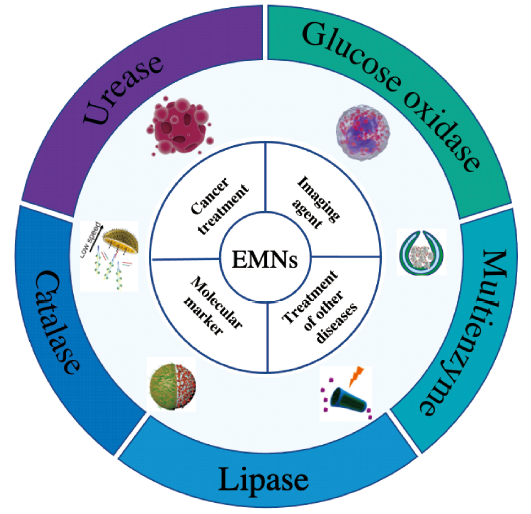
1 引言
2 生物酶驱动的微纳米马达在疾病的检测与诊断方面的应用
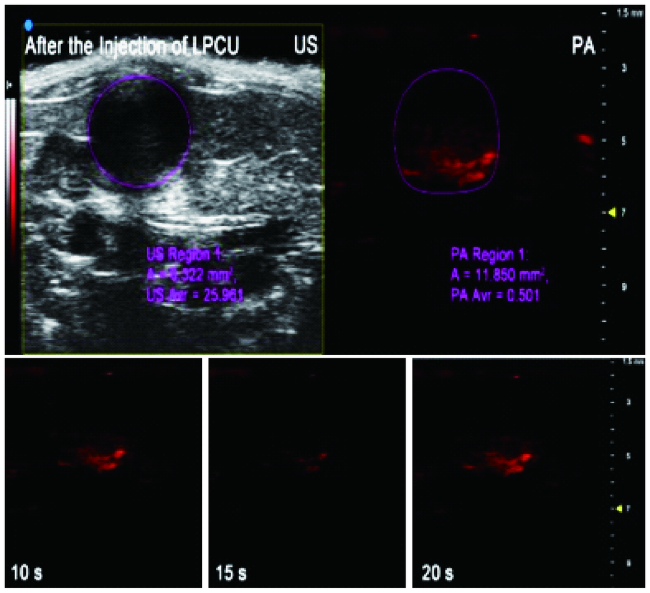
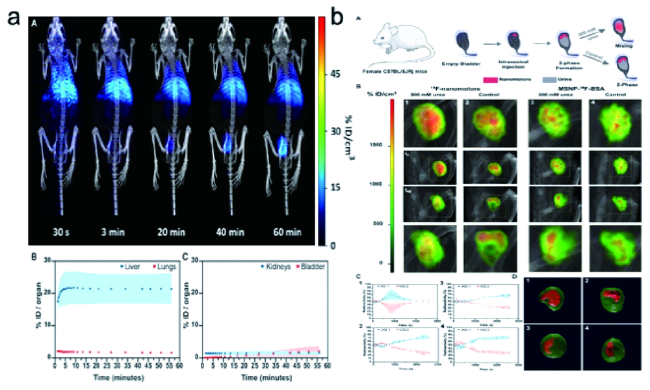
2.1 成像显像剂
2.2 生物分子标志物的检测
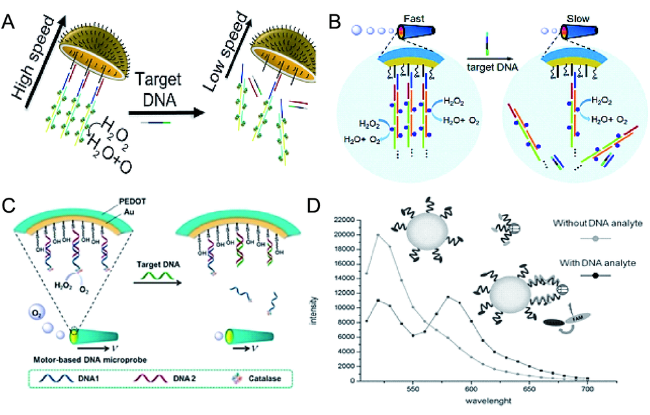
2.2.1 DNA分子的检测
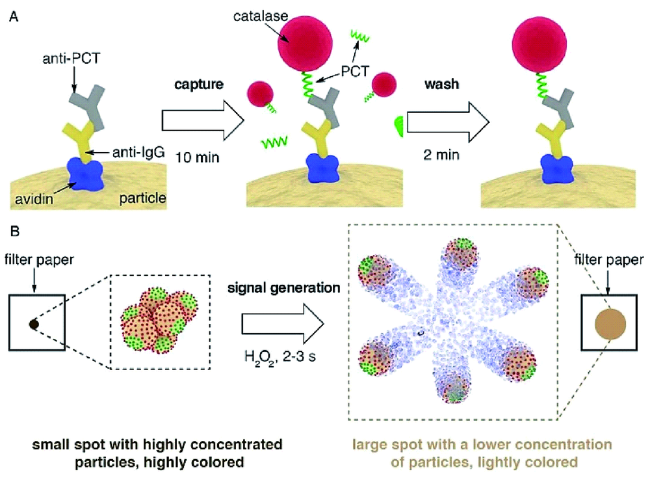
2.2.2 蛋白质分子的检测
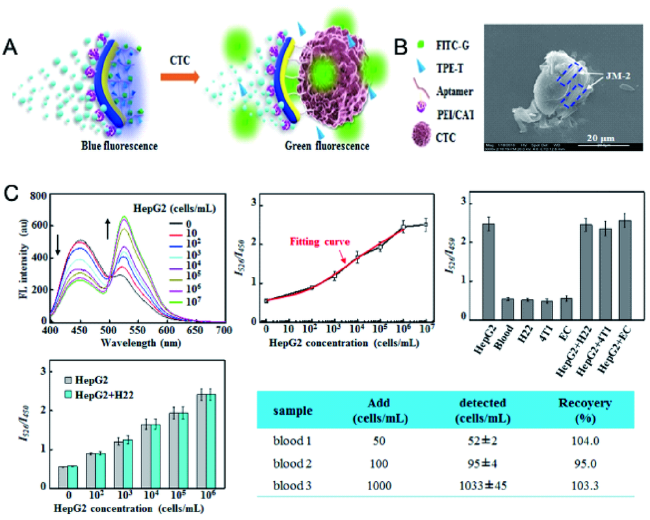
2.2.3 肿瘤细胞的检测
3 生物酶驱动的微纳米马达在疾病治疗方面的应用
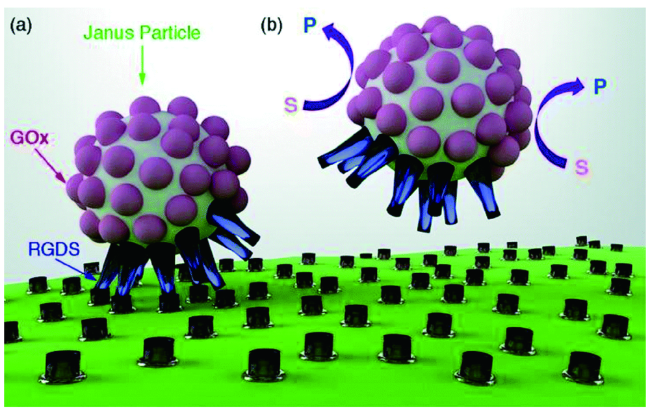
3.1 癌症的治疗
表1 生物酶驱动微纳米马达在疾病诊断中的代表示例Table 1 Summary of the representative examples in the diagnosis based on enzyme-powered micro/nanomotors |
| Types of EMNMs | Materials | Fuel | Velocity and medium | Application | ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Urease | Ga-In-Sn | Urea | — | Targeted transportation; Synergetic therapy;Imaging | 31 |
| Catalase | Au-Pt | H2O2 | — | Imaging agents | 32 |
| Au/Ag/Ni/DNA | H2O2 | 209 μm/s (1.5% H2O2) | Biosensing | 38 | |
| PEDOT-PSS/Au/DNA | H2O2 | 420 μm/s (2% H2O2 ) | DNA detection | 39 | |
