1 引言
2 LDH的基本结构和性质
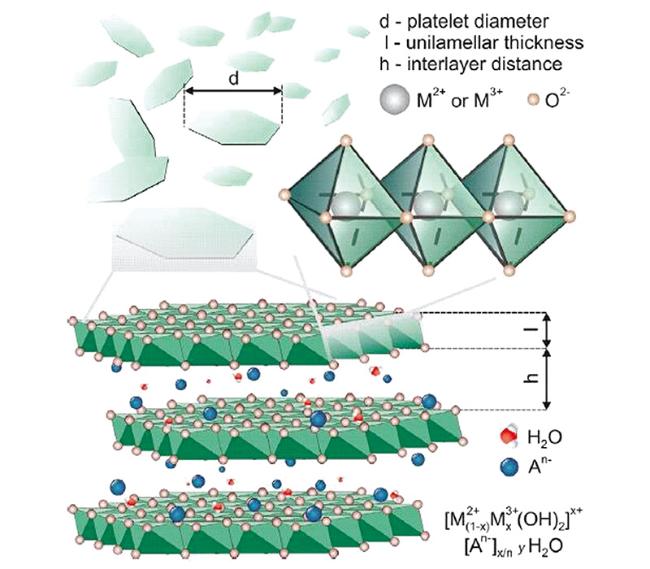
2.1 LDH的组成和结构
2.2 LDH的特殊性质
3 LDH的制备方法
3.1 常规形貌LDH的制备方法
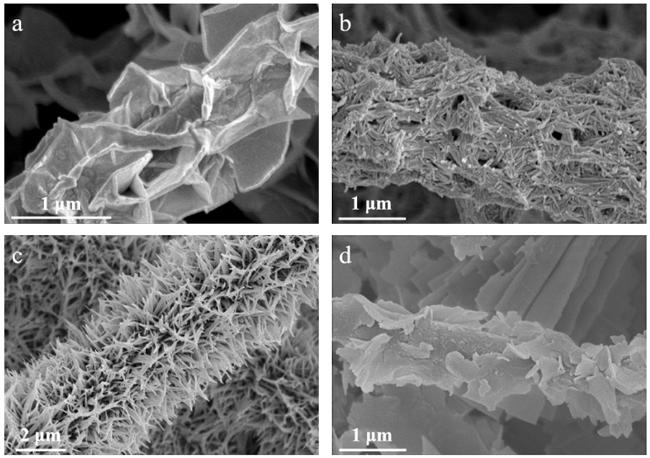
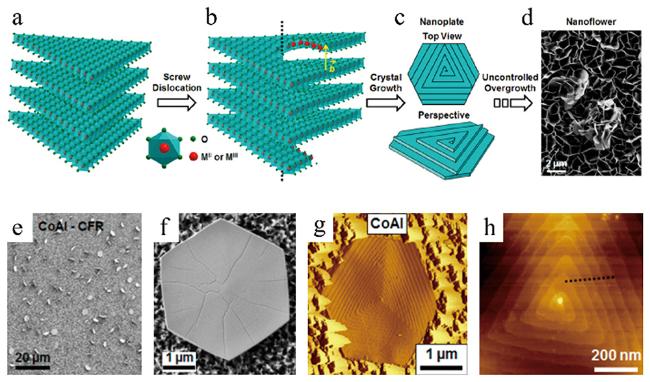
图2 (a~d)二维LDH的晶体结构以及螺旋位错机理驱动生成纳米片和纳米花结构的示意图,(e, f)不同倍率下LDH的SEM图,(g, h)敲击模式下LDH的AFM图[57]Fig.2 (a~d) Illustrations of the crystal structure and the screw dislocation-driven growth of 2D LDH into nanoplates and nanoflowers,(e, f) SEM images of LDH with different magnifications,(g, h) tapping mode AFM images of LDH[57] |
3.2 特殊形貌LDH的制备方法
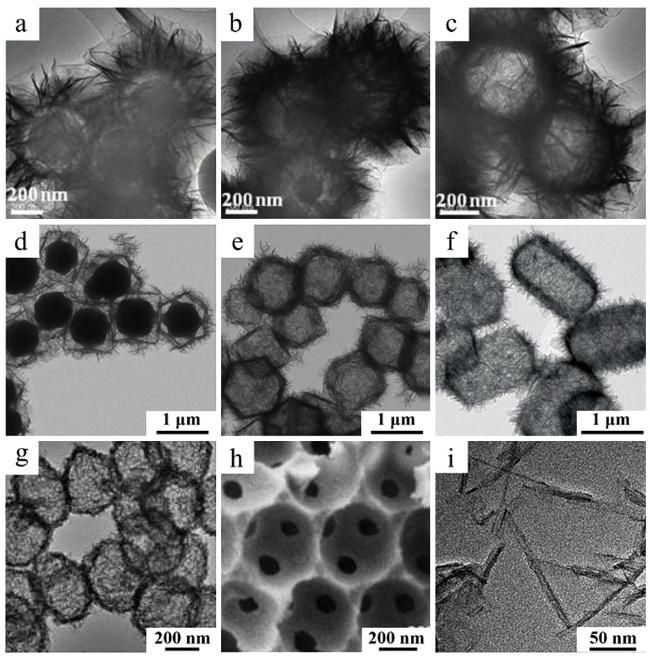
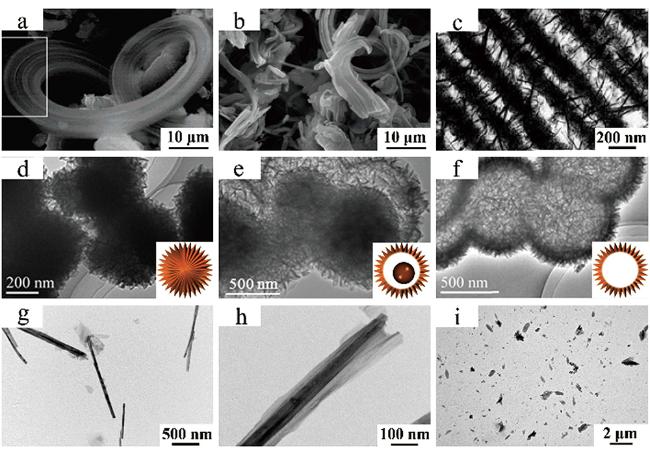
图3 通过牺牲模板法制备出不同结构LDH的SEM和TEM图:(a)核壳微球[85],(b)蛋黄壳微球[85],(c)空心微球[85],(d)内部含MOF的纳米笼[93],(e)空心纳米笼[93],(f)空心棱柱[94],(g)空心纳米球[97],(h)3 D阵列微孔结构[98]和(i)纳米线[99] Fig.3 TEM and SEM images of LDH synthesized by sacrificial template method with different morphologies: (a) core-shell microspheres[85],(b) yolk-shell microspheres[85],(c) hollow microspheres[85],(d) nanocages with MOF inside[93],(e) hollow nanocages[93],(f) hollow prism[94],(g) hollow nanospheres[97],(h) 3 D ordered microporous structure[98] and (i) nanowires[99] |
