1 引言
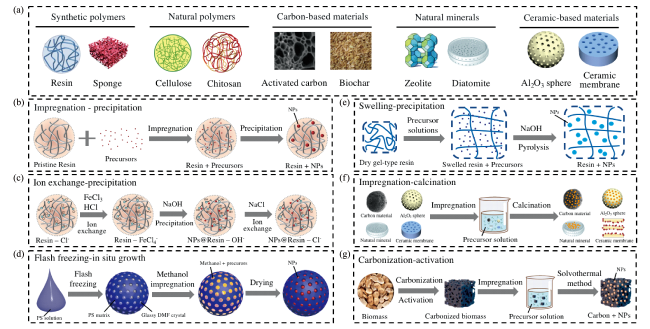
2 毫纳结构复合材料的常见载体及制备方法
2.1 有机聚合物载体
表1 以高分子聚合物为载体的毫纳结构复合材料应用于去除水中污染物的研究Table 1 Studies on millimeter-sized nanocomposites with polymers as hosts applied in water decontamination |
| Millimeter-scale hosts | Appearance size of hosts (mm) | Embedded nanoparticles | Size of nano- particles (nm) | Preparation methods | Target pollutants | Removal mechanism | Adsorption capacity (mg/g) | Removal efficiency | Treated water matrix | Experimental scale | Operation duration | ref | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Macroporous ion exchange resins | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| D201a | 0.7~0.9 | HZO | N.A.b | Impregnation-precipitation | Phosphate | Adsorption | 21.3 | N.A | Effluent from municipal WWTPe | Fixed-bed column | 1800 BV | 2 | |||||||||||
| D201 | 0.6~0.7 | HZO | 20~40 | Impregnation-precipitation | As(V) | Adsorption | 70.53 | N.A. | Acidic mining effluent | Fixed-bed column | 2900 BV | 3 | |||||||||||
| D201 | 0.4~1.0 | HLO | 3.56~ 67.23 | Impregnation-precipitation | Phosphate | Adsorption | N.A. | 91.23% | River water | Pilot-scale fixed-bed | 8 months, 10 m3/d | 5 | |||||||||||
| D201 | 0.9~1.1 | nZVI | 2~11 | Impregnation-precipitation | Cu(Ⅱ)- EDTA | Adsorption | N.A. | 88.3% | Synthetic solution | Fixed-bed column | 500 BV | 6 | |||||||||||
| D201 | 0.4~0.8 | HFO | N.A. | Impregnation-precipitation | Selenite | Adsorption | ~37 | N.A. | Simulated wastewater | Fixed-bed column | ~1200 BV | 107 | |||||||||||
| D201 | 0.6~1.0 | HFO | N.A. | Iron exchange- precipitation | Phosphate | Adsorption | 17.8 | N.A. | Industrial effluent from a pesticide plant | Fixed-bed column | ~930 BV | 10 | |||||||||||
| D201 | N.A. | Li/Al LDHsc | 5~20 | Iron exchange- precipitation | Fluoride | Adsorption | 32.6 | N.A. | Fluoride contaminated groundwater | Fixed-bed column | ~155 BV | 84 | |||||||||||
| D201 | 0.7~0.9 | CeO2 | 2.5~4.2 | Iron exchange- precipitation | As(Ⅲ) | Oxidation-adsorption | 9.96 | 99.6% | Simulated wastewater | Fixed-bed column | ~6500 BV | 108 | |||||||||||
| D201 | 0.6~0.8 | nZVI | 10~30 | Iron exchange-reduction | Se(Ⅵ) | Adsorption | N.A. | >99% | Simulated wastewater | Fixed-bed column | ~1240 BV | 109 | |||||||||||
| D201 (chloride type) | 0.6~1.0 | HFO | 12.3 | Iron exchange- precipitation | Phosphate | Adsorption | N.A. | <0.5 mg/L | Biochemical effluent from municipal WWTP | Field fixed-bed | 3500~4000 BV | 79 | |||||||||||
| Cation exchanger D001 | ~1 | HFO | N.A. | Impregnation-precipitation | Cu(Ⅱ)- citrate | Adsorption/ Oxidation | N.A. | 81.6% | Simulated wastewater | Fixed-bed column | 1300 BV | 110 | |||||||||||
