1 引言
表1 不同类型正极材料组成、结构、锂含量、主要用途、市场份额及回收经济效益对比[4,16,29]Table 1 Comparison of different types of cathode composition, structure, proportion of lithium, typical use, market share and recycling economic benefits[4,16,29] |
| Cathode types | LCO | NCM | LMO | LFP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical formular | LiCoO2 | LiNi0.33Co0.33Mn0.33O2 (NCM111) LiNi0.5Co0.3Mn0.2O2(NCM532) LiNi0.6Co0.2Mn0.2O2(NCM622) LiNi0.8Co0.1Mn0.1O2(NCM811) | LiMn2O4 | LiFePO4 |
| Structure | Layered | Layered | Spinel | Olivine |
| Theoretical lithium content | 7.09 wt% | 7.65 wt% (NCM111) | 3.84 wt% | 5.74 wt% |
| Typical use | Portable electronic devices and electric tools | Portable electronic devices and EVs | Electric tools and bikes | Electric bikes, large EVs and power tools |
| Characteristics | Low safety, high cost, medium performance | Medium safety, medium cost, higher energy density, high lifetime | Medium safety, low cost, medium energy density, low lifetime | Good safety, low cost, high thermal stability, medium energy density |
| Market share | Steady | Growing | Small | Growing |
| Recycling economic benefits | LCO > NCM > LMO > LFP | |||
