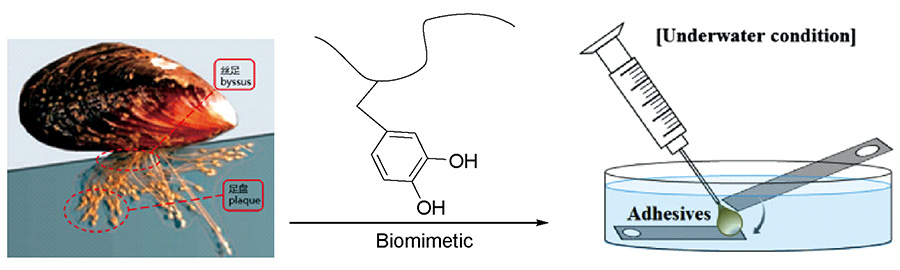
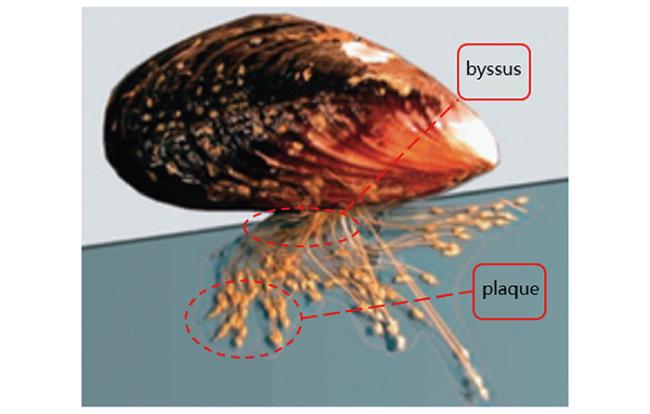
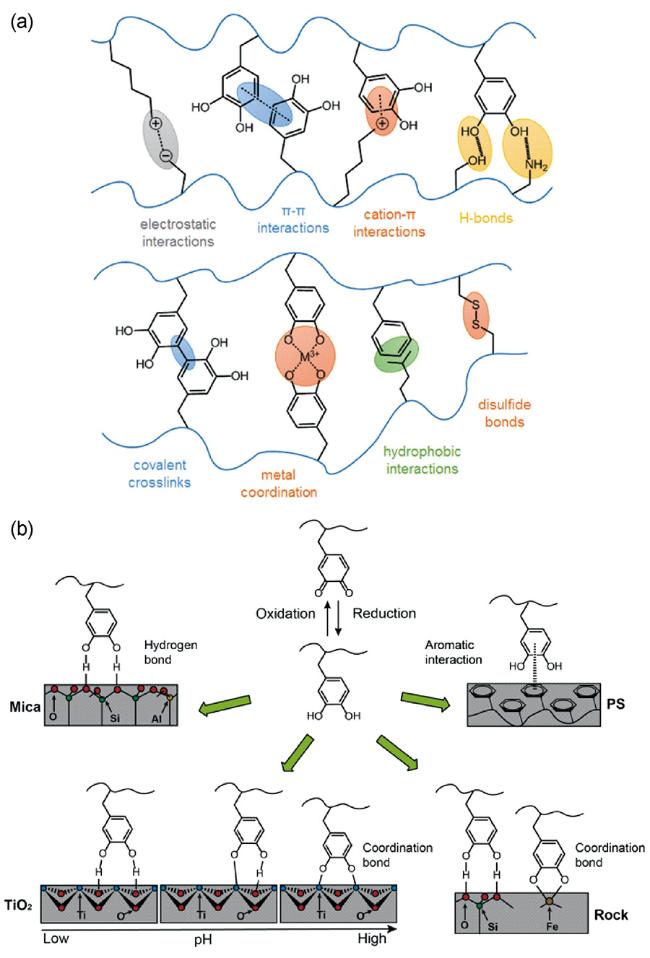
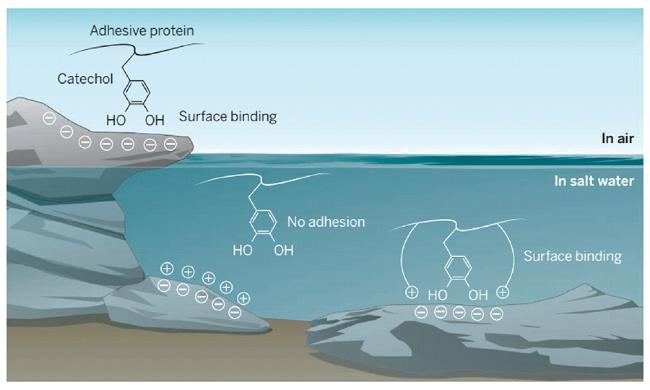
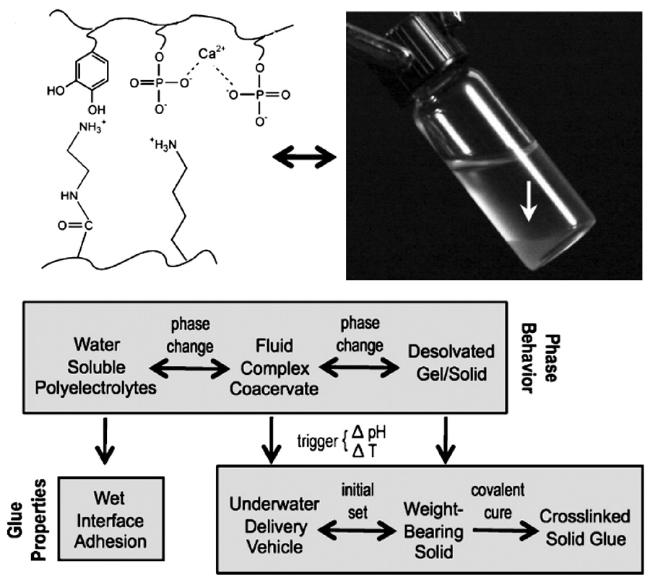
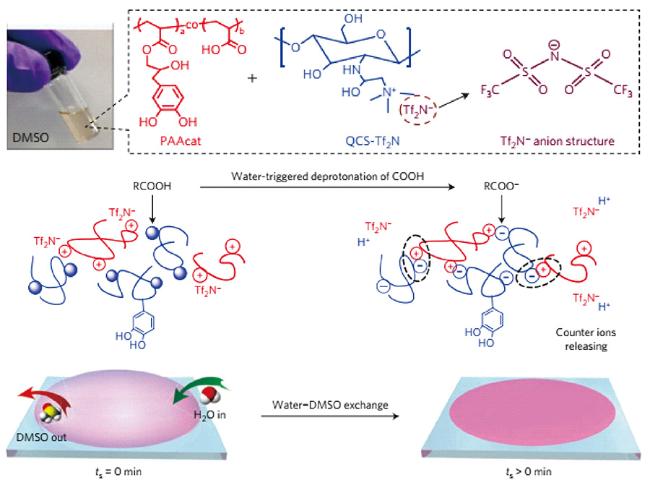
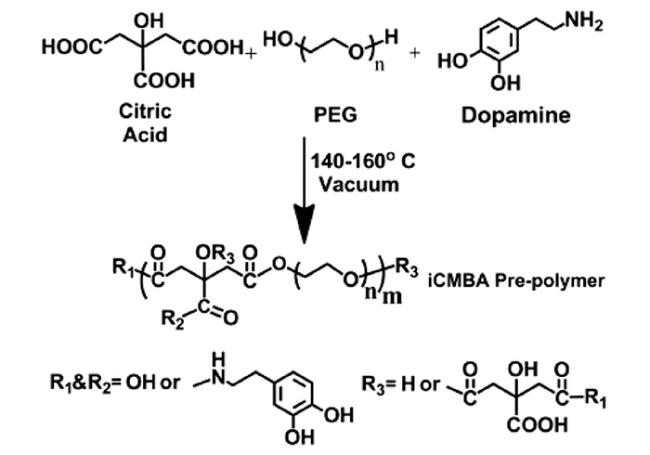
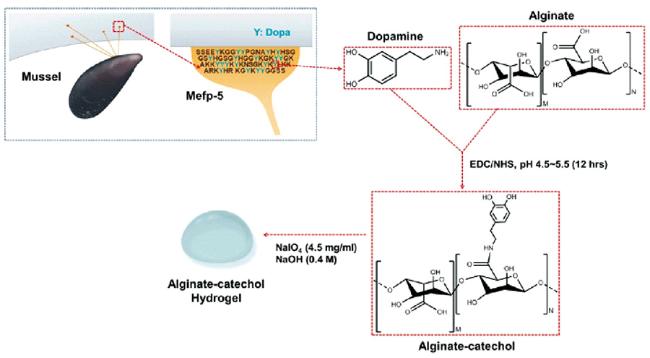
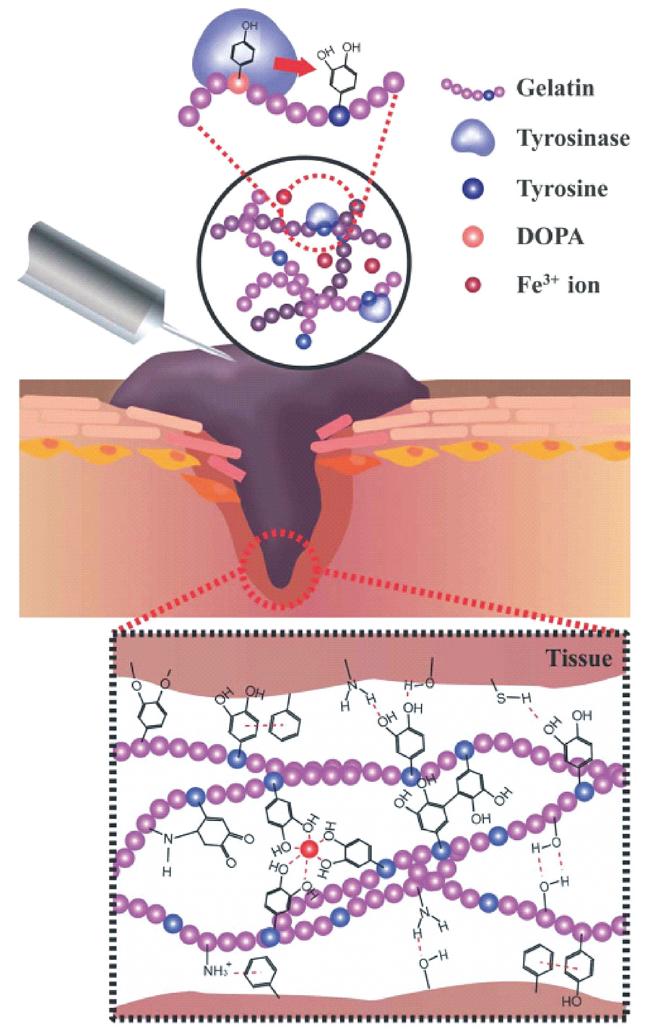
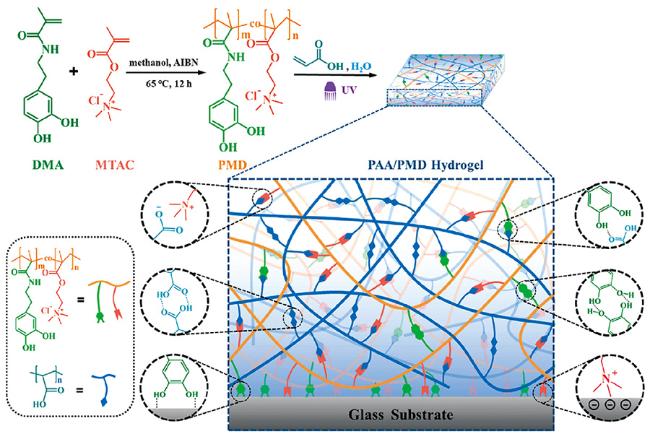
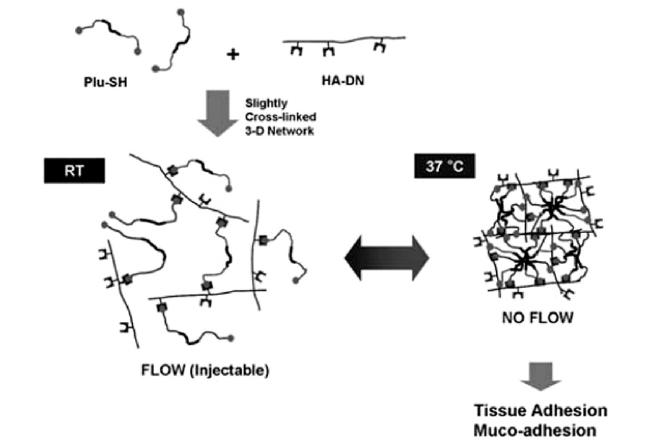
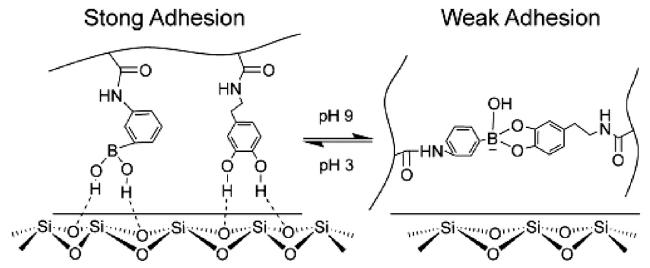
1 引言
2 贻贝黏附蛋白的组成