| Strongly basic anion exchanger HAIX | 0.5~0.7 | HFO | N.A. | Iron exchange- precipitation (commercial ArsenXnp) | As | Adsorption | N.A. | <50 μg/L | Arsenic well water | Field fixed-bed | 29 000 BV | 7 | |||||||||||
| Strongly basic anion exchanger HAIX | 0.3~1.2 | HFO | 3~5 | Iron exchange- precipitation (commercial ArsenXnp) | As(V) | Adsorption | N.A. | <10 μg/L | Arsenic drinking water | Field fixed-bed | 91~120 days | 86 | |||||||||||
| Anion exchanger IRA-900 | N.A. | HFO | N.A. | Iron exchange- precipitation | Phosphate | Adsorption | N.A. | <10 μg/L | Secondary effluent from municipal WWTP | Fixed-bed column | 1500 BV | 111 | |||||||||||
| Anion exchanger DOWEXTM M4195 | 0.3~0.8 | HFO | N.A. | Impregnation- precipitation | Phosphate | Adsorption | N.A. | <10 μg/L | Simulated wastewater | Fixed-bed column | ~320 BV | 112 | |||||||||||
| Cross-linked ion exchange resins | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Highly cross-linked anion exchanger of polystyrene matrix | 0.6~0.7 | HZO | N.A. | Impregnation-precipitation | Fluoride | Adsorption | 20.9 | <1.5 mg/L | Simulated fluoride- containing groundwater | Fixed-bed column | ~80 BV | 82 | |||||||||||
| Cross-linked anion exchanger | 0.45~ 0.55 | HFO | 11.6 | Impregnation-precipitation | As(V) | Adsorption | 31.6 | <10 μg/L | Simulated wastewater | Fixed-bed column | 2950 BV | 12 | |||||||||||
| Strongly basic anion exchanger of poly- styrene matrix | 0.7~1.0 | HMO | 5.0~7.0 | Impregnation-precipitation | Phosphate | Adsorption | N.A. | <0.5 mg/L | Simulated wastewater | Fixed-bed column | 460 BV | 54 | |||||||||||
| Gel type ion exchange resins | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gel anion exchanger IRA-900 | N.A. | HFO | N.A. | Swelling-precipitation | As(V) | Adsorption | N.A. | >90% | Simulated wastewater | Fixed-bed column | 10,000 BV | 64 | |||||||||||
| Gel cation exchanger C-100 | 0.3~0.5 | HFO | 20~100 | Coprecipitation | Pb(Ⅱ) | Adsorption | N.A. | <0.2 mg/L | Lead-acid battery wastewater | Field fixed-bed | 6500 BV | 88 | |||||||||||
| Gel strongly basic anion exchanger 201 × 4 | N.A. | HFO | N.A. | Iron exchange- precipitation | As(V) | Adsorption | N.A. | <10 μg/L | Simulated wastewater | Fixed-bed column | 3900 BV | 22 | |||||||||||
| Synthetic polymers | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Polystyrene bead | 2 | FeOOH | 2.0~7.3 | Flash freezing-in situ growth | As(V) | Adsorption | 140~190 | N.A. | Single contaminant solution | Laboratory beaker | N.A. | 13 | |||||||||||
| Polystyrene bead | 2 | α-Fe2O3 | 3 | Flash freezing-in situ growth | As(V) | Adsorption | 32.0 | <10 μg/L | Simulated wastewater | Fixed-bed column | ~2900 BV | 55 | |||||||||||