| SiO2/ Oligonucleotide | H2O2 | — | Target recognition;Cargo transport | 40 | |
| PEDOT/Au | H2O2 | 411±40 μm/s(5% H2O2) | DNA detection | 41 | |
| Iron oxide | H2O2 | — | Biosensing | 44 | |
| Janus fibers | H2O2 | 42 μm/s (3.5% H2O2) | Capture of circulating tumor cell | 47 |
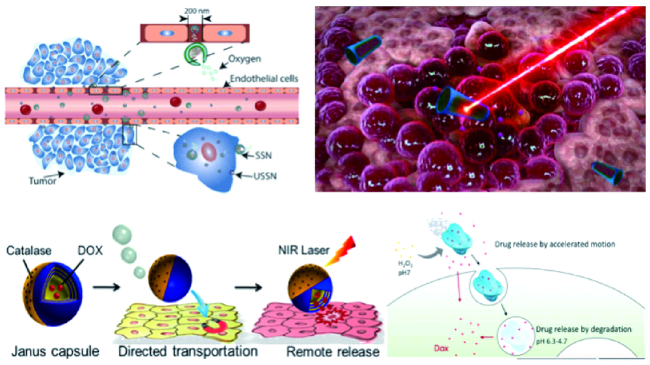
3.1.1 过氧化氢酶驱动的微纳米马达在肿瘤治疗中的应用
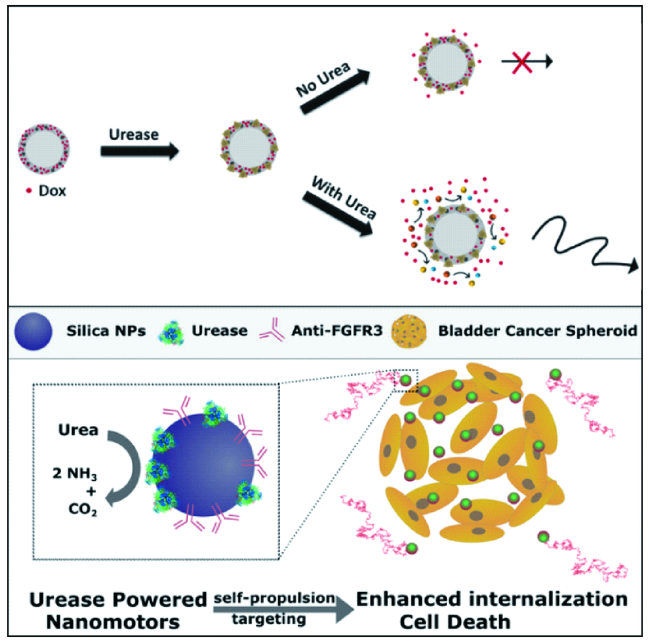
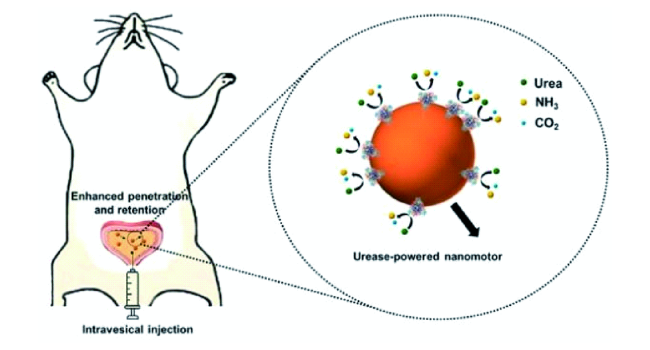
3.1.2 尿素酶驱动微纳米马达在肿瘤治疗中的应用
3.1.3 葡萄糖氧化酶驱动微纳米马达在肿瘤治疗中的应用
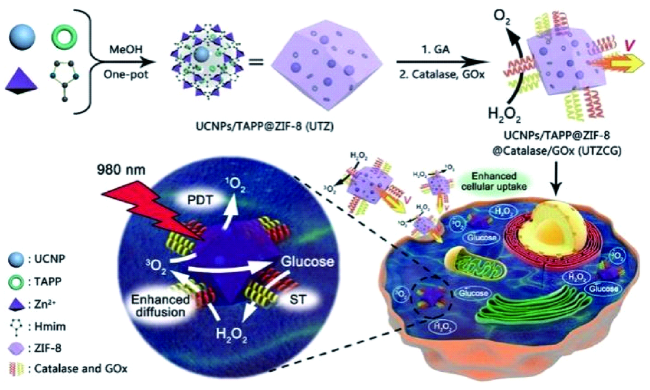
3.1.4 酶级联反应驱动微纳米马达在肿瘤治疗中的应用
3.2 其他疾病的治疗
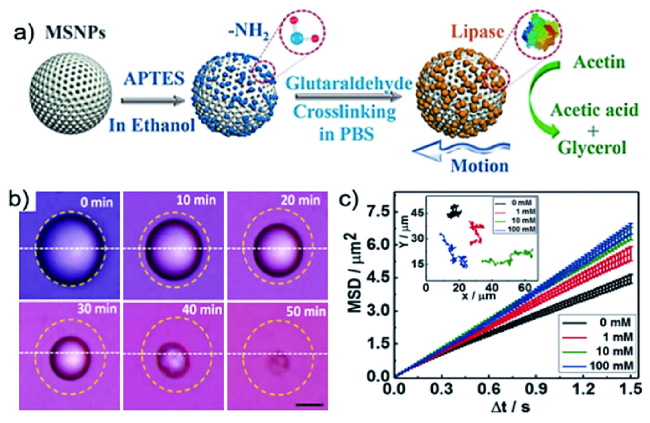
3.2.1 甘油三酯的降解
3.2.2 细菌感染的治疗
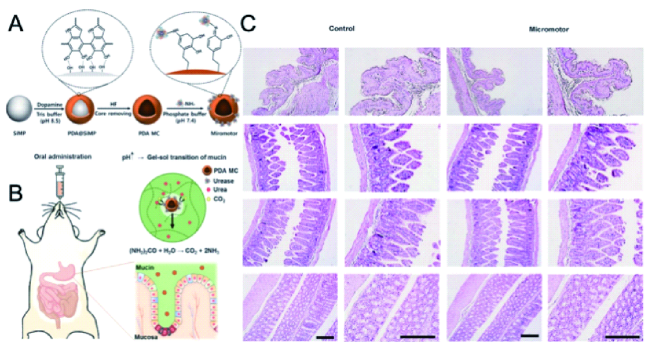
3.2.3 胃肠道疾病的治疗
表2 利用生物酶驱动的微纳米马达治疗各种疾病的代表示例Table 2 Summary of representative examples for disease treatment using enzyme-powered micro/nanomotors |
| Types of EMNMs | Materials | Fuel | Velocity and medium | Application | ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Catalase | Ti/Au-Thiol | H2O2 | 10 body lengths s-1(1.5 wt%) | 55 | |