表1 贻贝黏附蛋白的结构特点及分布位置[5,19⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓~40]Table 1 Composition characteristics and localization of mussel foot proteins[5,19⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓~40] |
| Mussel foot proteins | Mass (kDa) | PI | DOPA (mol %) | Location | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mfp-1 | 90~110 | 10.5 | 15 | surface of plaque | 19~23 |
| Mfp-2 | 45 | 9.5 | 5 | in the plaque | 24~28 |
| Mfp-3F | 5~7 | 9 | 7~20 | at interface of the plaque | 30 |
| Mfp-3S | 5~7 | 9 | 8~14 | at interface of the plaque | 30~32 |
| Mfp-4 | 93 | 9.5 | 4 | in the plaque | 34 |
| Mfp-5 | 10 | 9 | 30 | at interface of the plaque | 35~39 |
| Mfp-6 | 11.6 | 9.5 | 3 | at interface of the plaque | 40 |
3 贻贝黏附蛋白黏附机理
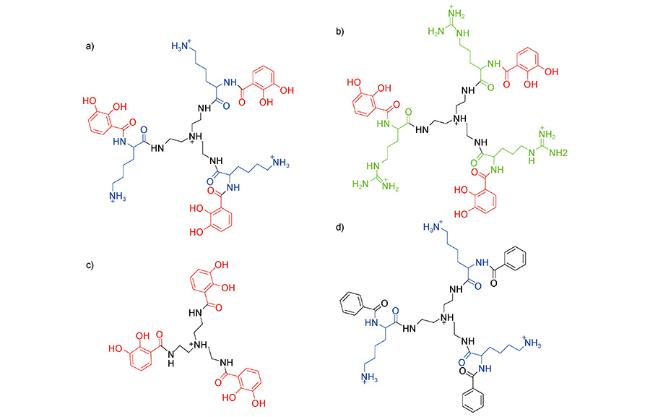
图3 阳离子对儿茶酚类胶黏剂的影响。(a)同时含有赖氨酸和儿茶酚结构;(b)同时含有精氨酸和儿茶酚结构;(c)只含有儿茶酚结构;(d)只含有阳离子结构[56]Fig.3 Chemical structures of catechol analogs that were used to investigate the influence of cations on the adhesive performance of catechol-containing tripeptides. (a) and (b) contain both catechols and cations; (c) only contains catechols, while (d) only contains cations[56] |
4 水下仿生胶黏剂研究进展
4.1 凝聚层类水下胶黏剂
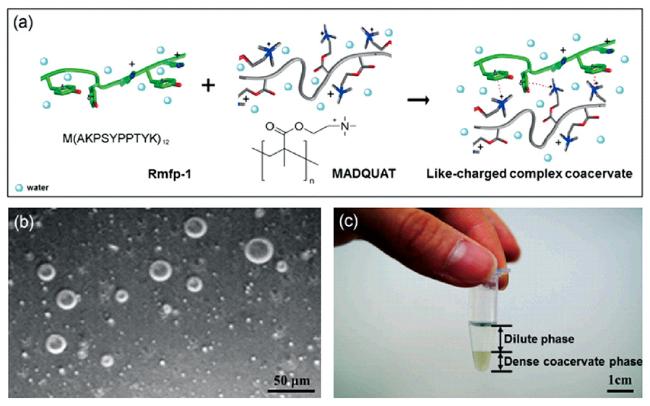