| PDMS sponged | 9 | TiO2-Au | 3~15 | Sugar-template method | RhB | Photocatalysis | N.A. | ~96% in 3 h | Single contaminant solution | Laboratory beaker | N.A. | 113 | |||||||||||
| Polyurethane sponge | N.A. | Iron oxide | N.A. | Hydrothermal growth method | As(Ⅲ), As(V) | Adsorption | As(Ⅲ): 4.2 As(V): 4.6 | <50 μg/L | Simulated wastewater | Fixed-bed column | As(Ⅲ): 123 BV As(V): 144 BV | 23 | |||||||||||
| Natural polymers | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chitosan | N.A. | Iron oxide | N.A. | Impregnation-deposition | Phosphate | Adsorption | N.A. | 52.3% | Stream water | Pilot-scale adsorption tower | 33 days | 81 | |||||||||||
| Bead cellulose | 0.3~0.9 | Fe(OH)3 | 200~300 | Impregnation-deposition | As(Ⅲ), As(V) | Adsorption | As(Ⅲ): 99.6 As(V): 33.2 | <10 μg/L | Simulated fluoride- containing groundwater | Fixed-bed column | As(Ⅲ): 2200 BV As(V): 5000 BV | 24 | |||||||||||
Note: a. Macroporous strongly basic anion exchanger of polystyrene matrix D201; b. Not available or Not applicable; c. Li/Al Layered double hydroxides; d. Polydimethylsiloxane sponge; e. Wastewater treatment plant |
2.2 碳基材料载体
2.3 天然矿物载体
表2 以碳基材料和天然矿物为载体的毫纳结构复合材料应用于水处理的研究Table 2 Studies on millimeter-sized nanocomposites with carbon-based materials and natural minerals as hosts applied in water decontamination |
| Millimeter-scale hosts | Appearance size of hosts (mm) | Nanoparticles | Size of na- noparticles (nm) | Preparation methods | Target pollutants | Removal mecha-nism | Adsorption capacity (mg/g) | Removal efficiency | Treated water matrix | Experimental scale | Operation duration | ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon-based material | ||||||||||||
| Activated carbon | 0.25~0.5 | HFO | 2 | Impregnation-calcination | As(V) | Adsorption | 5 | N.A.a | Single contaminant solution | Laboratory conical flask | N.A. | 28 |
| Straw biochar | 5~10 | Ce | 2~5 | Impregnation-precipitation- pyrolysis | Phosphate | Adsorption | 77.7 | N.A. | Single contaminant solution | Laboratory batch adsorption experiments | N.A. | 114 |
| Corncob biochar | N.A. | FeNi | 880 | Carbonization-activation | RhB | Photo-Fenton catalysis | N.A. | 97% in 90 min | Single contaminant solution | Laboratory photo-reactor | N.A. | 30 |
| Biochar aerogel | N.A. | nZVI | 50~100 | Impregnation-Pyrolysis reduction | U (Ⅵ) | Adsorption-reduction | 720.8 | 90.1% in 80 min | Single contaminant solution | Laboratory conical flask | N.A. | 31 |
