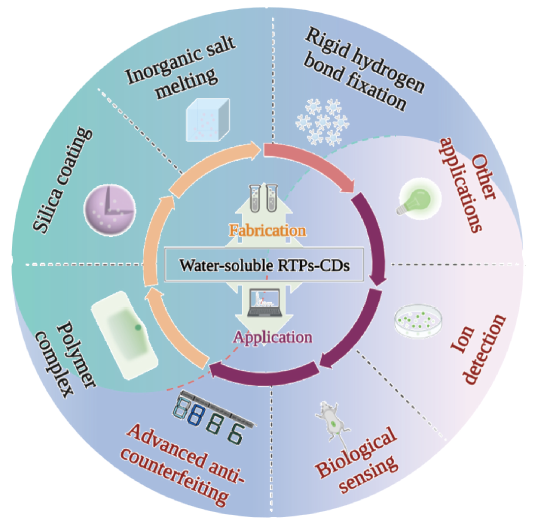
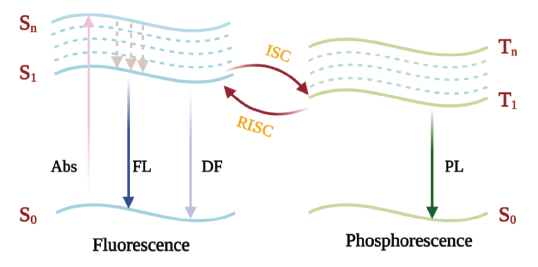
1 引言
2 合成策略
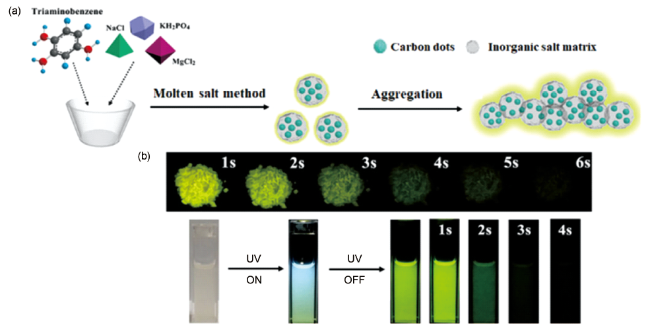
2.1 无机盐熔融法
2.2 SiO2包覆法
2.2.1 TEOS直接水解包覆
图4 (a)TEOS直接水解包覆的CDs-RhB@SiO2形成示意图[31];(b)表面共价固定法制备的CDs@SiO2形成示意图和紫外激发下的水相RTP照片[54]Fig.4 (a) Schematic diagram of the formation of CDs-RhB@SiO2 via a TEOS hydrolysis-based coating[31]; (b) schematic illustration of the preparation of CDs@SiO2 using surface covalent fixation and the RTP photographs in aqueous solution under the UV excitation[54] |
2.2.2 共价固定法
2.2.3 一步水解法
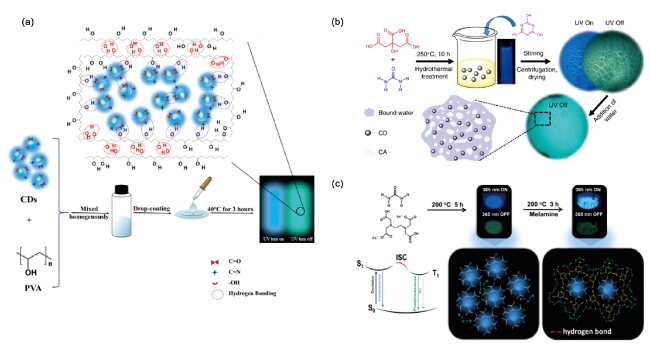
2.3 基于高分子复合的氢键固定法
图5 (a)CDs/PVA薄膜的构筑以及RTP产生的机理[65];(b)碳点-氰尿酸氢键网络复合体系的构筑与结构示意图[66];(c)碳点-三聚氰胺水相RTP纳米复合体系的制备与结构示意图[48]Fig.5 (a) Schematic illustration of the fabrication and RTP emission mechanism of the CDs/PVA film[65]; (b) the construction and structure schematic illustration of the CDs-CA hydrogen bond network[66]; (c) the fabrication and hydrogen bond structure schematic illustration of the CDs-melamine nano-hybrids[48] |
2.4 刚性氢键网络固定法
3 应用
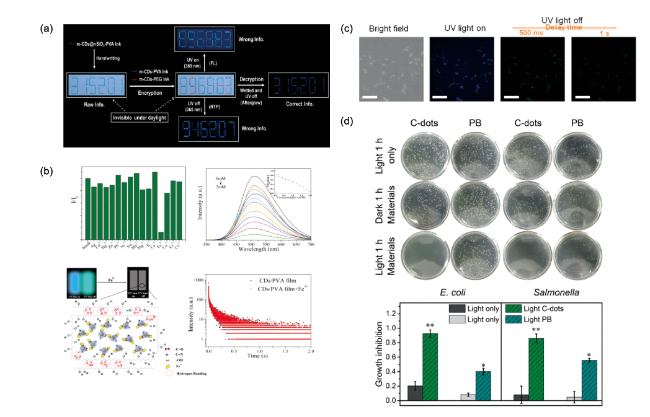
3.1 防伪与信息安全加密
图6 碳点基水相RTP材料的应用。(a)m-CDs@nSiO2复合材料用于信息加密与解密[47];(b)CDs-PVA磷光薄膜用于Fe3+传感[65];(c)CDs@SiO2水相RTP纳米复合体系应用于小鼠乳腺癌细胞的荧光与时间分辨成像[54];(d)氮掺杂磷光碳点用于光动力抗菌[87]Fig.6 The applications of CDs-based water-soluble RTP materials. (a) Information encryption and decryption via the m-CDs@nSiO2 composites[47]; (b) Schematic illustration of the CDs-PVA RTP thin film for Fe3+ sensing[65]; (c) Fluorescence and time resolution imaging via the CDs@SiO2 aqueous RTP nanocomposites[54]; (d) Photodynamic antibacterial application using the nitrogen-doped phosphorescent carbon-dots[87] |