Contents
1 引言
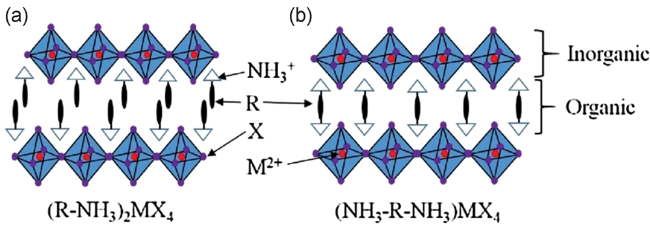
2 钙钛矿太阳能电池的结构及不稳定因素
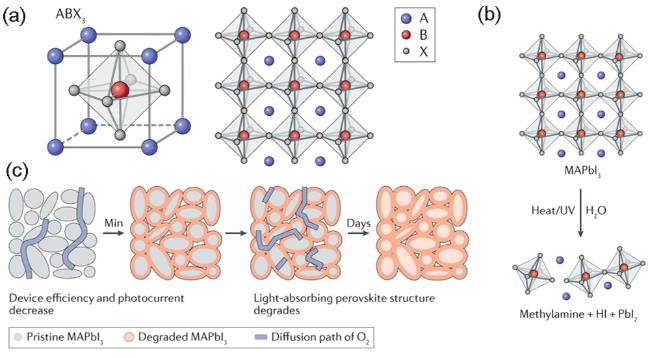
图1 (a) 三维混合钙钛矿ABX3结构图,显示角共享[BX6]4-八面体(A是有机阳离子,B是金属阳离子,X是卤化物);(b) 在潮湿、紫外光或热作用下,3D钙钛矿可分解为前体材料或0D水化相;(c) 显示了在三维钙钛矿中,O2通过晶粒渗透而开始的降解过程[23]Fig. 1 (a) Illustration of the 3D hybrid perovskite structure ABX3, showing the corner-sharing [BX6]4- octahedra (A is an organic cation, B is a metal cation and X is a halide); (b) Upon exposure to moisture, UV light or heat, 3D perovskites decompose into either the precursor materials or a 0D hydrated phase; (c) Illustration showing the degradation processes initiated by infiltration of O2 through the grains in a 3D perovskite[23] (Reproduced with permission from ref 23) |
3 界面钝化策略
3.1 二维钙钛矿作为钝化层
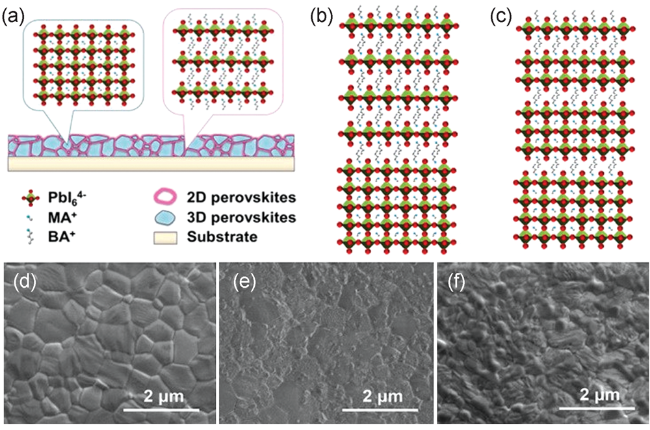
图4 (a) BA处理钙钛矿薄膜形成2D/3D堆积结构,(b,c) BA和BAI处理钙钛矿薄膜表面及晶界处2D/3D分子连接示意图,SEM图像:(d) MAPbI3膜,(e) BA处理的MAPbI3膜,(f) BAI处理的MAPbI3膜[57]Fig. 4 Schematic figure of (a) the perovskite film treated by BA to form a 2D/3D stacking structure and (b,c) 2D/3D molecular junctions on the surface and at grain boundaries of 3D perovskite films induced by BA and BAI treatments, respectively; SEM images of (d) MAPbI3 films, (e) BA-treated MAPbI3 films, and (f) BAI-treated MAPbI3 films[57] (Reproduced with permission from ref 57) |
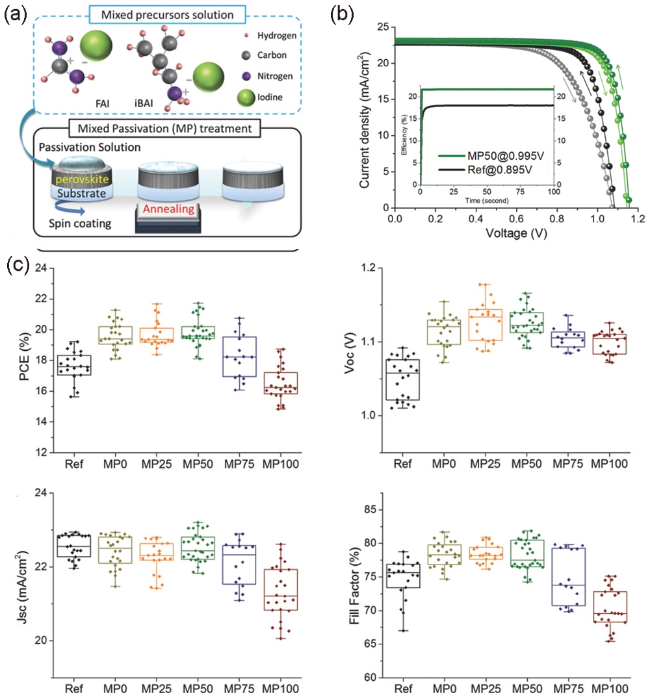
