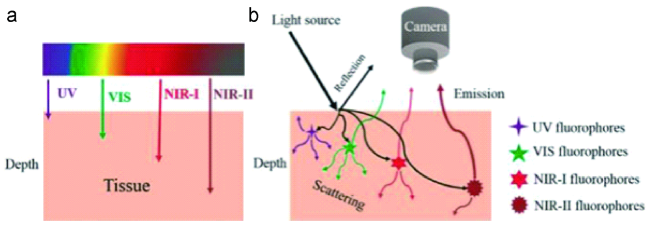
1 引言
2 可激活的NIR-Ⅱ荧光探针
2.1 pH
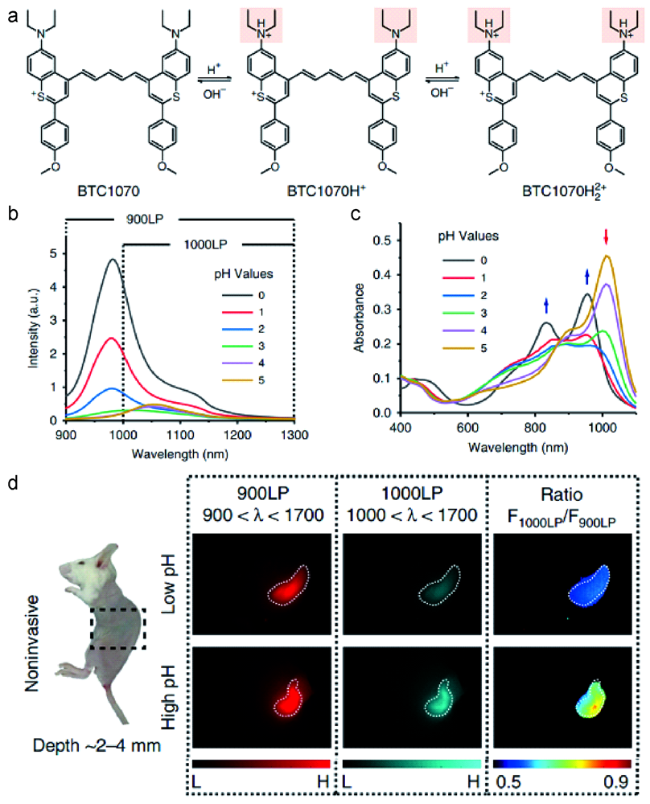
图2 (a)pH激活的NIR-Ⅱ荧光探针BTC1070的结构及其pH传感机理;BTC1070在不同pH值下的(b)吸收变化和(c)发射光谱;(d)无创的胃部pH荧光成像[35]Fig. 2 (a) The structure of pH-activatable NIR-Ⅱ fluorescence probe BTC1070 and its pH-sensing mechanism; (b) Changes in the absorption and (c) the emission spectra of BTC1070 at different pH; (d) In vivo ratiometric noninvasive fluorescence imaging of gastric pH[35] |
2.2 氧化还原
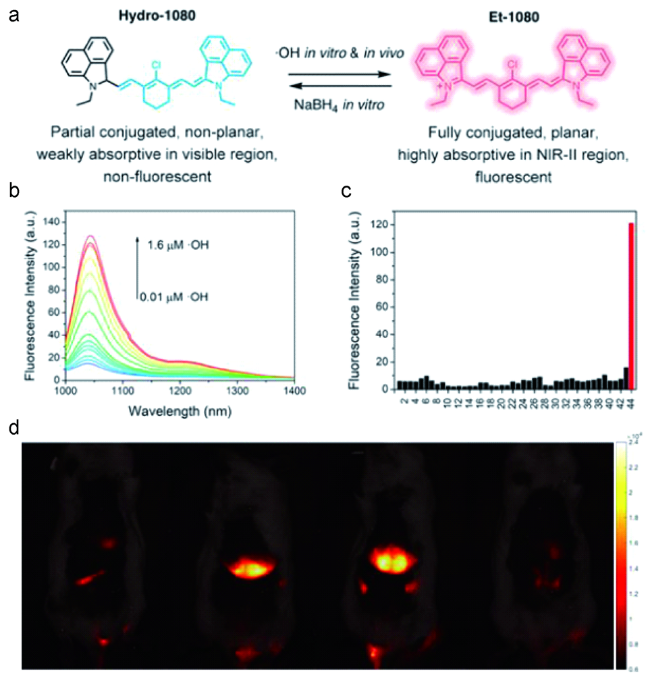
图3 (a)Hydro-1080和Et-1080的结构和转化;(b)在980 nm激发下,Hydro-1080响应0.01~1.6 μmol/L ·OH的NIR-Ⅱ荧光光谱;(c)10 μmol/L Hydro-1080对各种干扰物质和·OH的响应;(d)1064 nm激发下不同处理方式的小鼠肝脏NIR-Ⅱ荧光成像[36]Fig.3 (a) The structure and conversion of Hydro-1080 and Et-1080; (b) NIR-Ⅱ fluorescence spectra of Hydro-1080 in response to 0.01~1.6 μmol/L ·OH under 980 nm excitation; (c) Response of 10 μmol/L Hydro-1080 to various interfering species and ·OH; (d) NIR-Ⅱ fluorescence imaging of mouse liver with different processings under excitation at 1064 nm[36] |
