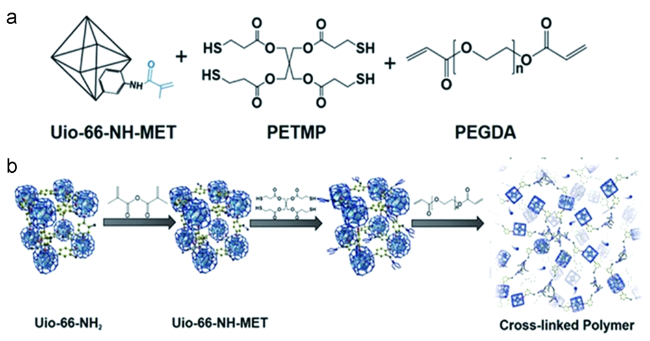
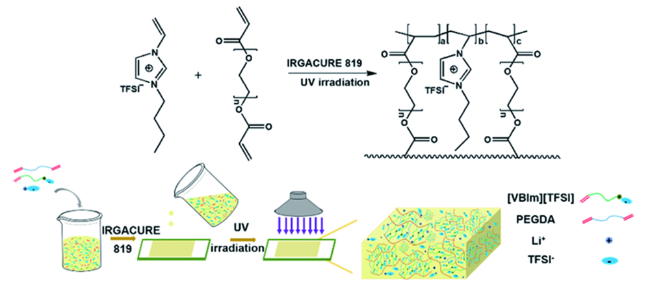
1 引言
表1 原位聚合物电解质中常用聚合物基质的性质Table 1 Properties of mostly used polymer host in in-situ polymer electrolytes |
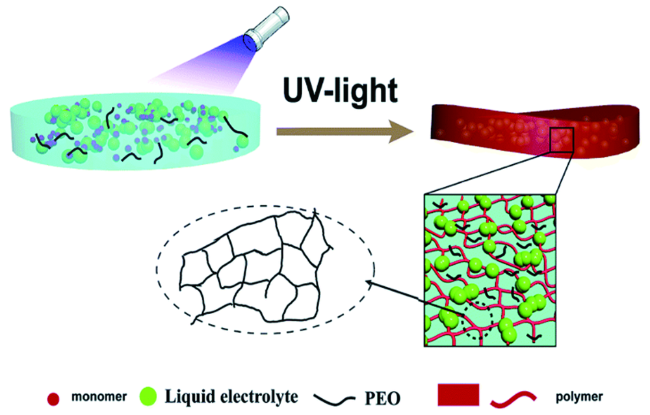
2 凝胶聚合物电解质的原位制备
2.1 PEO基GPE的原位制备
2.2 PMMA基GPE的原位制备
2.3 PVDF-HPF基GPE的原位制备
图3 (a)PHPG聚合物中PVDF-HFP、PEO和GO之间的分子间氢结合作用示意图;(b)PHPG分子间氢结合作用形成的三维多孔聚合物网络示意图[40]Fig.3 (a) Schematic of the intermolecular hydrogen binding effect between PVDF-HFP, PEO, and GO in the PHPG polymer;(b) Schematic of the 3D porous polymer network of PHPG formed by the intermolecular hydrogen binding effect[40]. Copyright 2018, Wiley Online Library |
2.4 其他GPE的原位制备
3 固态聚合物电解质的原位法制备
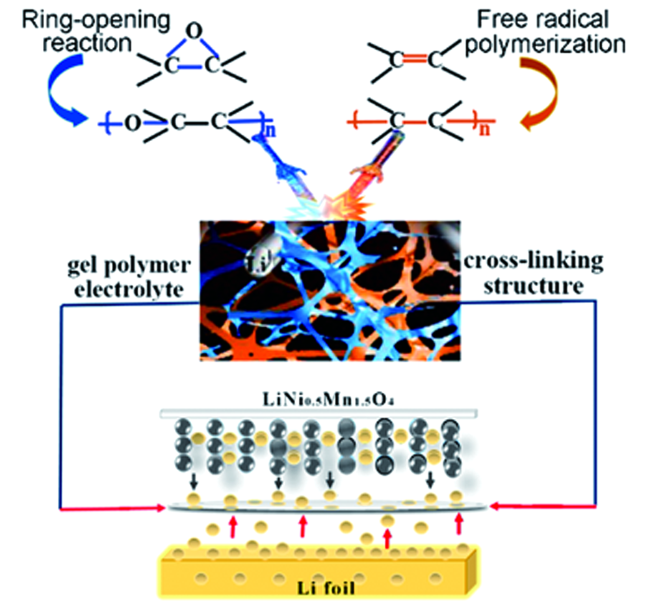
3.1 醚基类SPE的原位制备
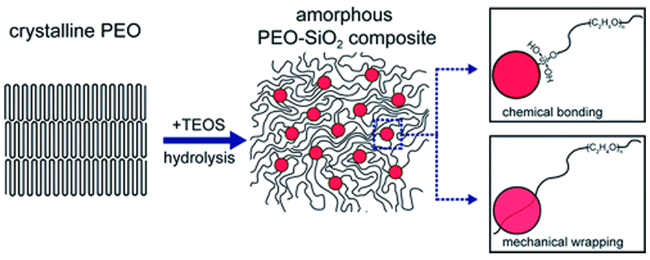
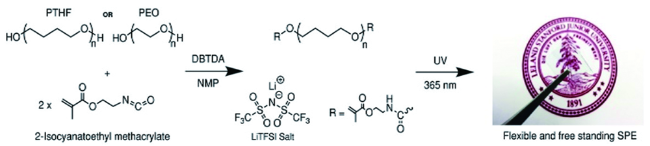
3.1.1 PEO基SPE原位制备
3.1.2 聚1,3-二氧戊环基SPE原位制备
图5 (a)安全电池设计说明示意图:用热敏聚合物抑制电极之间的离子传导以防止LMB的热失控;(b)TSPE(PDOL和PLAS)的组成示意图;(c)TSPE薄膜的实物图[23]Fig.5 (a) Illustration of the safe battery design: inhibition of the ionic conduction between electrodes with thermoresponsive polymer for preventing the thermal runaway of LMBs;(b) The schematic illustration of the composition of TSPE(PDOL and PLAS);(c) An optical image of the obtained TSPE film[23]. Copyright 2019, American Chemical Society |
3.1.3 聚四氢呋喃基SPE原位制备
3.2 酯基类SPE的原位制备
3.2.1 聚碳酸亚乙烯酯基SPE的原位制备
图7 (a)LFMP/PVCA-LSnPS/Li电池在0.1、0.3、0.5、1 C电流密度下的倍率性能以及在0.5 C电流密度下的室温循环性能;(b)PVCA-LSnPS复合材料循环后的元素映射分析;(c)基于元素映射分析和DFT计算结果,循环后PVCA-LSnP复合材料中可能存在的复杂结构[56]Fig.7 (a) Rate performance of LFMP/PVCA-LSnPS/Li cell at the rates of 0.1, 0.3, 0.5, and 1 C, and cycle performance at the rate of 0.5 C at room temperature;(b) Element mapping analysis of PVCA-LSnPS composite after cycling;(c) Possible complex structures in PVCA-LSnPS composite after cycling based on element mapping analysis and the DFT calculation results[56]. Copyright 2018, American Chemical Society |