图5 (a) FAI和iBAI钝化处理方法示意图;(b)稳定性测试:在75% RH条件下38 d的PCEs监控;(c) 各种钝化组合物的PCE、VOC、JSC、FF分布[59]Fig. 5 (a) Schematic of the MP passivation treatment method with FAI and iBAI; (b) Stability test: PCEs monitored in 75% RH condition over a period of 38 d; (c) Distribution of PCE, VOC, JSC, and FF of devices with various passivation compositions[59] (Reproduced with permission from ref 59) |
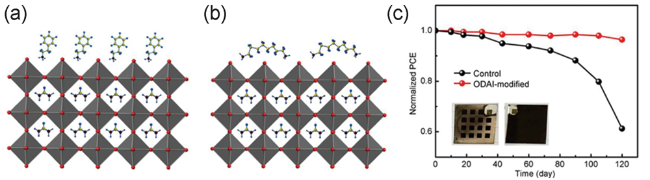
图6 钙钛矿表面示意图(a) PEAI改性,其中PEA+离子似乎垂直竖立;(b) ODAI改性,ODA2+离子似乎水平放置(颜色:原子,红色:I,灰色:铅,蓝色:H,黄色:C,棕色:N);(c)在黑暗条件下,设备在湿度约为20% ~ 40%的环境中,其性能是存储时间的函数,插图显示了对照(左)和ODAI修改的设备(右)的最终照片[60]Fig. 6 Schematic of the surface of perovskite with (a) PEAI modification wherein the PEA+ ion seemed to stand vertically and (b) ODAI modification wherein the ODA2+ ion seemed to lie horizontally (color: atom, red: I, gray: Pb, blue: H, yellow: C and brown: N); (c) Device performance as a function of storage time in an ambient environment with a humidity of about 20%~40% under the dark condition, and the inset shows the final photographs of control (left) and ODAI-modified (right) devices[60] (Reproduced with permission from ref 60) |
3.2 设计分子钝化钙钛矿
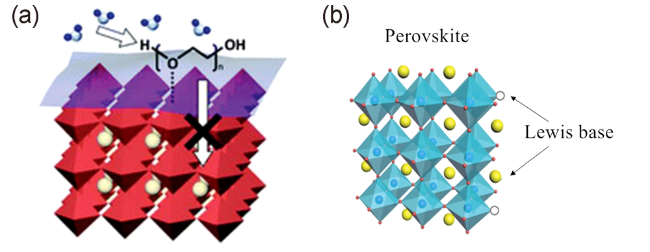
图7 (a)具有吸湿性分子的分子结构,(b)具有路易斯碱基官能团的分子结构[62,64]Fig. 7 (a) Molecular structure of the molecules with hygroscopic molecules, (b) Molecular structure of the molecules with Lewis base functional groups[62,64] (Figure a is reproduced with permission from ref 62, Figure b is reproduced with permission from ref 64) |