| Coffee ground biochar | N.A. | Pd | 2~11 | Impregnation-calcination | 4-nitrophenol and meth- ylene blue | Catalytic reduction | N.A. | N.A. | Single contaminant solution | Laboratory beaker | N.A. | 115 |
| Natural minerals | ||||||||||||
| Zeolite | N.A. | nZVI | 37~110 | Impregnation-reduction | As(V) | Adsorption | 47.3 | 59% in 180 min | Single contaminant solution | Laboratory batch adsorption experiments | N.A. | 116 |
| Zeolite | 0.8~1.2 | HAlO | N.A. | Impregnation-ion exchange | Phosphate | Adsorption | 7.0 | N.A. | Simulated wastewater | Fixed-bed column | 137 BV | 117 |
| Zeolite | N.A. | La | N.A. | Hydrothermal method | Phosphate | Adsorption | N.A. | >95% | Primary and secondary effluent from wastewater treatment plant | Laboratory batch adsorption experiments | N.A. | 118 |
| Zeolite | 0.18~0.25 | Mg-Al-La ternary hy-droxides | 82.1 | Coprecipitation | Phosphate | Adsorption | 80.8 | <0.5 mg/L | Single contaminant solution | Fixed-bed column | ~4800 BV | 119 |
| Diatomite | N.A. | HFO | N.A. | Impregnation-calcination | As | Adsorption | 20.5 | < 50 μg/L | Groundwater containing high concentrations of arsenic | Fixed-bed column | 937 BV, 44 d | 120 |
| Diatomite | N.A. | Magnetite | 15 | Hydrosol method | Cr(Ⅵ) | Adsorption | 69.2 | N.A. | Single contaminant solution | Laboratory batch adsorption experiments | N.A. | 121 |
| Diatomite | 0.15 | nZVI | 10 | Hydrothermal reduction method | Phosphate | Adsorption | 37.0 | N.A. | Single contaminant solution | Laboratory batch adsorption experiments | N.A. | 122 |
| Diatomite | 0.05 | nZVI | 20~60 | Impregnation-reduction | Simazine | Catalytic reduction | 0.97 | N.A. | Single contaminant solution | Laboratory beaker | N.A. | 123 |
2.4 陶瓷基载体
表3 以陶瓷基为载体的毫纳结构复合材料应用于/降解去除水中污染物的研究Table 3 Studies on millimeter-sized nanocomposites with ceramic-based materials as hosts applied in water decontamination |
| Millimeter-scale hosts | Appearance size of hosts | Nanoparticles | Size of nanoparticles | Preparation methods | Target pollutants | Removal mecha- nism | Adsorption capacity (mg/g) | Treated water matrix | Experimental scale | Operation duration | ref | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al2O3 spheres | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Al2O3 sphere | 3-5 mm | Cu-Co bi-mental | N.A.a | Impregnation- carbothermal reduction | COD of coal-gasification wastewater | Catalytic ozonation | 58.8% | Coal-gasification wastewater | Pilot-scale fixed- bed, 5 m3/d | 30 days | 39 | |||||||||||
| Al2O3 sphere | 3-5 mm | Fe | N.A. | Impregnation-calcination | P-nitrophenol | Catalytic ozonation | TOC: 68.1% | Single contaminant solution | Laboratory fixed bed reactor | 45 min | 40 | |||||||||||