图4 利用软模板法制备出不同结构LDH的TEM图:(a)带状结构[100],(b)纳米棒[100],(c)绳索结构[107],(d)核壳微球[108],(e)蛋黄壳微球[108],(f)空心微球[108],(g, h)纳米卷和(i)纳米片[109] Fig.4 TEM images of LDH synthesized by soft template method with different morphologies: (a) belt-like structure[100],(b) nanorods[100],(c) rope-like structure[107],(d) core-shell microspheres[108],(e) yolk-shell microspheres[108],(f) hollow microspheres[108],(g, h) nanoscrolls and (i) nanosheets[109] |
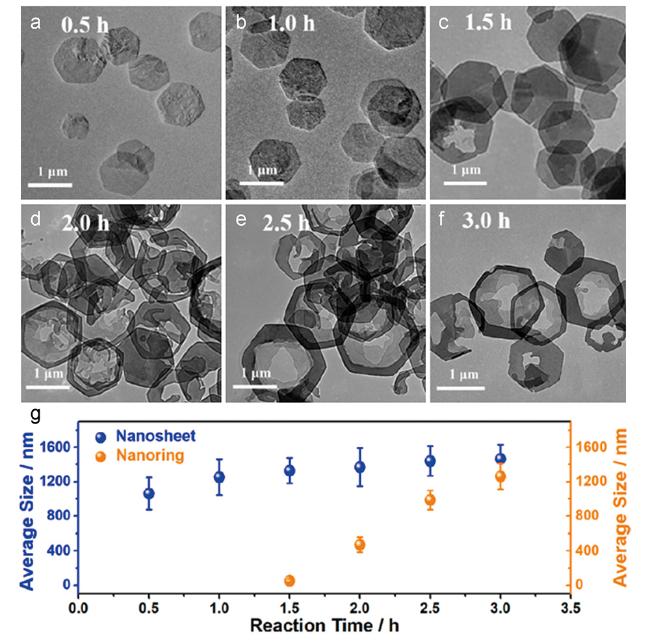
图5 不同反应时间下CoAl-LDH的TEM图:(a)0.5 h,(b)1 h,(c)1.5 h,(d)2 h,(e)2.5 h 和(f)3 h;(g)纳米片和纳米环在不同反应时间下的尺寸分布[112] Fig.5 TEM images of the CoAl-LDH at different reaction times: (a) 0.5 h,(b) 1 h,(c) 1.5 h,(d) 2 h,(e) 2.5 h and (f) 3 h.(g) The size distributions of both nanosheet and nanoring at different reaction times[112] |
4 LDH复合材料的可控制备
4.1 反应配方的影响
4.2 合成条件的影响
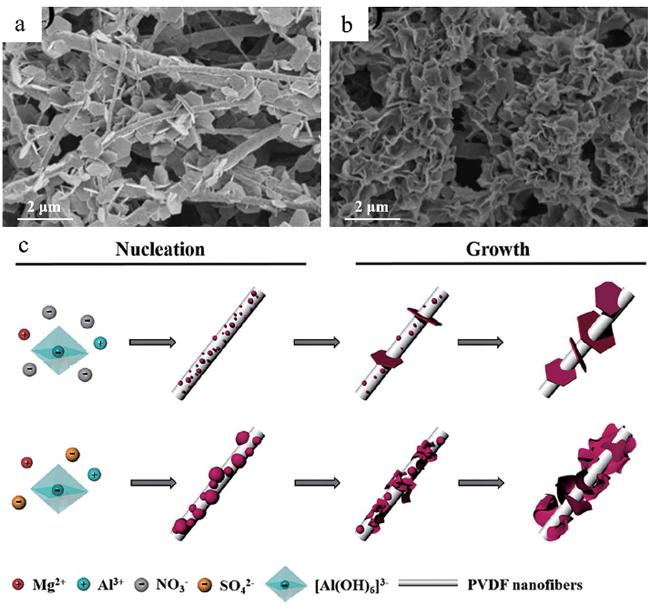
4.3 基体表面性质的影响
5 LDH及其复合材料在水处理中的应用
5.1 吸附材料
5.2 催化材料
5.3 分离材料
表1 不同形貌LDH应用于水处理时的性能对比Table 1 The performance comparison of LDH with different morphologies in water treatment |