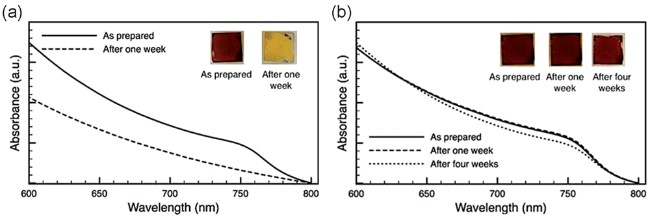
图9 在黑暗潮湿的环境中,使用或不使用OA表面钝化的老化MAPbI3薄膜的紫外-可见吸收光谱;(a) MAPbI3膜老化前后1周的吸收光谱;(b) 使用OA的MAPbI3膜在老化前后1周和4周的吸收光谱,插图显示相应样品的图像[68]Fig. 9 UV-vis absorption spectra of aged MAPbI3 films with and without surface passivation with OA in a dark and humid environment; (a) The absorption spectra of MAPbI3 before and after 1 week of aging; (b) The absorption spectra of MAPbI3 film with OA before and after 1 and 4 weeks of aging, Insets show photographic images of the corresponding samples[68] (Reproduced with permission from ref 68) |
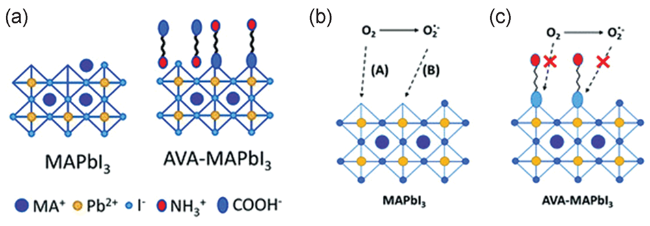
图12 (a) MAPbI3晶格末端处AVA钝化的示意图,MAPbI3表面缺陷位点经AVA钝化后稳定性增强的示意图;(b)在没有AVA的情况下,氧可以进入晶界的碘空位,从而导致在光辐射下超氧化物介导的光降解;(c)在有AVA存在的情况下,AVA与这些碘空位结合,抑制这种降解[71]Fig. 12 (a) Schematic representation of AVA passivation at lattice termination of MAPbI3, schematic representation of enhanced stability resulting from AVA passivation of surface defect sites of MAPbI3: in the absence of AVA (b), oxygen can access iodide vacancies at grain boundaries, resulting under irradiation in superoxide mediated photodegradation; in the presence of AVA (c), AVA binds to these iodide vacancies, inhibiting this degradation[71] (Reproduced with permission from ref 71) |
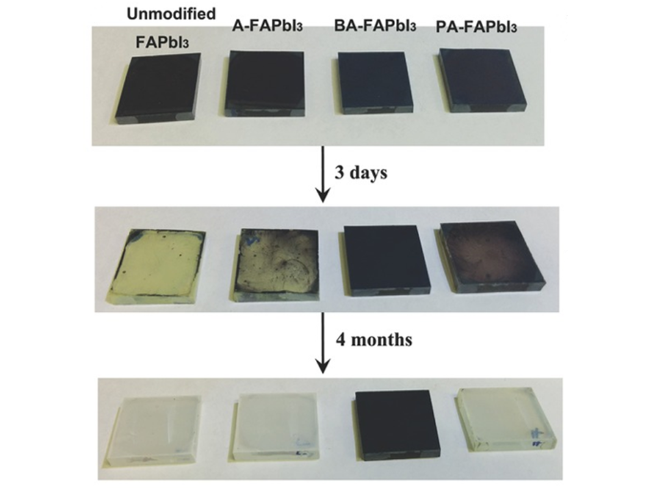
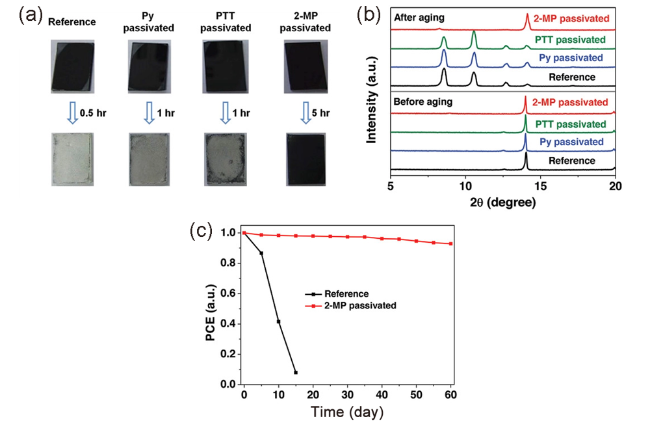
