1 引言
2 细菌耐药性的产生机制
3 无抗生素纳米抗菌剂
3.1 自体纳米抗菌剂
3.2 纳米酶
图5 (a) M-Art M制备过程; Fe-Art M中Fe2N6O作为催化中心通过(b)类POD和(c)类HPO催化产生·O2-和HClO; (d) MRSA与Fe-Art M共孵育后的SEM图像; (e)不同Art Ms捕获的MRSA数量; (g)不同Art Ms作用后的活/死细菌比率; (f) V-Art M和(h) Fe-Art M作用于MRSA活/死染色的共聚焦激光扫描显微镜(CLSM)图像的3D重建[81]Fig. 5 (a) The preparation process of M-Art M; Fe2N6O as a catalytic center in Fe-Art M for the production of·O2-and HClO through (b) POD-like and (c) HPO-like catalytic pathways; (d) SEM images after MRSA co-incubation with Fe-Art M; (e) number of MRSAs captured by different Art Ms; (g) different Art Ms act on live/dead bacteria ratios; 3D reconstructions from confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM) images of (f) V-Art M and (h) Fe-Art M when treated with MRSA[81]. Copyright 2021, Springer Nature |
3.3 智能响应纳米抗菌剂
3.3.1 感染微环境响应
表1 微环境响应型纳米抗菌剂的总结Table 1 Summary of microenvironment-responsive nanomaterial-based antibacterial agents |
| Nanomaterials | Triggers | Responsive units | Bactericidal moieties | Bacteria/Biofilm | ref | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rAgNAs | pH | PEG-PSB-PALA | Ag+ | MRSA | 90 | |
| AgNPs-LA-OB | pH | LA-OB | Ag+ | E.coli/S. aureus/S. aureus biofilm | 91 | |
| AgNCs | pH | POEC-SH | Ag+ | E.coli/MRSA | 92 | |
| IKFQFHFD-based nanofiber networks | pH | IKFQFHFD | Cypate(PTT) | E. coli/ B. subtilis/S. aureus/ P. aeruginosa/MRSA/MRSA biofilm | 89 | |
| MBP-Ce6 NSs | pH | MnO2 | Ce6(PDT) | MRSA biofilm | 93 | |
| CGNs | pH | P(GEMADA-co-DMA)-b-PBMA | CS(PTT),guanidyl | S. aureus biofilm | 94 | |
| PCB-Au NRs | pH | PCB | Au NRs(PTT) | E.coli/ S. aureus/MRSA | 95 | |
| Ag+-GCS-PDA@GNRs | pH | GCS | Ag+、GNRs(PTT) | MRSA/E.coli | 96 | |
| MCS@PDA@GCS | pH | GCS | Cu2+、PDA(PTT) | MRSA/E.coli | 97 | |
| FePAgPG | pH | GCS | Ag+、Fe3O4/PDA(PTT) | S. mutants/S. mutants biofilm | 98 | |
| Pd(H)@ZIF-8 | pH | ZIF-8 | Zn2+、H2 | H. pylori | 99 | |
| ICGZnS NPs | pH | ZnS NPs | Zn2+、H2S、ICG(PDT) | MRSA biofilm | 100 | |
| DCPNAs | pH | Cu2O NPs | Dextran、·OH | S. aureus/Salmonella typhimurium | 101 | |
| CuFe5O8 NCs | pH/H2O2 | Cu/Fe | ·OH | E.coli/S. aureus biofilm | 102 | |
| Cu2O NPs | H2S/H2O2 | Cu2O NPs | ·OH、Cu9S8 NPs(PTT) | MRSA | 103 | |
| AA@Ru@HA-MoS2 | Hydase | HA | ·OH、Ru NPs(PTT) | MDR S. aureus/P. aeruginosa | 104 | |
