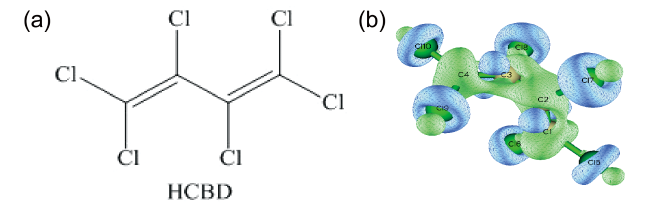
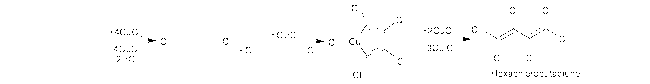1 引言
表1 HCBD的基本理化性质[1]Table 1 The main physical and chemical properties of HCBD |
| English Name | hexachlorobutadiene |
|---|---|
| CAS number | 87-68-3 |
| Physical state | Liquid |
| Boiling Point | 215℃ |
| Melting Point | -21℃ |
| Density | 1.68 g·cm-3 (20℃) |
| Vapor pressure | 20 Pa (20℃) |
| Water solubility | 3.2 mg·L-1 (25℃) |
| Henry's law constant | 1044 Pa·m3·mol-1 (experimental) |
| log Kow | 4.78 |
2 环境中的六氯丁二烯
2.1 大气中的六氯丁二烯
表2 大气环境中HCBD的浓度Table 2 Concentrations of hexachlorobutadiene in atmosphere in different areas |
| Time | Location | Country | Concentration (μg/m3) | ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2010 | Fongshan Stream, Taiwan | China | Mean: 225.844 Max: 844 | 28 |
| 2010 | Fongshan Stream, Taiwan | China | Mean:334.472 | 28 |
| 2010 | Fongshan Stream, Taiwan | China | n.d. - 716.517 | 28 |
| 2010 | Chengde, Hebei | China | 4. 88 ± 4. 67 | 29 |
| 2010 | Chongqing | China | < 0.05 | 29 |
| 2010 | Qinghai Lake | China | < 0.05 | 29 |
| 2011 | Qushui, Tibetan | China | 0. 89 ± 0. 39 | 29 |
| 2011 | Changdao, Shandong | China | 0. 32 ± 0. 32 | 29 |
| 2011 | Wuyi Mountain | China | 0. 11 ± 0. 11 | 29 |
| 2011 | Shennongjia | China | 1. 23 ± 0. 80 | 29 |
| 2011 | Qingyuan, Liaoning | China | < 0.05 | 29 |
| 2011 | Greater Khingan Mountains | China | < 0.05 | 29 |
| 2016 | Shanghai | China | 0.06 | 26 |
| 2017 | Jiangsu | China | < 2.23 ng/m3 | 22 |
| 2018 | Chongqing | China | < 2.23 ng/m3 | 22 |
| 2018 | Barcelona | Spain | 0.21 | 23 |
| 2018 | PCE plant (Acetylene method) | China | 1170 | 30 |
| 2018 | PCE plant (Carbon tetrachloride method) | China | 5530 | 30 |
| 2018 | PCE plant (Downwind) | China | 305 | 30 |
| 2017~2018 | Mountain Tai | China | 0.33 | 27 |
| 2017~2018 | Jinan, Shandong | China | 0.36 | 27 |
| 2017~2018 | Taian, Shandong | China | 0.38 | 27 |
2.2 水环境中的六氯丁二烯
表3 HCBD在不同水体中的赋存水平Table 3 Concentrations of hexachlorobutadiene in different water bodies |
| Time | Location | Type | Concentration (μg/L) | ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2002 | Greece | Industrial wastewater | n.d. - 0.70 | 47 |
| 2010 | Basel, Switzerland | surface water | < 0.05 | 48 |
| 2010 | Spain | Industrial wastewater | 0.0083~0.11 | 49 |
| 2011 | China | surface water and groundwater | 0.08~0.37 | 38 |
| 2011 | Saudi Arabia | surface water | 0.46~0.81 | 39 |
| 2011 | Southern Poland | Landfill leachate | 0.008~0.064 | 50 |
| 2012 | Huai River, China | surface water | 0.93 RQa: 7.75 | 37 |