图14 (a)高湿度老化前后原始和钝化钙钛矿薄膜的照片;(b)新制备和老化钙钛矿薄膜的XRD图谱;(c)在室温相对湿度为60%~70%的环境中贮存的参考装置和2-MP钝化装置的稳定性试验[77]Fig. 14 (a) Photographs of the pristine and passivated perovskite films before and after high humidity aging; (b) XRD patterns of freshly prepared and aged perovskite films. (c) Stability test of the reference and 2-MP passivated devices stored in ambient air with a relative humidity of 60%~70% at room temperature[77] (Reproduced with permission from ref 77) |
表1 PSCs缺陷钝化概述:钝化剂、结构、钙钛矿材料、钝化功能基团、钝化类型(二维钝化)/靶缺陷(分子钝化)、无(C)和有(P)钝化的光伏参数Table 1 Summary of defect passivation for PSCs: passivator, structure, perovskite materials, passivation functional group, passivation type (two-dimensional passivation)/targeted defect (molecular passivation) and photovoltaic parameters without (C) and with (P) passivation (A: average; PVK: perovskite) |
| Passivator | Structure | Perovskite | Passivation functional group | Passivation type/ Targeted defects | Jsc[mA/ cm2] (C/P) | Voc[V] (C/P) | FF (C/P) | PCE [%] (C/P) | ref | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PEAI | 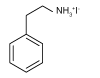 | MAPbI3 | Ammonium | 2D | 23.58/22.69 | 1.104/1.146 | 0.7685/0.7632 | 20.0/19.84 | 56 | |||||||||
| BA/BAI | 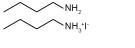 | MAPbI3 | Amine/Ammonium | 2D | 22.20/22.49、22.59 | 1.08/1.11, 1.09 | 0.74/0.78, 0.77 | 17.75/19.56、18.85 | 57 | |||||||||
| ZnPc |  | MAPbI3 | Ammonium | 2D | 22.93/23.23 | 1.08/1.09 | 0.76/0.77 | 18.83/19.56 | 58 | |||||||||