| Polydimethyl sulfoxane | H2O2 | 5.2 body lengths s-1(4%) | 56 | ||
| PEG-PS | H2O2 | 117 body lengths s-1 | Drug delivery | 59 | |
| Mesoporous SiO2 | H2O2 | 3.75 μm2/s(6 wt%) | Drug delivery | 9 | |
| Polymer based bottlebrush | H2O2 | 23.6 μm/s (10 mmol·L-1 H2O2 ) | Overcoming tissue Penetration barrier | 60 | |
| Bovine serum Albumin/poly-L-lysine (PLL/BSA) multilayer | H2O2 | 68 μm/s (0.5% H2O2) | Drug delivery | 61 | |
| Polymers/Au | H2O2 | 108 μm/s (1% H2O2) | Drug delivery | 62 | |
| MOF | H2O2 | Drug delivery | 63 | ||
| Urease | Tubular SiO2 | Urea | 66 | ||
| Mesoporous SiO2 | Urea | 5 body lengths·s-1 (25 mmol·L-1) | Drug delivery | 67 | |
| Mesoporous SiO2 | Urea | 6.24 μm2·s-1 (10 mmol·L-1) | Drug delivery | 69 | |
| Mesoporous SiO2 | Urea | Drug delivery | 70 | ||
| Mesoporous SiO2/ MSNP-Ur/PEG-Ab | Urea | Cancer therapy | 71 | ||
| Mesoporous SiO2 | Urea | 1.36±0.05 μm2/s 300 mmol·L-1 urea PBS | Drug delivery | 72 | |