图7 (a) 同电荷凝聚层的形成原理[Rmfp-1(绿色)、MADQUAT(灰色)];(b) Rmfp-1与MADQUAT同电荷凝聚层的光学显微镜图(比例尺, 50 μm.);(c)同电荷凝聚层的分相效果(比例尺, 1 cm.)。[73]Fig.7 (a) Schematic of like-charged complex coacervate formation [Rmfp-1 (green) and MADQUAT (gray)]; (b) Light microscopy image of microdroplets of Rmfp-1 and MADQUAT like-charged coacervate. (Scale bar, 50 μm.); (c) Bulk phase separation of the like-charged coacervate. (Scale bar, 1 cm.)[73] |
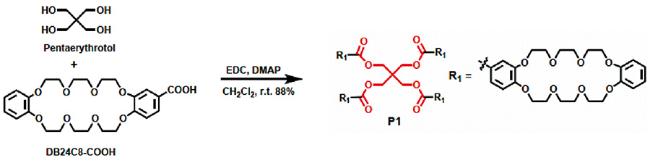
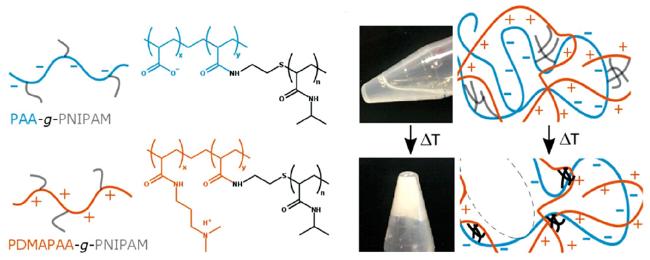
4.2 水凝胶类水下胶黏剂
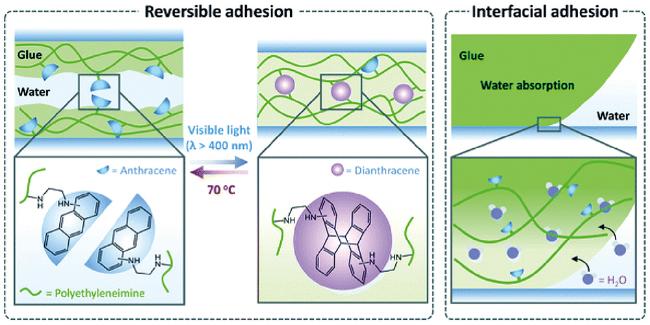
4.3 智能型水下胶黏剂
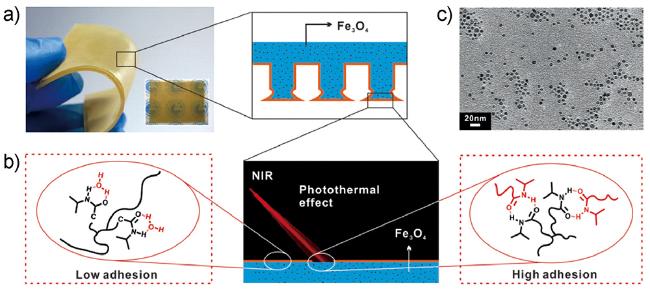
