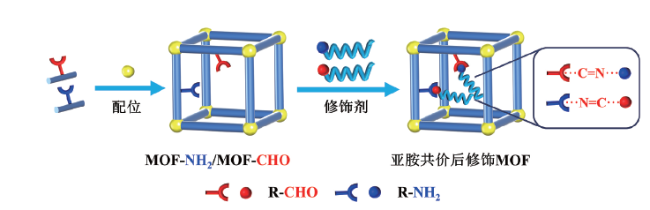
1 引言
2 MOF-NH2/CHO材料的合成策略
2.1 MOF-NH2材料的合成策略
2.1.1 直接合成法
表1 MOF-NH2材料的配体、合成策略及其结构参数Table 1 Ligands, synthesis strategies and structure parameters of MOF-NH2 |
| MOF-NH2 | Ligands | Synthesis strategies | BET/(m2·g-1) | Pore size/ (nm) | Pore volume/ (cm3·g-1) | ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IRMOF-3(Zn) | BDC-NH2 | DS (A single ligand) | 2185~2400 | 1.3 | - | 36,37 |
| UiO-66-NH2(Zr) | 1321 | 0.62 | 0.54 | 38 | ||
| CAU-1(Al)-NH2 | 1300~1530 | - | 0.54~0.64 | 39,40 | ||
| MIL-53(Al)-NH2 | 950~1309 | 1.3 | 1.03~2.61 | 41,42 | ||
| MIL-68(In)-NH2 | 451~655 | - | - | 43,44 | ||
| MIL-101(Fe)-NH2 | 2300~3438 | 2.5 | 1.64 | 45,46 | ||
| MIL-101(Al)-NH2 | 2100 | - | 0.77 | 46 | ||
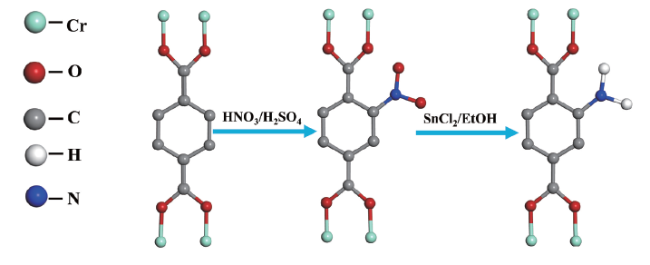
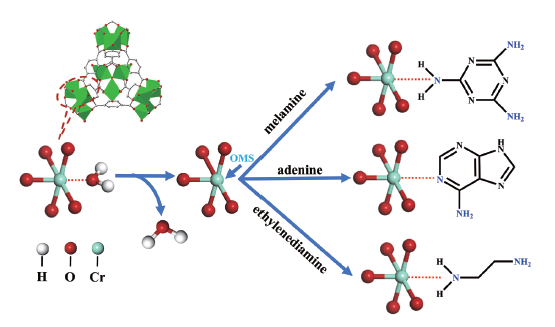
| MIL-101(Cr)-NH2 | 1443 | - | 0.67 | 47 | ||
| MIL-125(Ti)-NH2 | 1176 | 2.23 | 0.46 | 48 | ||
| MIL-88(Fe)-NH2 | 941 | 8.8 | 0.6 | 49 | ||
| UMCM-1(Zn)-NH2 | BDC-NH2、BTB | DS (Mixed ligand) | 3973 | - | - | 50 |
| DMOF-1(Zn)-NH2 | BDC-NH2、DABCO | 1510 | 0.56 | - | 50 | |
| MIL-101-NH2 | BDC | PSM | 1053~2313 | - | - | 64 |
| ZIF-8-NH2 | HATZ | PSM | 183~1848 | - | 0.17~1.48 | 67 |
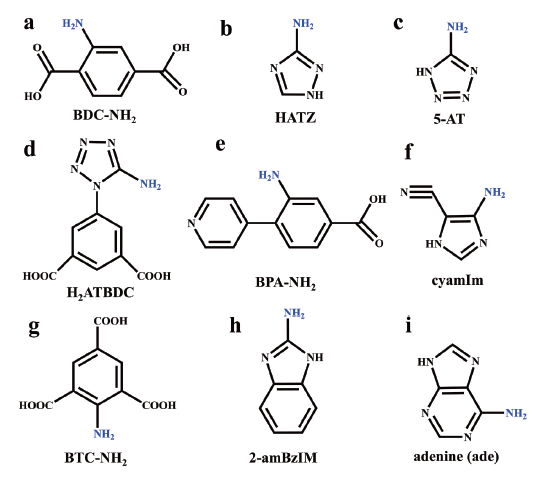
