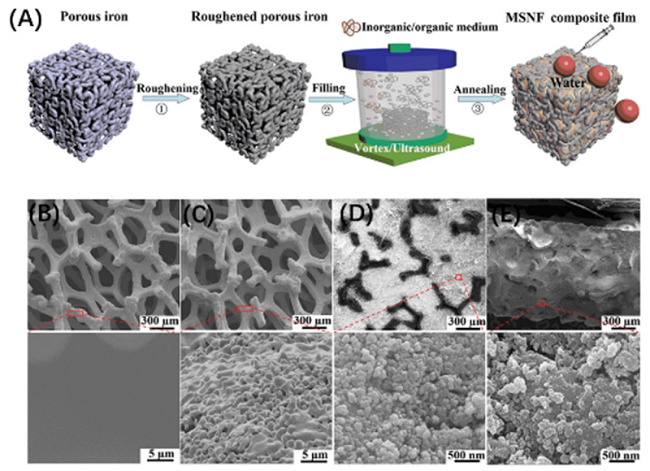
1 引言
2 表面浸润理论模型
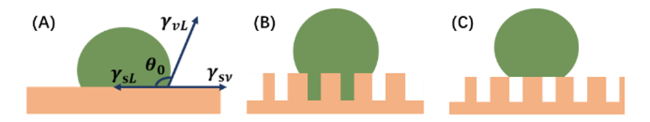
2.1 经典浸润理论
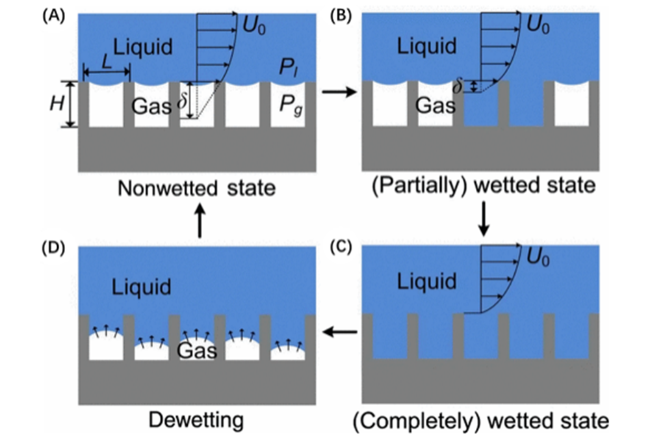
2.2 亚稳态润湿理论
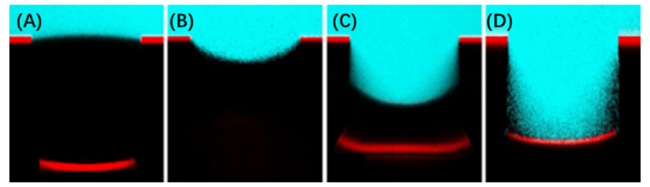
图2 激光共聚焦显微镜记录超疏水表面亚稳态在不同条件下的可视化动态形成过程[20]:在(A) 0 kPa、(B) 14 kPa、 (C) 50 kPa下浸泡5 min; (D) 50 kPa下浸泡15 minFig.2 Visualized dynamic formation process of metastable state of superhydrophobic surface by confocal microscopy[20]. after 5 min immersion under (A) 0 kPa; (B)14 kPa; (C) 50 kPa; and (D)15 min immersion under 50 kPa |
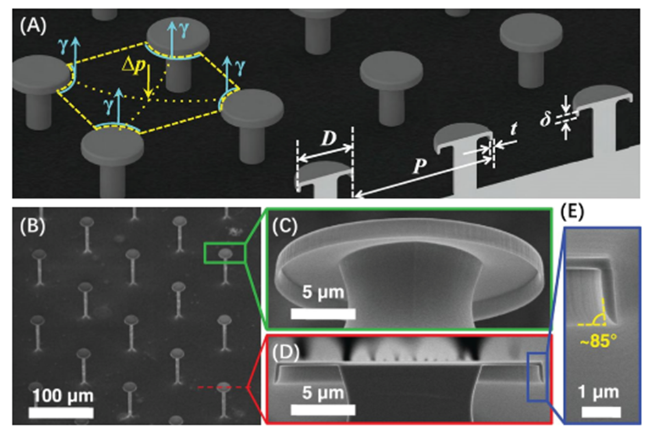
2.3 接触线理论
3 耐久型超疏水表面的制备策略
3.1 微纳米结构调控
3.2 胶黏+涂装
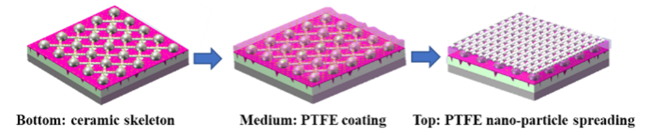
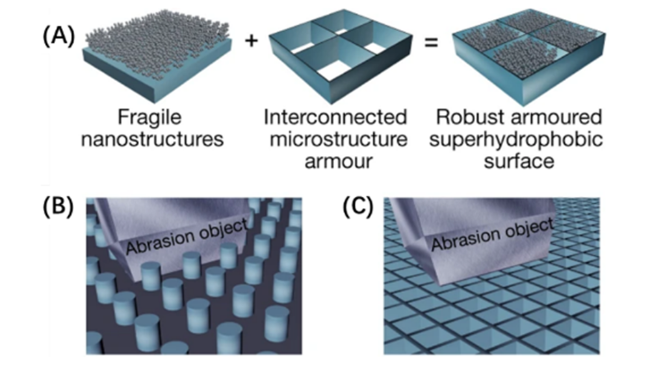
3.3 铠装防护
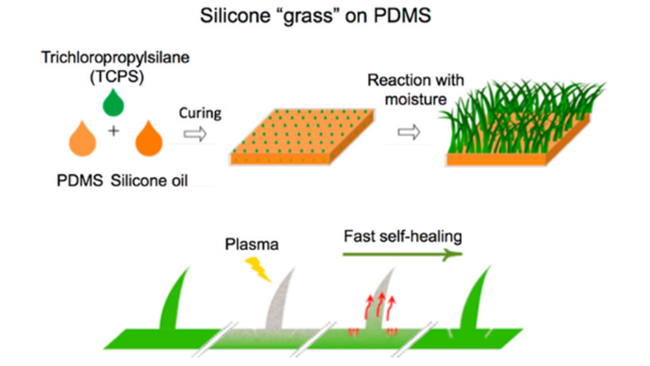
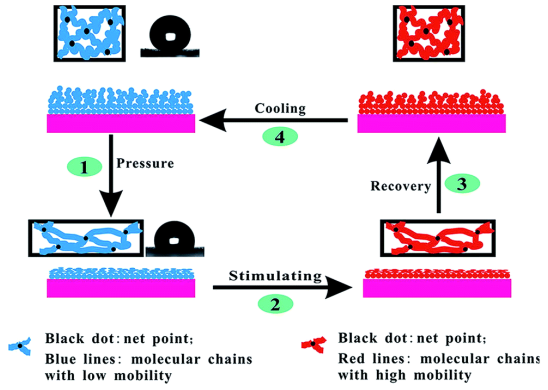
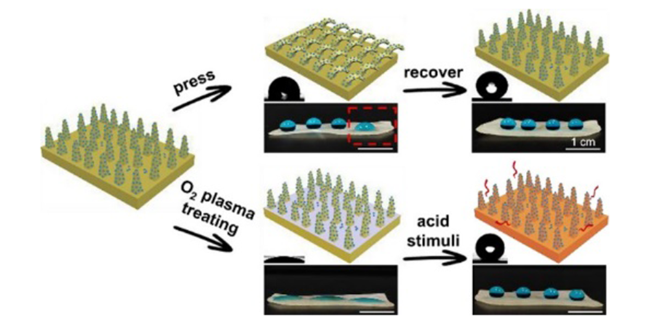
3.4 自修复
3.5 气膜补充或替换
4 耐久型超疏水表面的评价方法
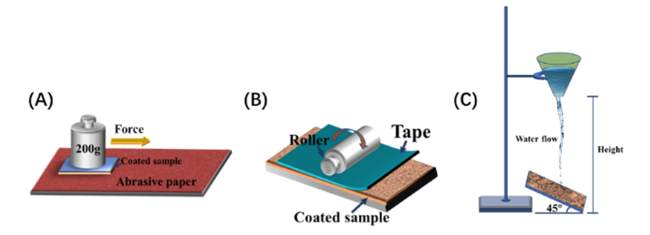
4.1 机械耐久性
4.2 化学耐久性
表1 不同制备策略下超疏水表面抗磨损和耐酸碱性能比较Table 1 Comparison of wear resistance and acid and alkali resistance of superhydrophobic surface under different preparation strategies |