| CHFH | Hydase | HA | ·OH、CuS NPs(PTT) | S. aureus | 105 | |
| UCMB-LYZ-HP | Hydase | HA | ε-PL、MB(PDT) | MRSA | 106 | |
| Ru-Se@GNP-RBCM | Gelatinase | GNPs | Ru-Se NPs | MRSA/E. coli | 107 | |
| Ag-MONs | GSH | Ag-MONs | Ag+ | E.coli/S. aureus | 28 |
Abbreviations: LA-OB, 2-[2-dithiolan-3-yl)pentanoyloxy]-N-(carboxymethyl)-N,N-dimethylethanaminium; MON, Mesoporous organosilica nanoparticles; Octapeptide IKFQFHFD, Ac-Leu-Lys-Phe-Gln-Phe-HisPhe-Asp-NH2; POEC-SH, PEG with ortho ester segment and -SH group on the chain; MBP-Ce6 NSs, MnO2-BSA/PEG-Ce6 nanosheets; PCB, Pendant carboxyl betaine; MCS, Copper-doped mesoporous silica; DCPNAs, Dextran-coated copper peroxide nanoaggregates; CHFH, CuSNPs-HA-Fe3+EDTA hydrogel; HA, hyaluronic acid. |
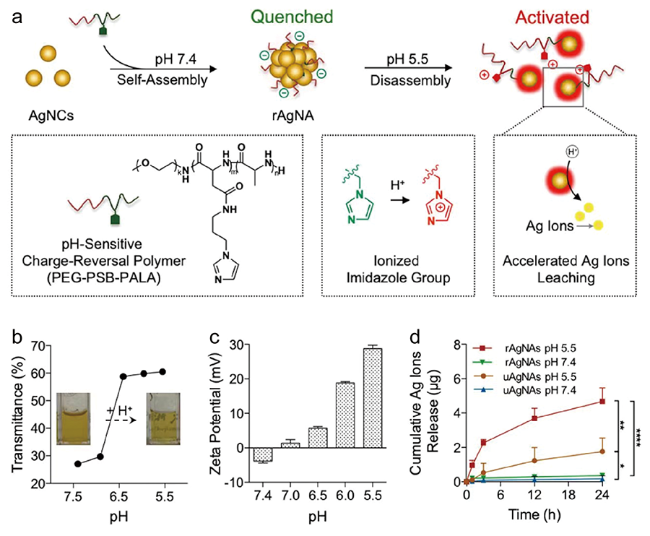
图7 (a) pH响应性纳米抗菌剂(rAgNAs)的构建以及机制; (b)不同pH值PBS中rAgNAs的透过率; (c) rAgNAs的表面电荷随pH值的变化; (d) pH=7.4和5.5(n = 3)时的累积Ag+释放量[90]Fig. 7 (a) The construction and mechanism of pH-responsive nanomaterial-based antibacterial agents (rAgNAs); (b) transmittance of rAgNAs in PBS with different pH values; (c) surface charge of rAgNAs along with changes in the pH value; (d) cumulative silver ion release amount at pH=7.4 and 5.5 (n = 3)[90]. Copyright 2019, American Chemical Society |
3.3.2 外部刺激响应
图9 (a)红光触发的胶束纳米粒子释放NO[129]; (b)可见光介导的PCNO胶束中NO和CO的共释放[130]Fig. 9 (a) Red light-triggered NO release from micellar nanoparticles[129] Copyright 2021, WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim; (b) visible light-mediated co-release of NO and CO from PCNO micelles[130]. Copyright 2022, WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim |
表2 光衍生的多模式协同抗菌治疗Table 2 Photo-derived multimodal synergistic antibacterial therapy |
| Synergistic antibacterial therapy | Light(wavelength/power/time) | Bacteria/Biofilm(Antibacterial concentration) | ref | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MoS2-BNN6 | NO/PTT | 808 nm, 1 W/cm2, 10min | Ampr E. coli/E. faecalis/S. aureus(MoS2:200 μg/mL, BNN6:80 μg/mL) | 133 | |
| SNP-PB | NO/PTT | 808 nm, 1 W/cm2, 5min | S. aureus/E. coli(>2 mg/mL) | 134 | |
| SNP@MOF@Au-Mal | NO/PTT | 808 nm, 1.5 W/cm2, 7min | P. aeruginosa(80 μg/mL) | 135 | |
| MPDA@GSNO | NO/PTT | 808 nm, 0.75 W/cm2, 10min | S. aureus/E. coli | 143 | |