图3 用于合成MOF-NH2材料的部分配体: (a) 2-氨基对苯二甲酸,(b) 3-氨基-1,2,4-三唑,(c) 5-氨基四氮唑,(d) 5-(5-氨基四氮唑)-1,3-苯二甲酸,(e) 3-氨基-4-(吡啶-4-基)苯甲酸,(f) 5-氨基-1H-咪唑-4-甲腈,(g) 2-氨基-1,3,5-苯三甲酸,(h) 2-氨基苯并咪唑,(i) 腺嘌呤Fig. 3 Partial ligands for the synthesis of MOF-NH2: (a) 2-aminoterephthalic acid (BDC-NH2), (b) 3-amino-1,2,4-triazole (HATZ), (c) 5-aminotetrazole (5-AT), (d) 5-(5-Amino-1H-tetrazol-1-yl)-1,3-benzenedicarboxylic acid (H2ATBDC), (e) 3-amino-4-(pyridin-4-yl) benzoic acid (BPA-NH2), (f) 5-Amino-1H-imidazole-4-carbonitrile (cyamIm), (g) 2-amino-1,3,5-benzenetricarboxylate (BTC-NH2), (h) 2-aminobenzimidazole (2-amBzIm), (i) adenine (ade) |
2.1.2 合成后修饰
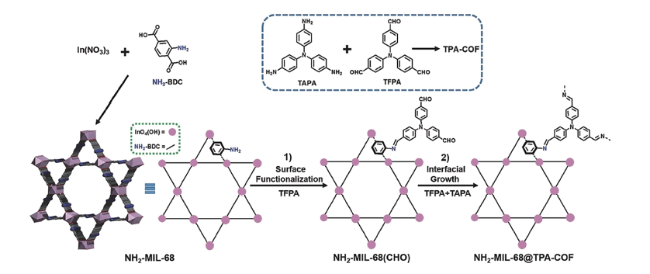
2.2 MOF-CHO材料的合成策略
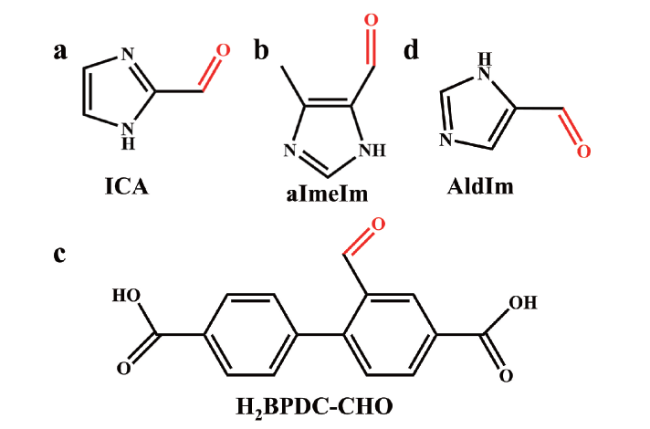
图6 用于合成MOF-CHO材料的部分配体:(a) 咪唑-2-甲醛,(b) 4-甲基咪唑-5-甲醛,(c) 2-甲醛联苯-4,4'-二羧酸, (d) 咪唑-4-甲醛Fig.6 Partial ligands for the synthesis of MOF-CHO: (a) imidazole-2-carboxaldehyde (ICA), (b) 4-methylimidazole-5-carboxaldehyde (aImeIm), (c) 2-formalbiphenyl-4,4'-dicarboxylicacid (H2BPDC-CHO), (d) imidazole-4-carboxaldehyde (AIdIm) |
表2 MOF-CHO材料的配体、合成策略及其结构参数Table 2 Ligands, synthesis strategies and structure parameters of MOF-CHO |
| MOF-CHO | Ligands | Synthesis strategies | BET/(m2·g-1) | Pore size/(nm) | Pore volume/(cm3·g-1) | ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZIF-90(Zn) | ICA | DS (A single ligand) | 189~1937 | 0.10~0.91 | 0.35 | 71,72 |
| ZIF-93(Zn) | aImeIm | 864 | 0.464 | 1.79 | 73 | |
| ZIF-94(Zn)(SIM-1) | aImeIm | 480 | 0.229 | 0.91 | 73 | |
| UiO-67(Zr)-CHO | H2BPDC-CHO | 1590 | 0.74 | - | 74 | |