| Preparation strategies | Surfaces | Abrasion test | Acid-base solution immersion | ref | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Load(kPa) | Friction distance(cm) | pH range | Immersion time(h) | |||||||||||
| Micro-nano structure design | PDMS | 10 | 1000 | 1~13 | 80 | 101 | ||||||||
| Copper | 1.2 | 200 | 102 | |||||||||||
| Adhesive + coating | TiO2 | 1.3 | 400 | 44 | ||||||||||
| PVDF/FEVE/GO@TiO2 | 3.42 | 28 000 | 1~14 | 72 | 103 | |||||||||
| Al2O3/Epoxy | 5 | 20 000 | 49 | |||||||||||
| PTFE-CP&MgO-AOP | 2.6 | 10 000 | 1~14 | 100 | ||||||||||
| PDMS@ZnSn(OH)6 | 2.2 | 300 | 2~13 | 28 | 6 | |||||||||
| QAS@SiO2 | 1~13 | 168 | 30 | |||||||||||
| SiO2/B-Epoxy | 1.6 | 2160 | 1~14 | 12 | 85 | |||||||||
| Armor protection | Metal/glass/ceramic | 12 000 | 10 000 | aqua regia | 4 | 50 | ||||||||
| ADP/Copper | 1~14 | 24 | 104 | |||||||||||
| Self-healing | SiO2/Epoxy | 7.5 | 1150 | 1~14 | 0.5 | 105 | ||||||||
| SiO2/PDMS | 5 | 10 000 | 62 | |||||||||||
| SiO2/F-Epoxy | 12.25 | 50 000 | 63 | |||||||||||
| PTFE/F-Epoxy | 5 | 1000 | aqua regia | 1 | 64 | |||||||||