| PDA/SiO2 | Urea | 10.67 μm/s (100 mmol·L-1) | Drug delivery | 73 | |
| Platelet | Urea | Drug delivery | 74 | ||
| Protein | Urea | 2.7±0.2 μm·s-1 100 mmol·L-1 urea PBS | 75 | ||
| SiO2 | Urea | Drug delivery | 76 | ||
| GOx | SiO2 | Glucose | 81 | ||
| GOx+Cat | SiO2/PDA PLL-g-PEG | Glucose | Drug delivery | 82 | |
| GOx+Cat | Polymer vesicle | Glucose | 176 body lengths·s-1(100 mM) | Drug delivery | 83 |
| GOx+trypsin | Pt/ MF-NPs | Glucose | Targeted transportation | 84 | |
| GOx | CNF | Glucose | 85 | ||
| GOx | Au/polymer | Glucose | 120 body lengths ·s-1 | Targeted transportation | 86 |
| GOx | Nanoparticles | Glucose | Drug delivery | 87 | |
| GOx+Cat | Polymer vesicle | Glucose | Drug delivery | 88 | |
| Lipase | SiO2 | Triglycerides | Biodegradation | 95 | |
| Lipase | SiO2 | Triglycerides | Biodegradation | 96 | |
| Lipase | SiO2 | Triglycerides | Biodegradation | 97 | |
| Lipase | PGMA/PS | Triglycerides | Biodegradation | 98 |