| Ald-ZIF(Zn) | 2-mIm、AldIM | DS (Mixed ligand) | 1130~1396 | 0.37~0.63 | - | 75 |
2.2.1 单一配体
2.2.2 混合配体
3 亚胺共价后修饰MOF-NH2/CHO材料
3.1 亚胺后修饰MOF-NH2材料(MOF-N=C—R)
图7 (a) 水杨醛修饰IRMOF-3,(b) 吡啶-2-甲醛修饰UMCM-1-NH2,(c) 甲醛修饰UiO-66-NH2,(d) 吡啶-2-甲醛修饰MIL-125-NH2(Ti)的示意图Fig. 7 Schematic diagram of (a) salicylaldehyde modified IRMOF-3, (b) pyridine-2-carbaldehyde modified UMCM-1-NH2, (c) formaldehyde modified UiO-66-NH2, (d) pyridine-2-carbaldehyde modified MIL-125-NH2(Ti) |
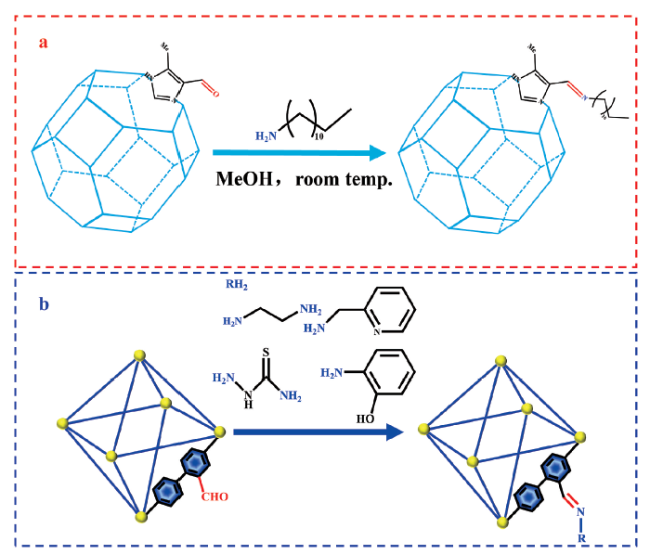
3.2 亚胺后修饰MOF-CHO材料(MOF-C=N—R)
4 ICPSM-MOF材料的吸附分离应用
4.1 气相吸附分离
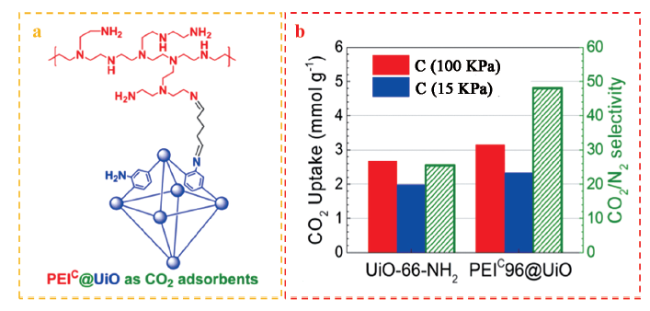
4.1.1 CO2捕集
4.1.2 H2纯化
表3 典型的ICPSM-MOF材料的反应条件、应用领域及作用机理Table 3 Reaction conditions, application areas and mechanism of action of typical ICPSM-MOF |
| ICPSM-MOF | Reaction conditions | Application areas | Mechanism | ref | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZIF-90/TETA | 25℃, 12 h | CO2 capture | Pore filling adsorption、Thermodynamic equilibrium (-NH2) | 100 | |
| PEIC/UiO | 25℃, 12 h | CO2 capture | Pore filling adsorption、Thermodynamic equilibrium (-NH2) | 93 | |
| S-ZIF-90 | 70℃, 24 h | CO2 capture | Pore filling adsorption、Thermodynamic equilibrium (F) | 95 | |
| ZIF-90/GO/EDA | 100℃, 18 h/50℃, 4 h | CO2 capture | Pore filling adsorption、Thermodynamic equilibrium (-NH2) | 97 | |
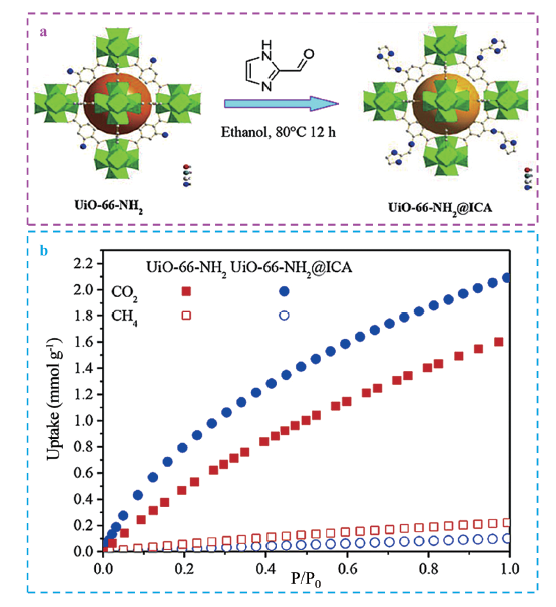
| UiO-66-NH2/ICA | 80℃, 12 h | CO2/CH4 | Thermodynamic equilibrium (N)、Size sieving effect | 96 | |