| 2012 | Dongxiang River Basin of China | groundwater | n.d. - 349.02 | 47 |
| 2013 | China’s five major river basins | surface water and groundwater | 0.10~ 1.23 Mean:0.61 | 37 |
| 2013 | Korea | surface water | 0.029~0.067 | 40 |
| 2013 | Yellow River,China | surface water | 1.23 RQmax: 10.3 RQmean: 5.29 | 37 |
| 2013 | Liaohe River, China | surface water | 0.76 RQmax: 6.33 RQmean: 5.33 | 37 |
| 2016 | Gran Canaria, Spain | surface water | 0.8 ×10-3 | 41 |
| 2016 | Portugal | sediment | n.d. - 11.1 | 46 |
| 2016 | Zhejiang,China | surface water | 0.4 | 51 |
| 2017 | Dianshan Lake, Shanghai | surface water | 0.109 | 33 |
a RQ(risk quotients): 风险熵值 |
2.3 土壤中的六氯丁二烯
2.4 生物体内六氯丁二烯的水平
表4 HCBD在不同地区生物体内的水平(μg·kg-1·lw)Table 4 Concentrations of hexachlorobutadiene detected in organisms in different areas |
| Species | Concentration | Location | Type | Time | ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Herbivorous insects | 1.3~8.2 | Eastern China | Terrestrial life | 2014 | 15 |
| Earthworm | 1.3~8.2 | Eastern China | Terrestrial life | 2014 | 8 |
| Chinese toad | 1.3~8.2 | Eastern China | Terrestrial life | 2014 | 8 |
| Insects and birds | 1.65~3.80 | Southwest China | Terrestrial life | 2015 | 8 |
| Knotweed | 0.03~24.6 | Southwest China | Plant | 2015 | 54 |
| Fish | 0.6×10-4~ 1.29×10-3 | South China | Aquatic life | 2021 | 60 |
| Fish | 0.17~0.64 ng· g-1·lw | North pole | Aquatic life | 2012 | 61 |
| Fish | n.d. - 0.012 ng·g-1·ww | Pearl River Estuary, China | Aquatic life | 2012 | 2 |
| Fish | 112.8~827.3 | Mississippi River | Aquatic life | 1976 | 62 |
| Fish | 2.7±0.59 ng/g ww | Mexico | Aquatic life | 2018~2019 | 63 |
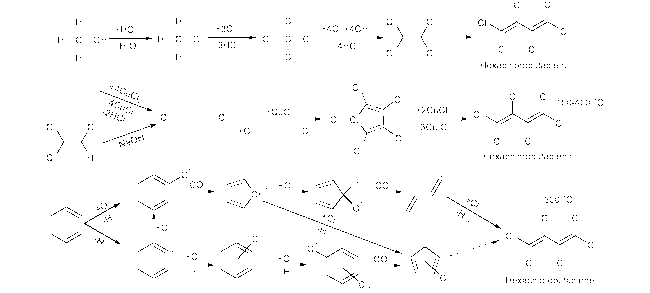
3 中国六氯丁二烯的排放源
3.1 化工生产源的非故意产生
3.2 垃圾焚烧和填埋源
4 六氯丁二烯的降解
5 国内外六氯丁二烯的管控情况
表5 HCBD的国内管控和测试标准Table 5 Management and control of hexachlorobutadiene in China |
| Year | Standard name | Limits Of HCBD |
|---|---|---|
| 1997 | Water quality-Determination of volatile halogenated organic compounds-Headspace gas (GB/T 17130 - 1997) | The minimum detection limit is 0.00002 mg/L[90] |
| 2002 | Environmental quality standards for surface water (GB 3838 - 2002) | 0.0006 mg/L[91] |
| 2007 | Standard of Soil Quality Assessment for Exhibition Sites (HJ 350 - 2007) | 1 μg/g |
| 2007 | Standards for drinking water quality (GB5749 - 2006) | 0.0006 mg/L[92] |
| 2014 | Water quality-Determination of volatile organic compounds Purge and trap/gas chromatography | The minimum detection limit is 0.1 mg/L[93] |
| 2015 | Emission standard of pollutants for petroleum chemistry industry (GB 31571 - 2015) | 0.006 mg/L[94] |