Contents
1 引言
2 LDHs作为阳极析氧反应(OER)催化剂
2.1 催化剂电子结构调控
2.2 催化剂形貌调控
图2 (a)自模板法制备层级中空Ni-Fe LDH纳米棱柱体流程;水解反应后的层级中空Ni-Fe LDH棱柱体的(b) FESEM(c) TEM图[31]Fig. 2 (a) Formation of hierarchical Ni-Fe LDH hollow nanoprisms by a self-templated strategy;(b) FESEM and(c) TEM images of the hierarchical Ni-Fe LDH hollow prisms obtained after hydrolysis reaction[31]. Copyright 2018, John Wiley&Sons, Inc. |
2.3 催化剂界面调控
表1 不同调控方式所得的LDHs材料OER性能总结Table 1 Summary of OER performance of LDHs obtained using different tuning methods |
| Main method | OER catalyst | Current density (mA·cm-2) | η (mV) | Tafel slope (mV·dec-1) | ref | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Electronic structure | Hydrothermal | Fe-Ni8-Co2 LDH | 10 | 200 | 42 | 32 |
| Hydrothermal | Fe-Ni9-Co LDH | 10 | 210 | 52 | 32 | |
| Hydrothermal | NiFeV LDH | 20 | 195 | 42 | 33 | |
| Co-precipitation | NiFeMn LDH | 20 | 289 | 47 | 34 | |
| Hydrothermal | NiFeCr LDH@CP | 25 | 225 | 69 | 35 | |
| Dry exfoliation | CoFe LDHs-Ar/NF | 10 | 237 | - | 36 | |
| Acid etching | Acid-etched CoFe-LDH | 10 | 300 | 41 | 37 | |
| N2 plasma exfoliation | N-doped ultrathin CoFe LDHs | 10 | 233 | 40.03 | 38 | |
| Morphology | Liquid-phase exfoliation | Single layered Ni-Co LDH | 10 | 334 | 41 | 30 |
| In situ growth on NF | 3D NiFe LDH film | 10 | 230 | 50 | 40 | |
| Self-templated strategy | Ni-Fe LDH hollow prisms | 10 | 280 | 49.4 | 31 | |
| Interface interaction | Self-assembly | 3DGN/CoAl-NS | 10 | 252 | 64 | 46 |
| Electro-deposition | Cu@NiFe LDH | 10 | 199 | 27.6 | 48 | |
| Electro-deposition | CoFe/LDH | 10 | 286 | 48 | 50 | |
3 LDHs作为催化剂载体
3.1 有机小分子电催化氧化
3.2 全解水
4 LDHs作为催化剂前驱体
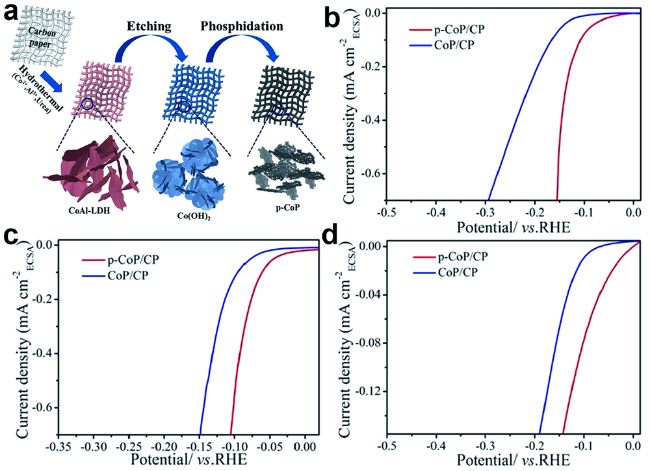
图3 (a)以CoAl-LDH/CP 制备P-CoP/CP的流程图;(b) 1.0 M KOH(c) 0.5 M H2SO4(d) 1.0 M PBS电解质中基于电化学活性面积的CoP/CP和p-CoP/CP的HER性能[73]Fig. 3 (a) Schematic illustration showing the fabrication of p-CoP/CP from CoAl-LDH/CP; The HER performance for CoP/CP and p-CoP/CP after normalization of the electrochemical active area in(b) 1.0 M KOH(c) 0.5 M H2SO4 and(d) 1.0 M PBS[73]. Copyright 2018, the Royal Society of Chemistry. |