图4 (a)V&A@Ag2S探针的构建和体内ONOO-检测的示意图;(b)V&A@Ag2S响应的NIR-Ⅱ荧光光谱;(c)注射V@Ag2S、V&A@Ag2S和A@Ag2S后不同时间点的脑血管损伤和健康小鼠的NIR-Ⅱ荧光成像图[41]Fig. 4 (a) Schematic illustration of the construction of the V&A@Ag2S probe and detection of ONOO- in vivo; (b) NIR-Ⅱ fluorescence spectra of V&A@Ag2S in response to ONOO-; (c) Timespan of NIR-Ⅱ fluorescence in brain vascular injury and healthy mice at different time points after injection of V@Ag2S, V&A@Ag2S, and A@Ag2S[41] |
图5 (a)H2S激活的NIR-Ⅱ荧光探针ZX-NIR的结构和传感机制;(b)NaHS处理后,ZX-NIR的荧光光谱变化;(c)注射ZX-NIR后,荷瘤小鼠的肿瘤区域图像[42]Fig. 5 (a) The structure and sensing mechanism of H2S-activated NIR-Ⅱ fluorescent probe ZX-NIR; (b) the fluorescence spectrum of ZX-NIR after NaHS treatment; (c)Image of the tumor area in tumor-bearing mice after injection of ZX-NIR[42] |
2.3 酶
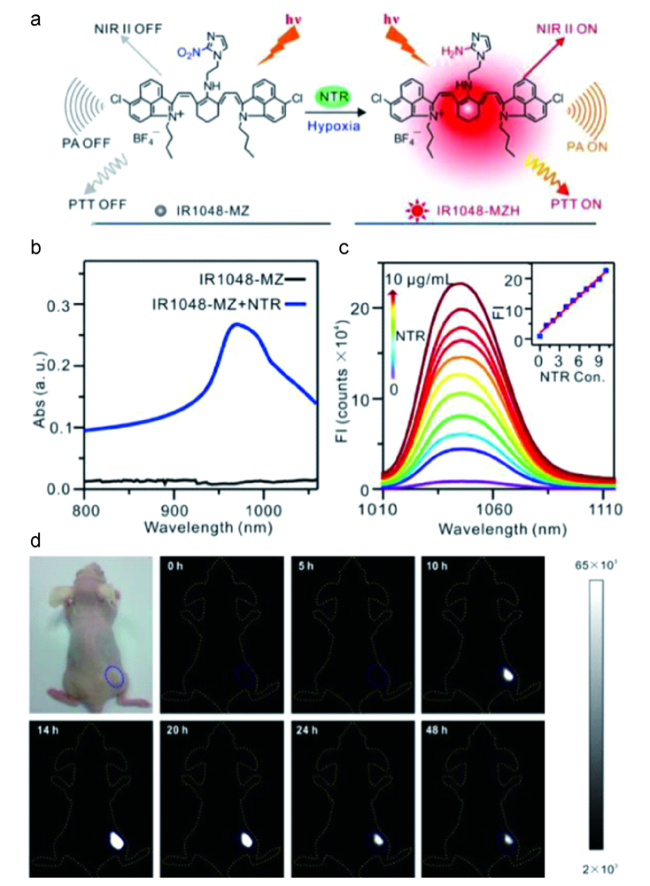