| Al2O3 sphere | 10.3 mm | Fe2O3 | N.A. | Impregnation-calcination | COD and color of distillery wastewater | Catalytic ozonation | COD: ~78% Color: ~90% | Distillery wastewater | Laboratory ozone reaction column | 30 min | 124 | |||||||||||
| γ-Al2O3 sphere | 3-5 mm | MnxCe1-xO2 | ≤25nm | Impregnation-calcination | COD of coking wastewater | Catalytic ozonation | COD: >45.6% | Bio-treated coking wastewater | Full-scale applica- tion, 100 m3/h | 885 days | 104 | |||||||||||
| γ-Al2O3 sphere | N.A. | Mn-CeOx | N.A. | Impregnation-calcination | Bromaminic acid | Catalytic ozonation | TOC: 64.7% | Chemical industry wastewater | Pilot-scale ozone oxidation tower | 22 days | 106 | |||||||||||
| γ-Al2O3 sphere | 2 mm | Cu-Mn oxides | 5~10nm | High-gravity-assisted im-pregnation | Nitrobenzene | Catalytic ozonation | TOC: 81.7% | Single contaminant solution | Laboratory high- gravity rotating packed bed | 60 min | 125 | |||||||||||
| γ-Al2O3 sphere | 2 mm | Ce-MnOx | N.A. | High-gravity-assisted im-pregnation | Nitrobenzene | Catalytic ozonation | TOC: 98.3% | Single contaminant solution | Fixed-bed column | 100 min | 126 | |||||||||||
| Ceramic membranes | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ZrO2/TiO2 flat ceramic mem-brane | Diameter 47 mm, thickness 2.5 mm | FeOCl | N.A. | Impregnation-calcination | Bisphenol A | Fenton-like | >82% | Simulated wastewater | Laboratory mem- brane filtration | 120 h | 75 | |||||||||||
| α-Al2O3 flat ceramic membrane | Length 1046 mm, width 280 mm | Mn oxides | N.A. | Impregnation-calcination | DOC, PPCPs, EDCs | Ozonation-ceramic membrane filtra-tion-biologically active carbon filtra-tion | DOC:47.5% PPCPs:98.5% EDCs:99.8% | Secondary effluent from WWTP | Pilot-scale, 20 m3/d | 48 days | 46 | |||||||||||
| α-Al2O3 flat ceramic mem-brane | Diameter 22 mm, thickness 2 mm | Co3O4 | N.A. | Impregnation-calcination | Sulfamethoxazole | PMS fenton-like | 59% | Single contaminant solution | Laboratory mem- brane filtration | 100 min | 44 | |||||||||||
| α-Al2O3 flat ceramic membrane | Diameter 38 mm, thickness 2.5 mm | Ti-Mn/TiO2 | 100nm | Dip coating- calcination | Dye Red-3BS and Aniline | Catalytic ozonation | CODCr:52.1% | Simulated wastewater | Laboratory mem- brane filtration | 6 h | 93 | |||||||||||
| Al2O3 spheres | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| α-Al2O3 tubular ceramic membrane | Length 1016 mm, diameter 30 mm | Ti-Mn/TiO2 | 20nm | Dip coating- calcination | Aquaculture wastewater | Catalytic ozonation-membrane filtration | CODMn: 38.0% Color: 93.1% | Aquaculture wastewater | Pilot-scale | 240 min | 45 | |||||||||||