| Application | Sample | Metbod | Morphology | Pollutant | Property | ref | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adsorbents | CoAl-LDH | Surfasctant template | Nanoscrolls | Mecthyl orange | 1153.94 mg/g | 109 | |
| (Capacity) | Coprecipitation | Nanosheets | 347.11 mgg | ||||
| MgAl-LDH | Surfisctant template | Foum-like | Bromate | 59.34 mg/g | 113 | ||
| Coprecipitation | Platc-like | 16.36 mgg | |||||
| ZnAl-LDO | Sarificial template | Hollow spheres | Orange II | 849.7 mg/g | 173 | ||
| Coprecipitation | Plate-like | 676.1 mg/g | 174 | ||||
| CaAl-LDH | Solvothermal | Nanorods | Unanium | 266.5 mg/g | 175 | ||
| Coprecipitation | Plate-like | 54.8 mg/g | 176 | ||||
| Catalysts | ZnTi-LDH | Sufuctant template | Particles arangement | Mecthyl orange | 95.4% | 158 | |
| (Removal rate) | Hydrothermnal | Sheet-like | 71.0% | ||||
| NiFe-LDH | Hydrothermal | Spheres | Methylene blue | 67.87%(COD) | 177 | ||
| Coprecipitation | Sheet-like | 58.96%(COD) | |||||
| Separation materials | NiCo-LDH/PVDF | Hydrothermal(6h) | Grass-like | Peroleum ether | ~ 690 Lm-2·h-1 | 170 | |
| (Flux) | Hydrothermal(3h) | Nanosleets | ~590 Lm -2·h -1 |