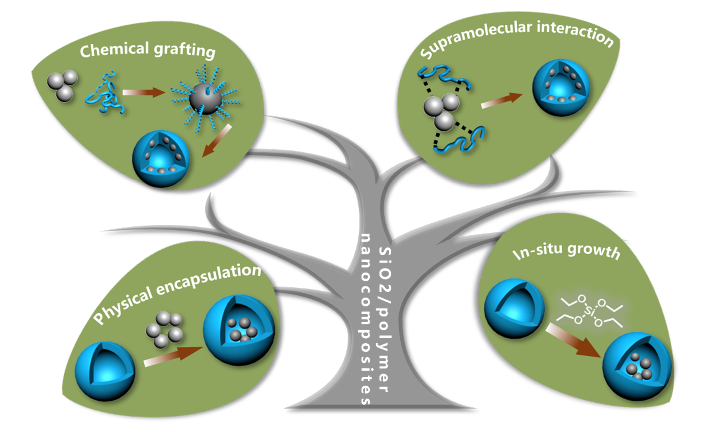
1 引言
2 物理包封法
3 化学接枝法
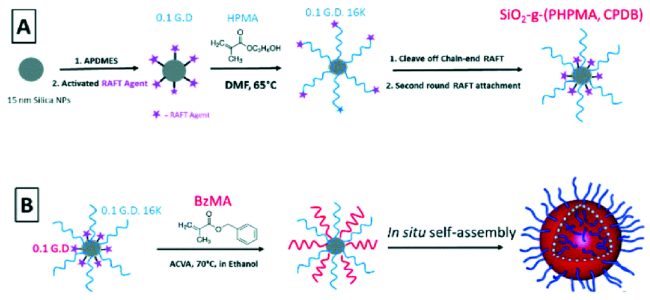
3.1 Grafting to化学接枝法
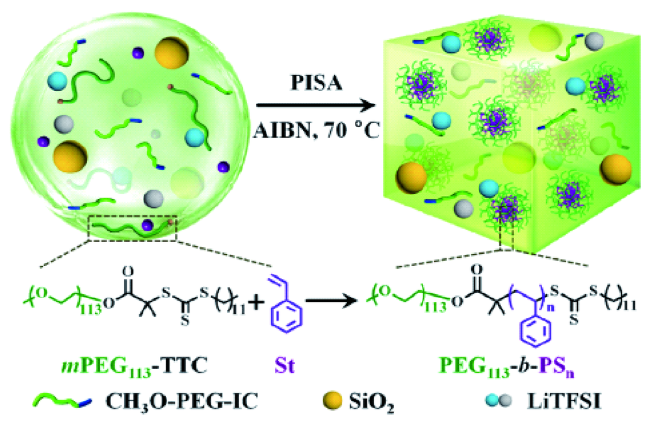
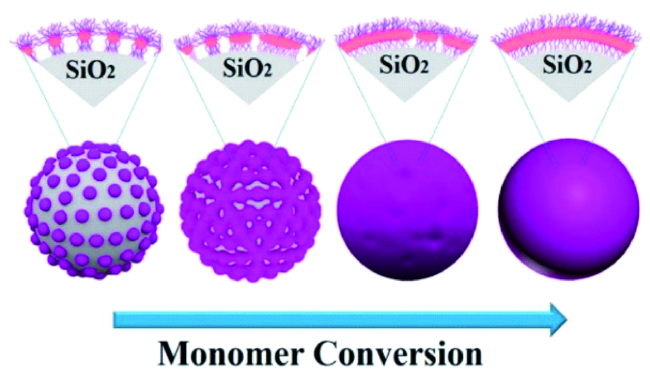
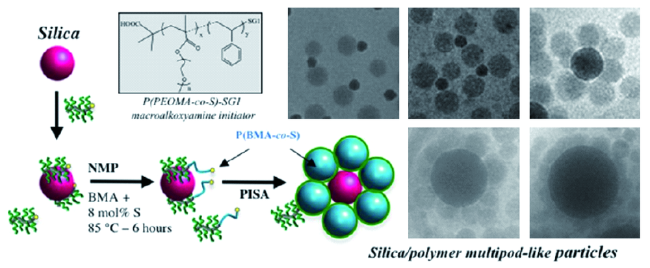
3.2 Grafting from化学接枝法
4 超分子作用法
4.1 超分子氢键作用
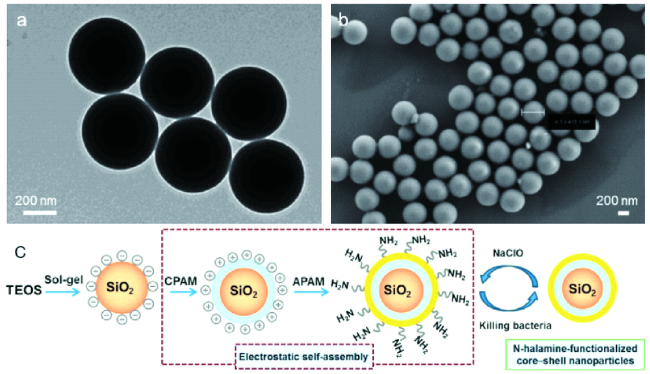
4.2 超分子静电作用
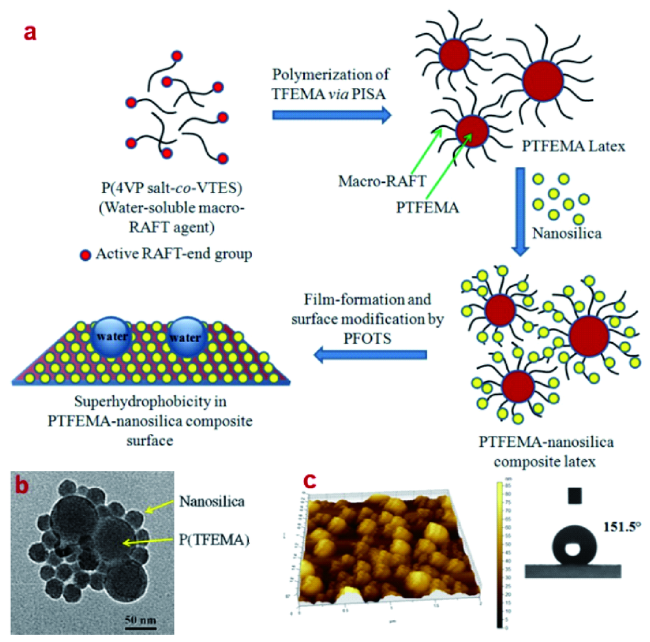
5 原位生长法
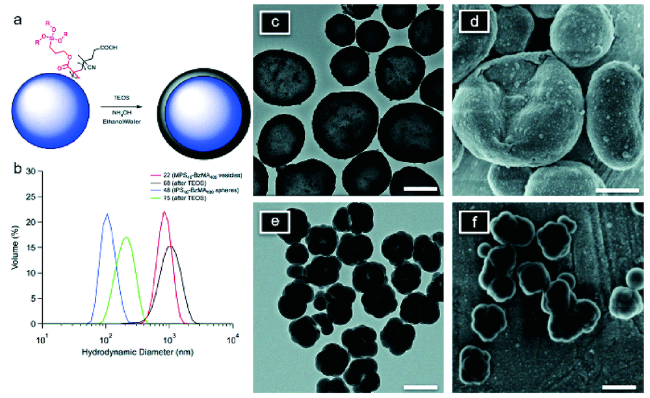
图9 (a)硅壳的生长示意图(通过TEOS水解和缩合);(b)硅胶壳生长前后DLS的体积分布;(c~f)硅壳生长后颗粒的TEM和SEM图像[49]Fig. 9 (a) Schematic diagram of silicon shell growth(through TEOS hydrolysis and condensation);(b) volume distribution of DLS before and after the growth of silica shell;(c~f) TEM and SEM images of particles after silicon shell growth[49] |
6 结论与展望
表1 四种合成方法优劣势比较Table 1 The comparison of four synthesis methods |
| synthesis method | morphologies | advantages | disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| physical encapsulation | vesicle[10⇓⇓~13] | simple and readily prepared in large quantities | non-rigid performance requirements |
| chemical grafting | sphere[20,25],vesicle[26], nanowire[27] | firm Chemical bonding and stable performance | harsh reaction conditions and low graft efficiency |
| supramolecular interaction | raspberry shape[35], core-shell[37,41,42],snowman shape[37],sphere[39] | simple method | low bonding strength |
| in-situ growth | core-shell[49,51],nanowire[50], raspberry shape[51] | simple and readily prepared in large quantities | harsh reaction conditions and low bonding strength |