图6 (a)BOD-M-β-Gal的β-Gal酶促活化的传感机制;加入β-Gal后BOD-M-β-Gal NIR-Ⅱ(b)吸收和(c)荧光变化图;(d)注射BOD-M-β-Gal或BOD-M-β-Gal+ D-半乳糖的小鼠的时间依赖性NIR-Ⅱ成像[44]Fig. 6 (a) Proposed sensing mechanism for β-Gal enzymatic activation of BOD-M-β-Gal; (b) Absorption, (c) NIR-Ⅱ fluorescence of BOD-M-β-Gal upon addition of β-Gal in aqueous solution; (d) Time-dependent NIR-Ⅱ imaging of mice injected with BOD-M-β-Gal or BOD-M-β-Gal + D-galactose[44] |
3 可激活的NIR-Ⅱ光声成像
3.1 pH
3.2 氧化还原
图9 (a)AB-DS@BSA-N3结构;AB@BSA、 AB-DS@BSA和AB-DS@BSA-N3的(b)吸收和(c)发射光谱;(d)AB@BSA和AB-DS@BSA-N3静脉注射前后Hep2荷瘤裸鼠的PA图像[59]Fig. 9 (a) AB-DS@BSA-N3 structure; (b) absorption and (c) emission spectra of AB@BSA, AB-DS@BSA and AB-DS@BSA-N3; (d) PA images of Hep2 tumor-bearing nude mice before and after intravenous injection of AB@BSA and AB-DS@BSA- |
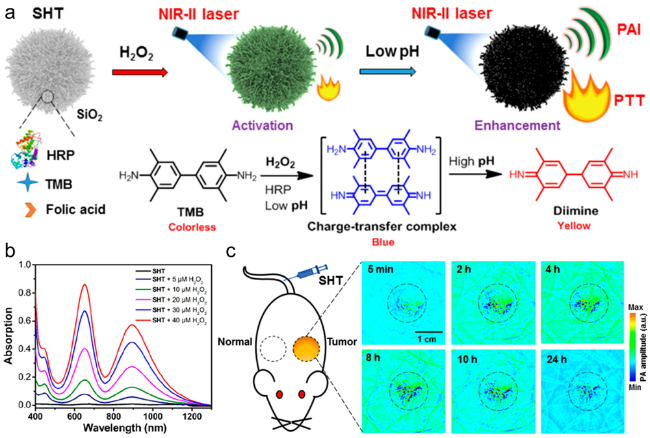
图10 (a)可激活的NIR-Ⅱ PA成像SHT的制备;(b)在PBS缓冲液中具有不同H2O2浓度的SHT的吸收光谱;(c)注射SHT后的4T1荷瘤小鼠的代表性PA图像[61]Fig.10 (a)Preparation of the activatable NIR-Ⅱ PA imaging SHT. (b) UV-vis-NIR absorbance spectra of SHT with different H2O2 concentrations in PBS buffer. (c) Representative PA images of the 4T1-tumor-bearing mice post injection of SHT[61] |