| ODAI | 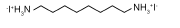 | FAPbI3 | Ammonium | 2D | 24.81/24.90 | 1.04/1.13 | 0.78/0.75 | 20.23/21.18 | 60 | |||||||||
| FPEAI | 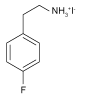 | Cs0.1(FA0.83 MA0.17)0.9 Pb(I0.83Br0.17)3 | Ammonium | 2D | 22.04/22.80 | 1.090/1.126 | 0.80/0.80 | 19.22/20.54 | 61 | |||||||||
| BA | 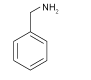 | FAPbI3 | Amine | Undercoor- dinated Pb2+ or the iodide ions | 22.7/23.6 | 1.01/1.12 | 0.70/0.73 | 15.7/19.2 | 65 | |||||||||
| PVP |  | MAPbI3 | N donor (pyridine group) | Undercoordinated Pb2+ | 20.1/22.0 | 0.90/1.05 | 0.64/0.66 | 11.6/15.1 | 66 | |||||||||
| PEO | 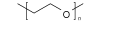 | MAPbI3 | O donor | Undercoordinated Pb2+ | 19.823/20.850 | 1.055/1.105 | 0.750/0.754 | 15.552/17.194 | 67 | |||||||||
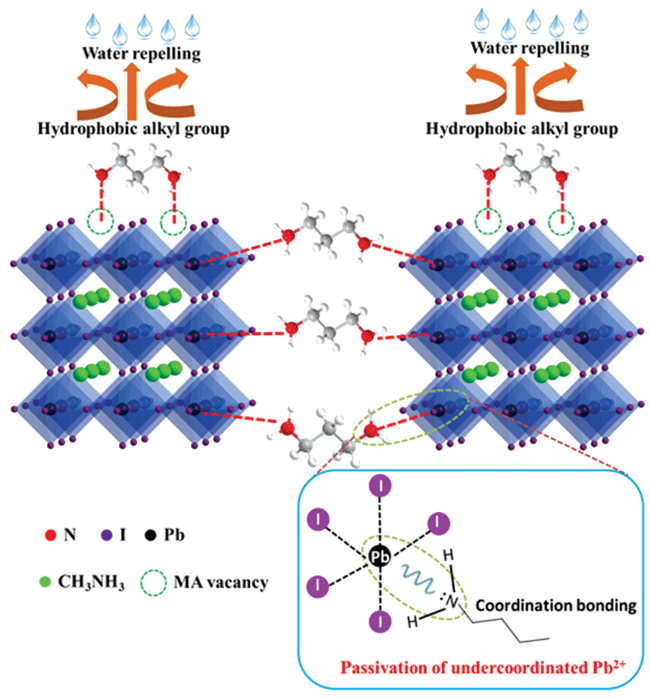
| OA | 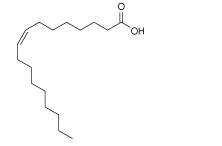 | MAPbI3 | Carboxyl group | Surface Pb2+ and/or CH3N | 24.4/23.5 | 0.86/0.93 | 36.0/41.7 | 7.62/9.11 | 68 | |||||||||
| Passivator | Structure | Perovskite | Passivation functional group | Passivation type/ Targeted defects | Jsc[mA/ cm2] (C/P) | Voc[V] (C/P) | FF (C/P) | PCE [%] (C/P) | ref | |||||||||
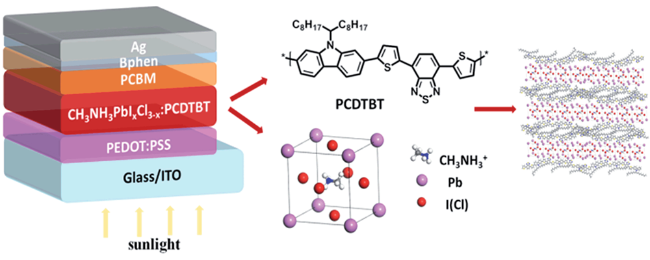
| PCDTBT | 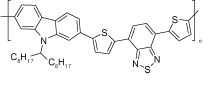 | CH3NH3 PbIxCl3-x | S, N donor | Undercoordinated Pb2+ | 20.87/21.71 | 0.91/0.94 | 0.69/0.77 | 13.19/15.76 | 69 | |||||||||