| α-Al2O3 tubular ceramic membrane | Length 250 mm, outer diameter 10 mm, inner diam-eter 7 mm | Ce/TiOx | 8.3nm | Sol-impregnation-calcination | Diethyltoluamide | Catalytic ozonation- membrane filtration | 40% | Single contaminant solution | Laboratory mem- brane filtration | 30 min | 47 | |||||||||||
| Tubular ceramic membrane | Length 1000 mm, diameter 30 mm | TiO2 | 200~ 500nm | Impregnation-calcination | COD of dyestuff wastewater | Membrane filtration- catalytic ozonation | CODCr: >90% | Secondary effluent from dyestuff WWTP | Pilot-scale, 10 t/d | 30 days | 43 | |||||||||||
| AAO template | Diameter 24 mm, thickness 0.06 mm | Fe3O4 | N.A. | Solvothermal method | Para-chlorobenzoic acid | Heterogeneous Fenton | N.A. | Single contaminant solution | Laboratory con- tinuous flow-through experiment | N.A. | 66 | |||||||||||
3 毫纳结构的限域效应及协同净污机制
3.1 毫米级载体内纳米颗粒的限域生长特性
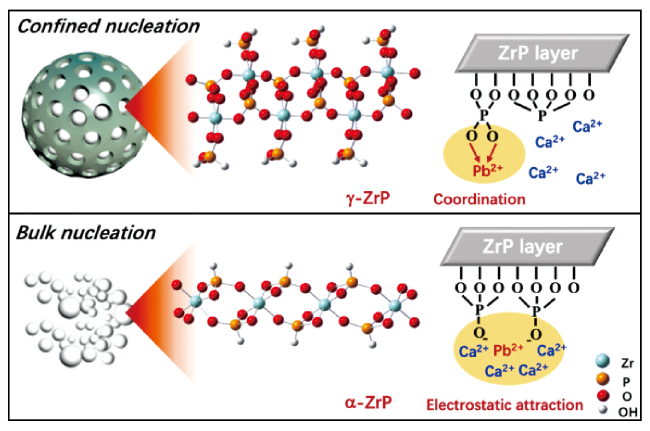
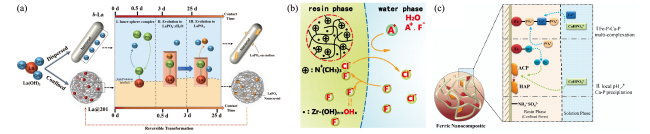
3.2 毫米级载体内纳米颗粒的限域吸附及再生特性
图3 限域体系中纳米颗粒对污染物的吸附特性:(a)La(OH)3吸附磷酸根的晶型变化[63];(b)离子交换树脂的Donnan膜效应对污染物的富集及离子交换作用[11];(c)限域驱动磷酸钙分区结晶并提升抗污染能力[65]Fig.3 Confined adsorption properties of milli-sized nanocomposites. (a) Changes in crystal phase of La(OH)3 for phosphate adsorption[63]; (b) The Donnan membrane effect of ion exchange resin for the enrichment and ion exchange of pollutants[11]; (c) The confinement-driven calcium phosphate partitioning crystallization and improved anti-pollution ability[65] |
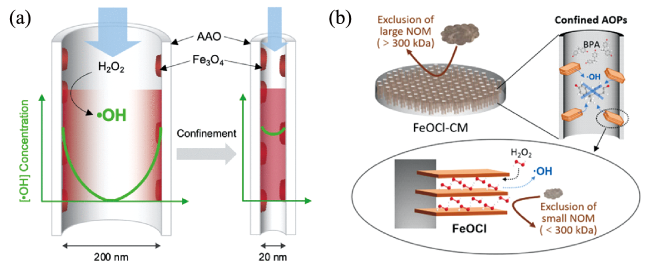
3.3 毫米级载体内纳米颗粒的限域催化氧化特性
图4 膜孔的限域催化氧化特性:(a)限域空间内HO·高强度、集约化的高效利用[66];(b)膜孔对大分子有机物的尺寸排阻效应及对小分子有机物限域氧化[75]Fig.4 Confined catalytic oxidation in membrane pores. (a) Intensive utilization of HO· in confined space[66]; (b) Size exclusion effect of membrane pores on large molecular organic compounds and confined oxidation of small molecular organic compounds[75] |
4 毫纳结构复合材料在水处理中的实际应用
4.1 毫纳结构复合材料在吸附分离净污领域的实际应用
4.1.1 除磷
图5 潘丙才等开发的毫纳结构复合材料。(a)不同复合材料的外观;(b)材料样品;(c)规模化量产的毫纳结构复合材料和(d)固定床水处理工程装置。Fig.5 Millimeter-sized nanocomposites developed by Prof. Bingcai Pan’s research group. (a) Appearance of different composite materials; (b) Material samples; (c) Large-scale production of nanoscale composite materials; and (d) Fixed-bed water treatment engineering equipment |
4.1.2 除氟
4.1.3 除砷
4.1.4 除重金属
4.2 毫纳结构复合材料在催化降解净污领域的实际应用
4.2.1 臭氧氧化/催化膜过滤耦合技术
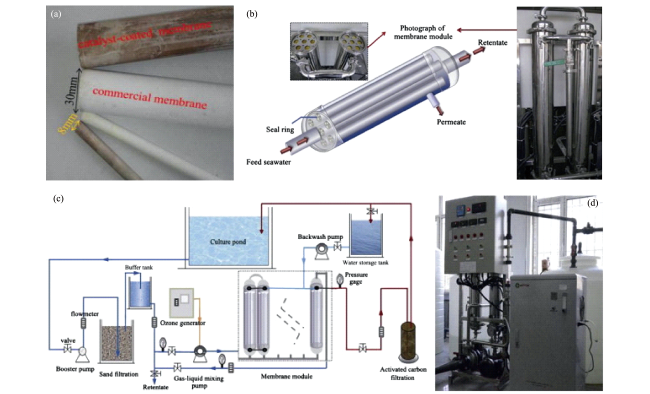
图7 张锡辉等研发的(a)平板陶瓷膜、(b)膜组件、(c)臭氧氧化-陶瓷膜过滤-BAC中试实验现场装置图及(d)流程示意图[95]Fig.7 Flat ceramic membrane developed by Prof. Xihui Zhang’s research group. (a) flat ceramic membrane sheet; (b) ceramic membrane modules; (c) on-site photos and (d) process flow diagram of the pilot-scale ozone-ceramic membrane-BAC experimental equipment[95] |