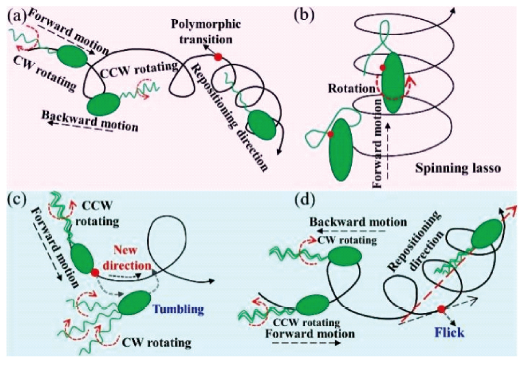
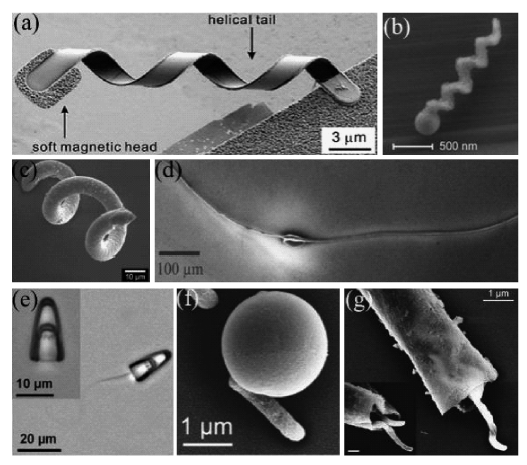
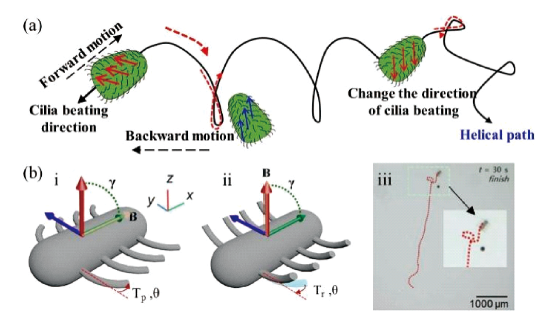
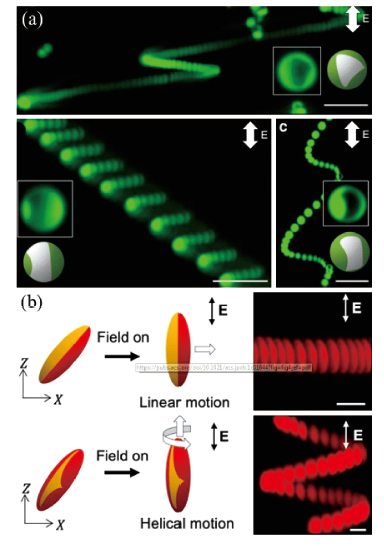
1 引言
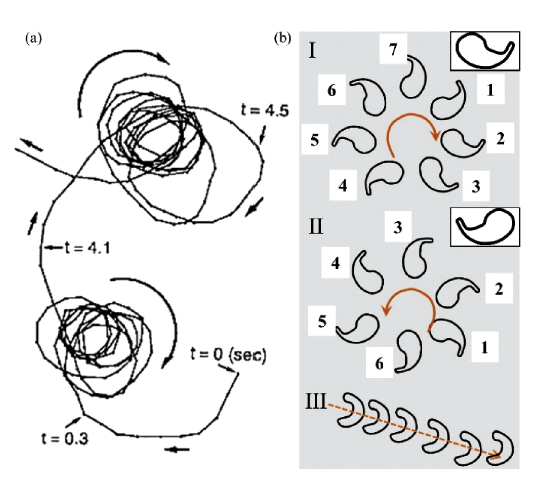
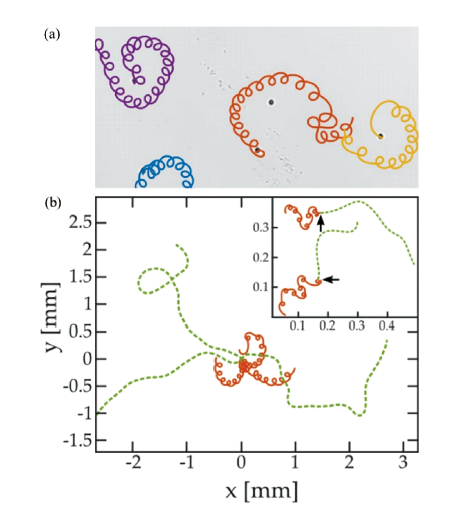
2 生物游泳体的螺旋运动与仿生设计
2.1 仿生鞭毛驱动游泳体
2.2 仿生纤毛驱动游泳体
3 人工游泳体螺旋运动的驱动力和运动控制
3.1 外物理场驱动的螺旋运动
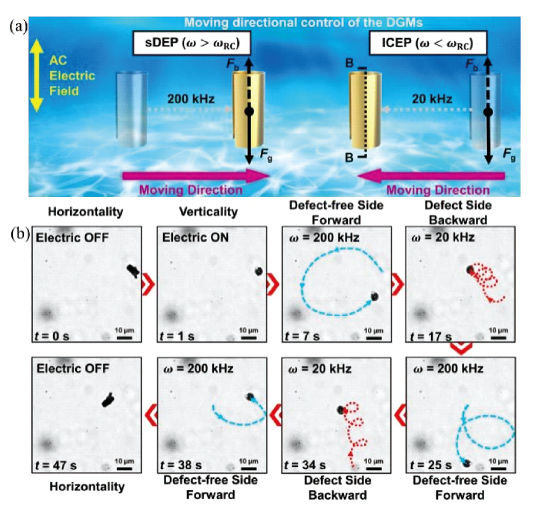
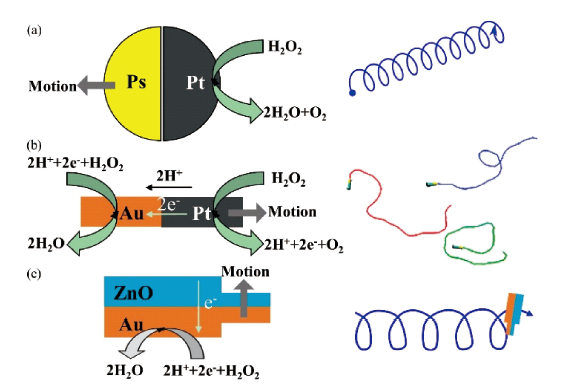
3.1.1 电场驱动游泳体
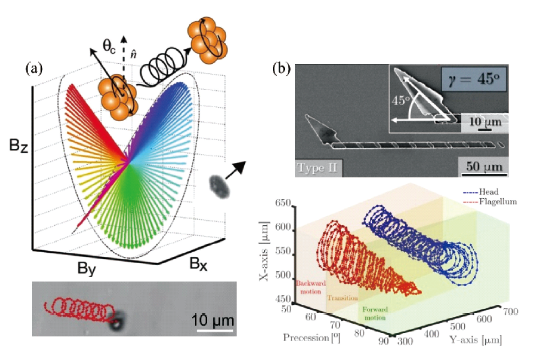