| GNS/HPDA-BNN6 | NO/PTT | 808 nm, 1.5 W/cm2, 10min | S. aureus/E. coli/MRSA(100 μg/mL) | 132 | |
| α-CD-Ce6-NO-DA | NO/PDT | 660 nm, 0.2 W/cm2, 1min | MRSA biofilms(Ce6:40 μg/mL, NO:80 μg/mL) | 144 | |
| UCNP@PCN@LA-PVDF | NO/PDT | 980 nm, 2.5 W/cm2, 5min | P. aeruginosa/S. aureus | 145 | |
| Ce6&CO@FADP | CO/PDT | 665 nm, 11 W/cm2, 8min | S. aureus/E. coli(200 μg/mL)S. aureus/E. coli biofilms(800 μg/mL) | 146 | |
| Ce6@Arg-ADP | NO/PDT | 665 nm, 115 mW/cm2, 30min | MRSA/E. coli(32 μg/mL); MRSA/E. coli biofilms | 125 | |
| TPP-HF micelles | CO/PDT | 650 nm, 26 mW/cm2, 30min | S. aureus/MRSA(0.1 g/L)/E. coli | 136 | |
| MAO+ZI | PDT/I | 808 nm,1 W/cm2, 10min | S. aureus | 147 | |
| CuTCPP-Fe2O3 | PDT/Fe3+/Cu2+ | 660 nm, 20min | P. gingivalis/F. nucleatum/S. aureus | 148 | |
| Ti-RP-IR780-RGDC | PTT/PDT | 808 nm, 0.5 W/cm2, 10min | S. aureus biofilms | 149 | |
| MOF-PDA | PTT/PDT | 660 nm, 0.7 W/cm2, 20min | S. aureus/E. coli | 140 | |
| Ti-MoS2-IR780-PDA-RGDC | PTT/PDT | 808 nm, 0.5 W/cm2, 20min | S. aureus biofilms | 137 | |
| UCNPs@PFC-55 | PTT/PDT | 980 nm, 1.5 W/cm2 | E. coli | 150 | |
| CuS@BSA/rGO-PDA | PTT/PDT | 808 nm, 1 W/cm2, 10min | S. aureus/E. coli | 142 | |
| CuS@HKUST-PDA | PTT/PDT | 808 nm, 20min | S. aureus/E. coli(300 mg/L) | 141 | |
| SCN-Zn2+@GO | PTT/PDT | 808 nm, 1 W/cm2, 10min, 660 nm | S. aureus/E. coli(50 μg/mL) | 151 | |
| ZIF-8-ICG | PTT/Zn2+ | 808 nm,1 W/cm2,30min | MRSA(15.6 μg/mL) | 152 | |
| ZnO-CNP-TRGL | PTT/Zn2+ | 808 nm, 2 W/cm2, 5min | S. aureus/E. coli(50 μg/mL) | 153 | |
| HuA@ZIF-8 | PTT/Zn2+ | 808 nm, 20min | S. aureus/E. coli(1000 μg/mL) | 154 | |
| GNR-PDA@Zn | PTT/Zn2+ | 808 nm, 1.5 W/cm2, 5min | S. aureus/E. coli | 155 | |
| Au-Ag@SiO2 NCs | PTT/Ag+ | 808 nm, 1 W/cm2, 5min | S. aureus/E. coli(128 μg/mL) | 156 | |
| Ag-Bi@SiO2 NPs | PTT/Ag+ | 808 nm,1 W/cm2, 15min | MRSA(128 μg/mL)/MRSA biofilms | 157 | |
| Au/Ag NRs | PTT/Ag+ | 1064 nm, 0.8 W/cm2, 10min | MRSA(100 μM Ag) | 158 | |
| PB@PDA@Ag | PTT/Ag+ | 808 nm, 1 W/cm2, 5min | S. aureus/MRSA/MRSA biofilms/E. coli/Ampr E. coli(200 μg/mL PB) | 159 | |
| GSNCs-Cyh | PTT/Ag+ | 1064 nm, 0.75 W/cm2, 10min | MRSA/MDR E. coli | 160 | |
| C-Zn/Ag | PTT/Zn2+/Ag+ | 808 nm, 3 W/cm2, 10min | S. aureus/E. coli(0.16 mg/mL) | 161 | |
| CNSs@FeS2 | PTT/Fe2+ | 808 nm, 2.5 W/cm2, 10min | S. aureus/E. coli/S. typhimurium/P. aeruginosa/S. mutants/M. albicans(500 μg/mL) | 162 | |
