepared at different reaction times[51]. (C,D) glum spectra of CCDs prepared at different reaction temperatures and times[60] |
3.5 水热炭化时间的影响
4 水热CCDs的结构特性
4.1 手性特征
4.2 物理结构
4.3 化学结构
4.4 光学性质
4.5 电学性质
5 应用
5.1 生物医学
5.1.1 生物成像
5.1.2 调节细胞代谢和蛋白酶活性
5.1.3 手性纳米疫苗
5.1.4 促进植物生长
5.1.5 抗菌活性
5.2 传感
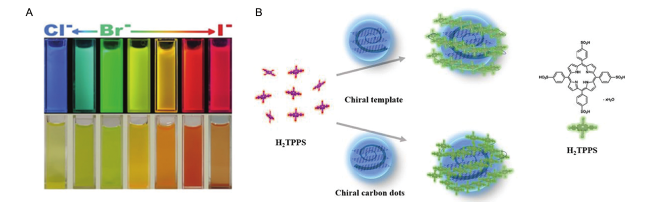
5.2.1 手性识别
图12 (A) 紫外光照射下加入不同浓度的L-/D-Lys后CCDs水溶液和将CCDs嵌入纳米纸的颜色变化[9]; (B) 基于CCDs在On-Off-On模式下测定Sn2+和L-Lys纳米探针的制备[30]; (C) CCDs对异亮氨酸对映体的识别[47]Fig. 12 (A) Color change of CCDs aqueous solution and CCDs embedded in nanopaper after adding L-/D-Lys of different concentrations under UV irradiation[9]. (B) Fabricating CCDs-based nanoprobes for assaying Sn2+ and L-Lys in On-Off-On mode[30]. (C) Chiral recognition method based on CCDs towards isoleucine enantiomers[47] |
5.2.2 电化学传感催化
5.2.3 检测探针
5.3 不对称催化
5.4 光电材料
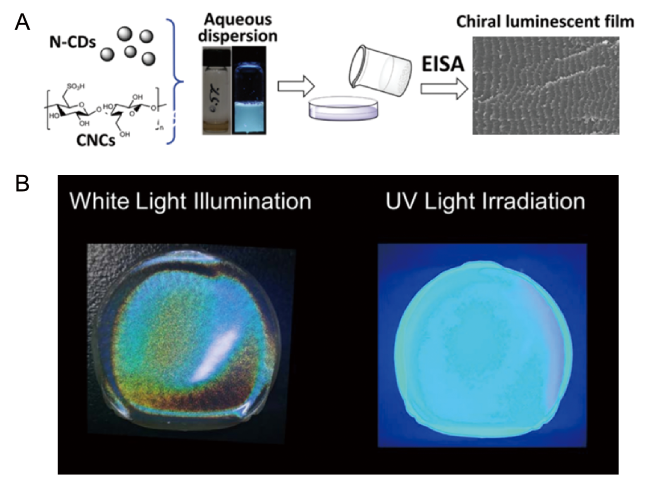
5.5 复合材料
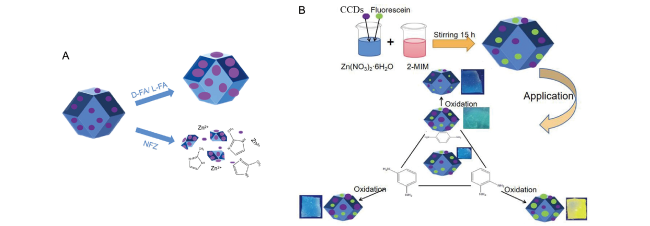
图17 (A) 将CCDs封装在ZIF-8纳米颗粒中用于识别叶酸和硝基呋喃酮[58];(B) 手性双发射复合材料荧光素/CCDs@ZIF-8用于苯二胺(PD)异构体及其氧化产物的高灵敏度鉴别 (2-MIM: 2-甲基咪唑)[82]Fig. 17 (A) CCDs encapsulated in ZIF-8 nanoparticles for turn-on recognition of chiral folic acid and nitrofurazone[58]. (B) Chiral dual-emission composite material fluorescein/CCDs@ZIF-8 for highly sensitive discrimination of phenylenediamine (PD) isomers and their oxidized product (2-MIM: 2-methylimidazole)[82] |