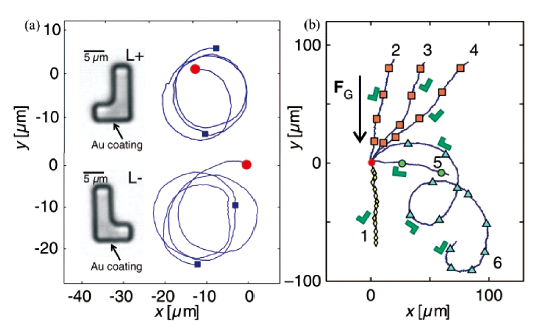
3.1.2 磁场驱动游泳体
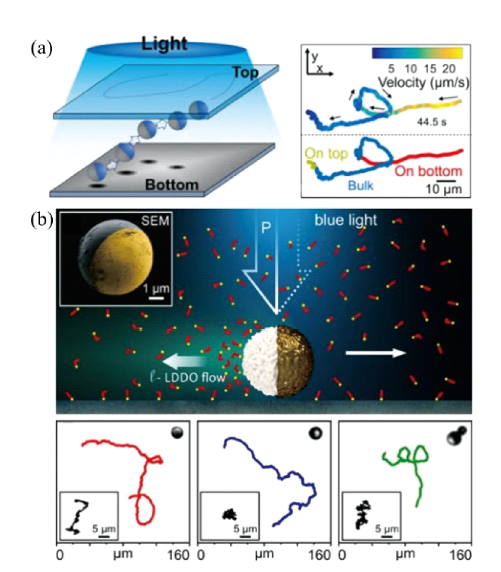
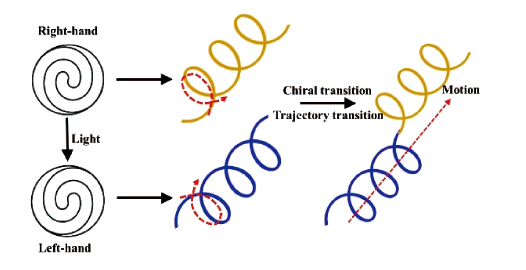
3.1.3 光驱动游泳体
图7 光驱动游泳体的运动行为:(a) 光诱导离子扩散电泳驱动AgCl-Janus 粒子的运动[63];(b) 光诱导扩散渗透流驱动SiO2 颗粒的运动[64]Fig.7 Light-driven kinematic behavior of swimmers: (a) Light-induced ion diffusion electrophoresis driving the motion of AgCl-Janus particles[63]; (b) Light-induced diffusion permeation flow driving the motion of SiO2 particles[64] |
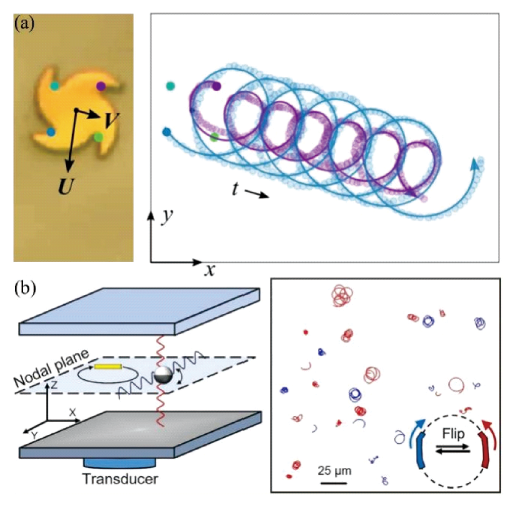