| BAA | 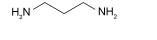 | Cs/FA/MA PVK MAPbI3 | Amine | Undercoordinated Pb2+ | 23.4/23.4 22.0/22.5 | 1.06/1.16 1.08/1.18 | 0.684/0.794 0.772/0.817 | 17.0/21.5 18.3/21.7 | 70 | |||||||||
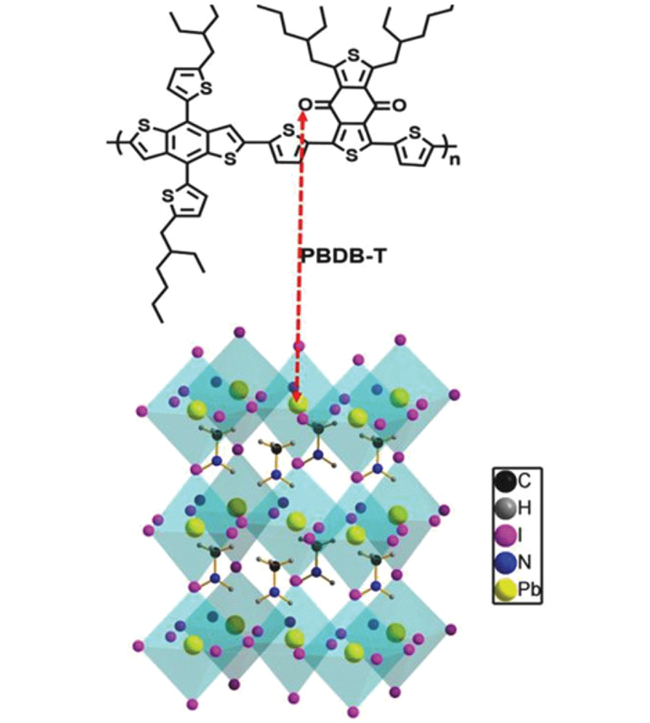
| PBDB-T | 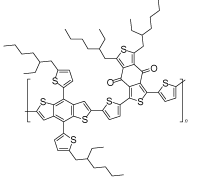 | (CsPbI3)0.04 (FAPbI3)0.82 (MAPbBr3)0.14 | O donor | Undercoordinated Pb2+ | 21.73/22.39 | 1.075/1.113 | 0.740/0.778 | 17.28/19.38 | 72 | |||||||||
| AQ310 | 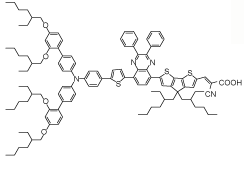 | (FAPbI3)0.85 (MAPbBr3)0.15 | Carboxyl group | Undercoordinated Pb2+ | 21.76/21.80 | 1.11/1.15 | 0.780/0.784 | 18.84(17.98 A)/19.66(19.43 A) | 73 | |||||||||
| LL | 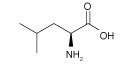 | MAPbI3 | Bipolarity | Anionic defects | 21.35/24.09 | 1.00/1.02 | 0.728/0.741 | 15.55/18.20 | 74 | |||||||||
| FAL | 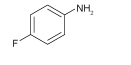 | Cs0.05(MA0.17 FA0.83)0.95 Pb(I0.83Br0.17)3 | Amine | The sites of MA/FA vacancies | 22.56/23.33 | 1.02/1.33 | 0.743/0.777 | 17.08/20.48 | 75 | |||||||||
| 2-MP | 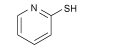 | MAPbI3 | N donor (pyridine ring) and S donor | Undercoordinated Pb2+ | 22.56/22.61 | 1.09/1.16 | 0.7464/0.7744 | 18.35/20.28 | 77 | |||||||||
| HS | 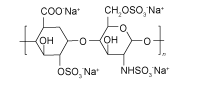 | MAPbI3 | the-COO-/-S anionic and Na+ cationic groups | Undersaturated Pb2+ and I- in MAPbI3 and Ti4+ in TiO2 | 21.29/23.34 | 1.090/1.114 | 0.7407/0.7731 | 17.20/20.10 | 78 | |||||||||