| UIO-66-NH2/TpPa-1 | 80℃, 1 h | CO2/CH4 | Size sieving effect | 87 | |
| ZIF-90/EA | 60℃, 10 h/24 h | H2/CO2 | Size sieving effect | 101 | |
| ZIF-90/APTES | 110℃, 0.5 h | H2/CO2、CO2/CH4 | Size sieving effect | 100 | |
| UiO-66-NH2/sal | 40℃, 2 h | H2/CO2、H2/CH4 | Size sieving effect | 38 |
4.2 液相吸附分离
4.2.1 无机污染物去除
4.2.2 有机污染物去除
表4 典型的ICPSM-MOF材料的反应条件、应用领域及作用机理Table 4 Reaction conditions, application areas and mechanism of action of typical ICPSM-MOF |
| ICPSM-MOF | Reaction conditions | Application areas | Mechanism | ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UiO-66-PTC | 80℃, 36 h | Pb(Ⅱ) | Chelation of S、N with Pb(Ⅱ) | 107 |
| ZIF-90-OM | 60℃, 24 h | U(Ⅳ) | Interaction between oxygen in -CHO、Zn-OH and N-OH and U(Ⅳ) | 108 |
| ZIF-90-ABOA | 100℃, 24 h | U(Ⅳ) | Chelation of amine oxime group with U(Ⅳ) | 109 |
| ZIF-90-SH | 60℃, 24 h | Hg(Ⅱ) | Chelation of S、N with Hg(Ⅱ) | 106 |
| TSC-ZIF | 100℃, 24 h | Hg(Ⅱ) | Chelation of S、N with Hg(Ⅱ) | 75 |
| MIL-101(Cr)-N-2-pyc | 40℃, 12 h | ANI、FUR、BPA | Hydrogen bonding, π-π bonding interactions and electrostatic gravity | 47 |
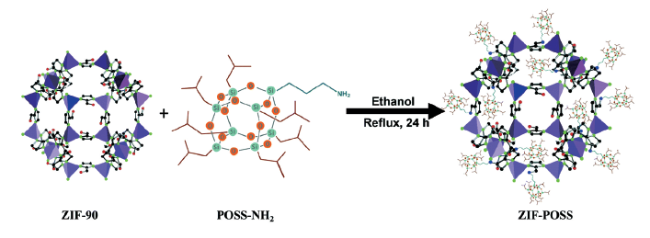
| ZIF-POSS | 80℃, 24 h | Organic solvents (n-hexane, toluene, chloroform, sec- butanol)/water | Hydrophobic, lipophilic | 114 |
| M5C | 180℃, 12 h | AO、RB | Electrostatic interactions, van der Waals forces, hydrogen bonding, the Lewis acid-base and π-π bond interactions | 113 |