| CP@WS2 NFs | PTT/CDT | 808 nm, 1 W/cm2, 10min | S. aureus/E. coli(100 μg/mL) | 163 | |
| Au/MoO3-x | PTT/CDT | 808 nm, 1 W/cm2, 10min | MRSA(128 μg/mL) | 164 | |
| RCF | PTT/CDT | 1064 nm, 0.5 W/cm2, 5min | MRSA(256 μg/mL)/S. aureus(256 μg/mL)/E. coli(128 μg/mL) | 165 | |
| Ni@Co-NC | PTT/CDT | 808 nm,1 W/cm2, 5min | MRSA(62.5 μg/mL) | 166 | |
| Cu SASs/NPC | PTT/CDT | 808 nm, 1 W/cm2, 10min | E. coli/MRSA(300 μg/mL) | 167 | |
| AI-MPDA | PTT/PDT/NO | 808 nm,1 W/cm2, 10min | S. aureus biofilms(0.2 mg/mL) | 35 | |
| GNR@mSiO2-SNO/ICG | PTT/PDT/NO | 808 nm, 1 W/cm2, 5min | P. gingivalis/F. nucleatum/S. gordonii biofilm | 168 | |
| ICG&CO@G3KBPY | PTT/PDT/CO | 808 nm, 1 W/cm2, 5min | MRSA/MRSA biofilms(150 μg/mL) | 169 | |
| DNase-AuNCs | PTT/PDT/DNase I | 808 nm, 2 W/cm2, 10min | S. aureus/P. aeruginosa/S. epidermidis/E. coli biofilms(400 μg/mL) | 170 | |
| MoS2/ICG/Ag | PTT/PDT/Ag+ | 808 nm, 1 W/cm2, 10min | S. aureus(150 μg/mL)/E. coli(250 μg/mL) | 171 | |
| AgB NDs | PTT/PDT/Ag+ | 808 nm, 1 W/cm2, 5min | MRSA(250 μg/mL) | 172 | |
| CuFe2O4/GO | PTT/PDT/CDT | 808 nm, 1 W/cm2, 10min | S. aureus/E. coli | 173 | |
| Ag-PCN@Ti3C2-BC | PTT/PDT/Ag+ | 780 nm | S. aureus/E. coli | 174 | |
| ZnO/CDots/g-C3N4 | PTT/PDT/Zn2+ | visible light, 1 W/cm, 15min | S. aureus/E. coli(200 μg/mL) | 175 | |
| CuS/GO | PTT/PDT/Cu2+ | 0.2 W/cm2, 15min | S. aureus/E. coli | 176 | |
| ZnDMZ | PTT/PDT/Zn2+ | 660 nm, 0.45 W/cm2, 20min | S. aureus | 177 | |
| MoO3-x NDs | PTT/PDT/CDT | 808 nm, 2 W/cm2, 20min | MRSA/ESBL-producing E. coli(90 μg/mL) | 178 | |
| ICG-ZnS NPs | PTT/H2S/Zn2+ | 808 nm, 1 W/cm2, 10min | MRSA biofilm(32 μg/mL) | 100 | |
| DNase-CO@MPDA NPs | PTT/CO/DNase I | 808 nm, 1 W/cm2, 10min | MRSA biofilms(200 μg/mL) | 179 | |
| Fe3O4@MoS2-Ag | PTT/CDT/Ag+ | 808 nm, 1 W/cm2, 15min | S. aureus/B. subtilis/MRSA/C. albicans | 180 | |
| SM@CuFeSe2 | PTT/CDT/immunity | 808 nm, 4 W/cm2, 15min | S. aureus | 181 | |
| FPMLC | PTT/carvacrol/LYZ | 808 nm, 3 W/cm2, 10min | S. aureus/E. coli(100 μg/mL) | 182 | |
| CuS/Cur | PTT/PDT/SDT/Cur/Cu2+ | 808 nm, 0.5 W/cm2, 15min | S. aureus/E. coli(2 mg/mL) | 183 |