图14 (a) Fe3O4-TRGA的示意图及实拍图片;(b) Fe3O4-TRGA的NIR响应黏附能力转换机制示意图;(c)透射电镜(TEM)图像显示掺杂Fe3O4 NPs (0.2 wt%)在TRGA中的分布[86]Fig.14 (a) Schematic diagram and real photos of the Fe3O4-TRGA; (b) Schematic diagram showing NIR-responsive adhesion switching mechanism for the Fe3O4-TRGA;(c) Transmission electron microscope (TEM) image showing the distribution of doped Fe3O4 NPs (0.2 wt%) in the TRGA[86] |
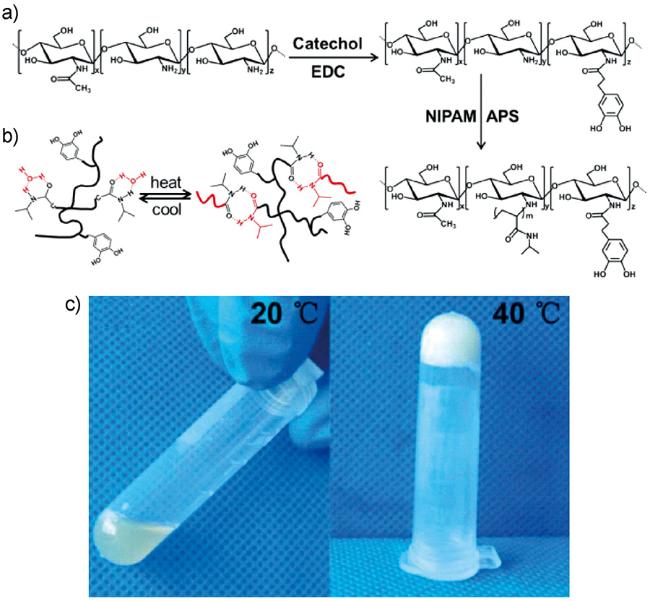
图15 (a) Chitosan-Catechol-pNIPAM水下胶黏剂制备示意图;(b) Chitosan-Catechol-pNIPAM胶黏剂的可逆热响应机制;(c) 20 ℃; (d) 40 ℃, Chitosan-Catechol-pNIPAM溶液状态(50 mg/mL) (20 ℃为流动状态,40 ℃为交联态)[87]Fig.15 (a) A schematic illustration of the preparation of the Chitosan-Catechol-pNIPAM biomacromolecular wet adhesive; (b) The mechanism for the chain state of the Chitosan-Catechol-pNIPAM biomacromolecule induced by the reversible thermo-responsive conformational change of pNIPAM side chains on the chitosan backbone (below the LCST, Chitosan-Catechol-pNIPAM is a linear branched macromolecule; above the LCST, Chitosan-Catechol-pNIPAM is a crosslinked macromolecule);(c) 20 ℃; (d) 40 ℃. Optical photographs showing the solution states (50 mg/mL) of Chitosan-Catechol-pNIPAM (20 ℃ is the flow state and 40 ℃ is cross-linked).[87] |