2 废旧LIBs正极材料选择性提锂
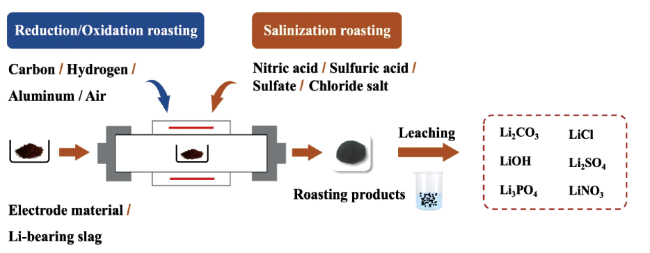
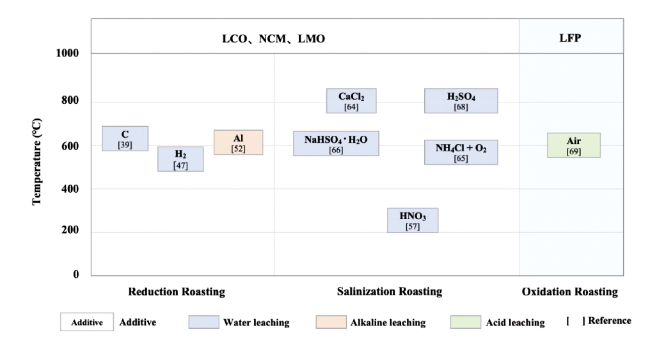
2.1 高温转型
2.1.1 熔渣提锂
2.1.2 碳热还原
2.1.3 氢还原
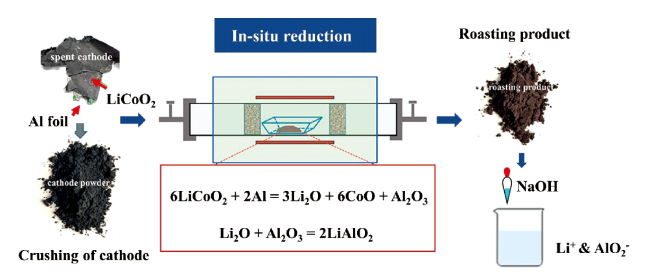
2.1.4 铝热还原
2.1.5 硝酸化焙烧
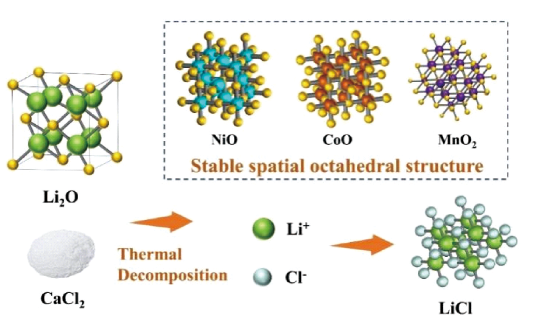
2.1.6 氯化焙烧
2.1.7 硫酸化焙烧
2.1.8 氧化焙烧
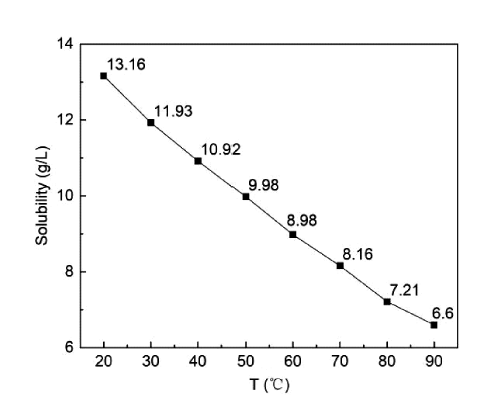
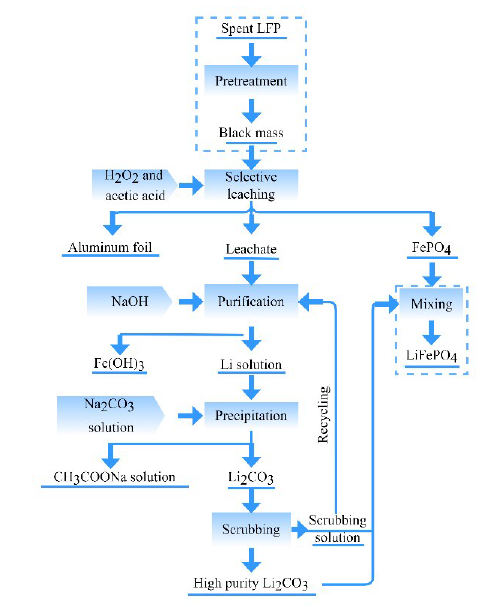
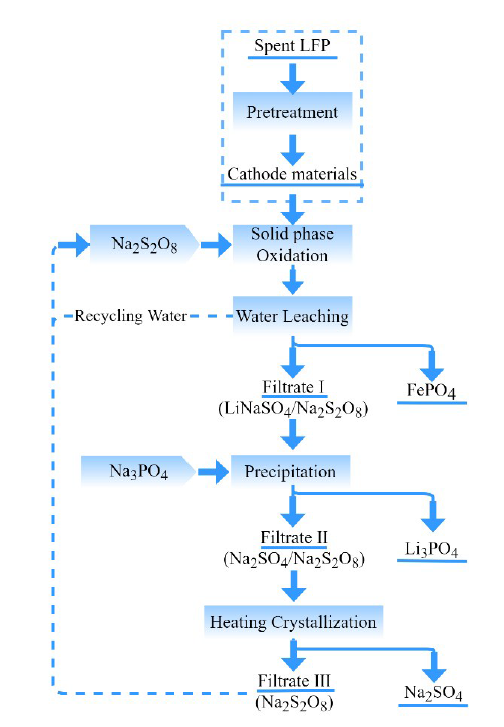
2.2 选择性浸出
2.2.1 酸性浸出
2.2.2 氧化浸出
2.3 机械/电化学强化
2.4 不同选择性提锂方法优缺点对比
表4 选择性提锂不同方法的能量消耗、试剂成本、尾气排放、浸出体系、处理能力对比Table 4 Comparision of various process treatments in terms of the required energy, reagent costs, exhaust gas emission, acid/alkaline leaching, and processing capacity |
| Process Treatments | Required Energy | Reagent Costs | Exhaust Gas Emission | Acid/Alkaline Reagent Leaching | Processing Capacity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| High temperature transition | High | Medium | Yes | No (Except in-situ reduction and oxidation roasting) | High |
| Selective leaching | Medium | High | No | Yes | High |
| Mechanical chemistry | High | High | No | No | Low |
| Electrochemical treatment | Medium | Low | No | No | Low |