Abbreviations: GSNO, S-nitrosoglutathione; GNS, Gold nanostar; HPDA, Hollow PDA; DA, 2,3-dimethylmaleic anhydride; LA, L-arginine; PVDF, Polyvinylidene fluoride; FADP,Fluorinated ADP; MAO, Micro arc oxidized; ZI, ZIF-8/Iodine; CuTCPP, 2D porphyrinic MOF; ICG, Indocyanine Green; GNR, Gold nanorod; GSNCs, Gold silver nanocages; Cyh, Cysteamine hydrochloride; MoO3-x NPs, Substoichiometric molybdenum trioxide nanoparticles; Cu SASs/NPC, Cu single-atom sites/N doped porous carbon; AI-MPDA, LA/ICG/MPDA; SNO, S-nitrosothiols; G3KBPY, Peptide dendrimer-based nanogel; AuNCs, Gold nanoclusters; NDs, Nanodots; Cur, Curcumin; HKUST, Cu-based metal-organic framework (MOF); SCN-Zn2+@GO, g-C3N4-Zn2+@graphene oxide; g-C3N4, graphitic carbon nitride; ZnDMZ, Zn-MoS2-ZIF-8. |
图10 (a)核壳UCNPs@PFC-55的制备和(b)从UCNPs“核”到PFC-55“壳”的RET过程以实现NIR响应的光热和光动力效应[150]Fig. 10 (a) Fabrication of core-shell UCNPs@PFC-55; (b) the RET process from UCNPs“core” to PFC-55“shell” for achieving NIR-response photothermal and photodynamic effects[150]. Copyright 2021, WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim |
图11 (a) RCF纳米杂化物的制备和协同抗菌机制; (b)用RCF (0~1024 μg/mL)处理的MRSA形成的细菌菌落平板照片,有或无NIR照射和H2O2; (c) MRSA在用RCF处理后通过平板计数法测定的不同组中的相应细菌存活率[165]Fig. 11 (a) Preparation of RCF nanohybrid and the antibacterial mechanism; (b) photographs of bacterial colonies formed by MRSA treated with RCF (0~1024 μg/mL) with or without NIR irradiation and H2O2; (c) the corresponding bacterial viabilities of MRSA after treatment with RCF in different groups determined by the plate counting method[165]. Copyright 2021, American Chemical Society |
图14 (a) RBC-HNTM-Pt@Au的合成、声催化机制以及通过高效SDT治疗骨髓炎; (b)不同条件处理后的MRSA菌落数和(c)相应SEM图像及活/死细菌荧光染色图像; (d)不同条件处理后MRSA内蛋白释放量; (e)用US+1-RBC-HNTM-Pt@Au、US+2-RBC-HNTM-Pt@Au和US+3-RBC-HNTM-Pt@Au处理后的MRSA菌落数及(f), (g)细胞活力(1d、3d)[190]Fig. 14 (a) Synthesis of RBC-HNTM-Pt@Au, sonocatalytic mechanism, and the treatment of osteomyelitis by efficient SDT; (b) number of MRSA colonies treated under different conditions and (c) the corresponding SEM images and fluorescent staining images of live/dead bacteria; (d) the amount of MRSA protein leaked after treatment under different conditions; (e) number of MRSA colonies and (f),(g) cell viability (1 and 3 days) after treatment with US + 1-RBC-HNTM-Pt@Au, US + 2-RBC-HNTM-Pt@Au, and US + 3-RBC-HNTM-Pt@Au[190]. Copyright 2021, American Chemical Society |