3.1.4 超声驱动游泳体
3.2 界面/表面张力驱动的螺旋运动
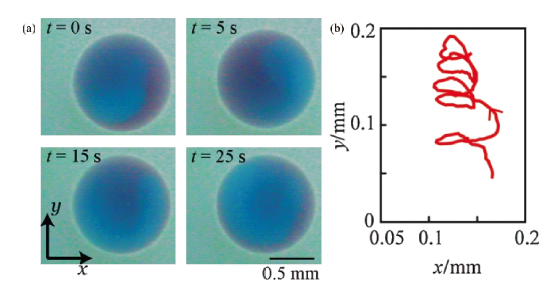
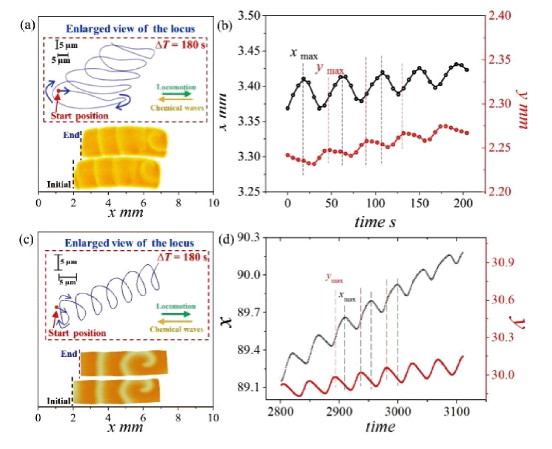
3.2.1 马兰戈尼效应驱动游泳体
图10 温度控制人工游泳体的运动轨迹转变,液晶滴(向列)在34 ℃的轨迹以实线示出,液晶滴(各向异性)在37 ℃的轨迹以虚线示出[71]Fig.10 Temperature-controlled shifts in the trajectory of artificial swimmers. The trajectory of the liquid crystal droplet (nematic) at a temperature of 34 ℃ is shown as a solid line;the trajectory of the liquid crystal droplet (isotropic) at a temperature of 37 ℃ is shown as a dashed line[71] |