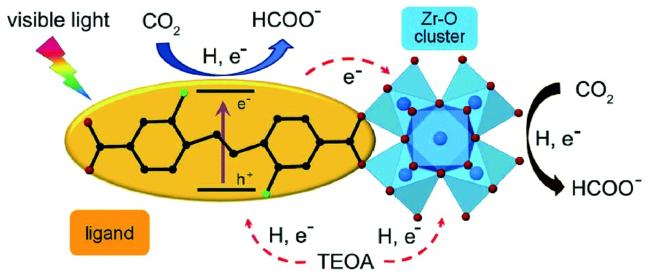
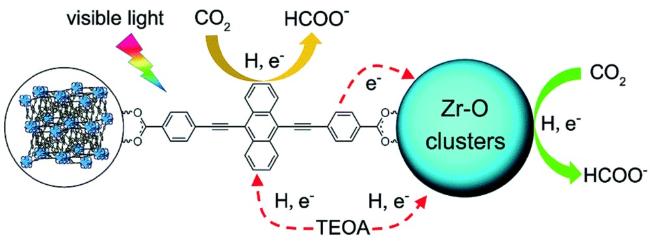
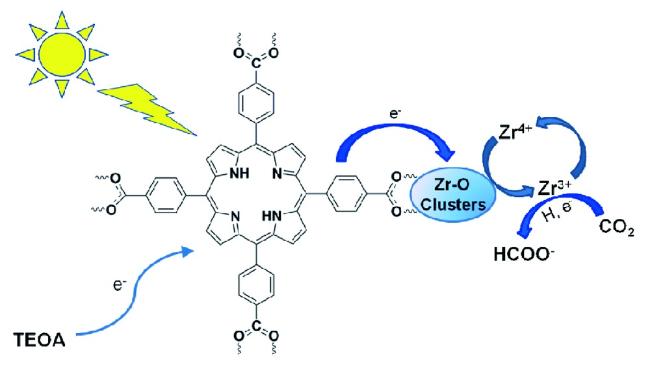
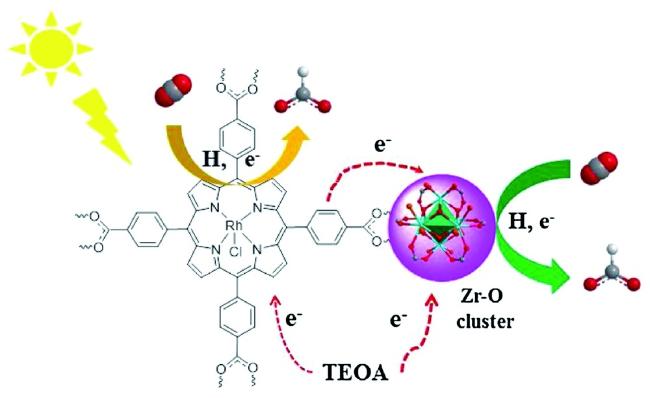
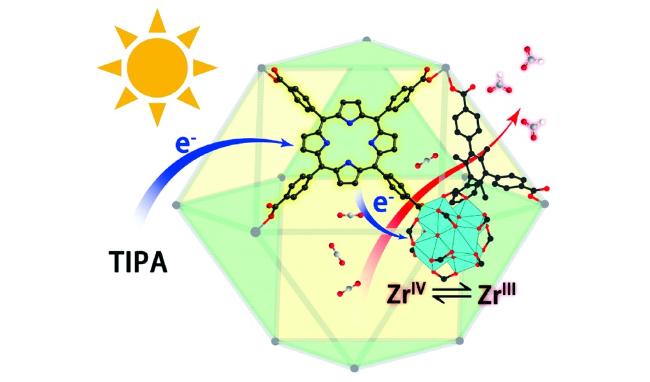
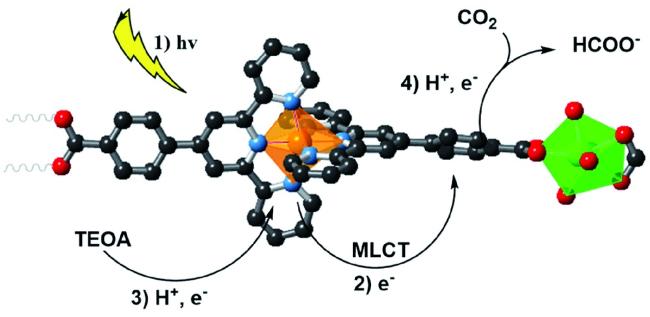
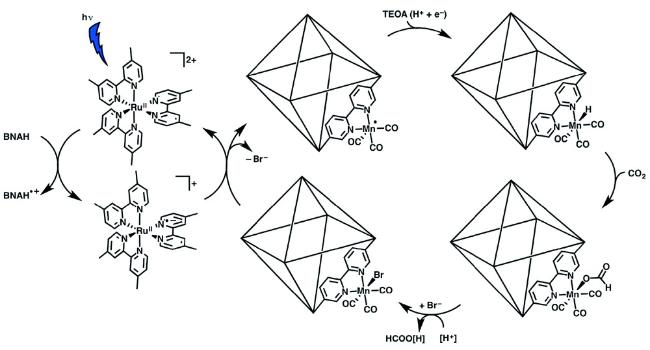
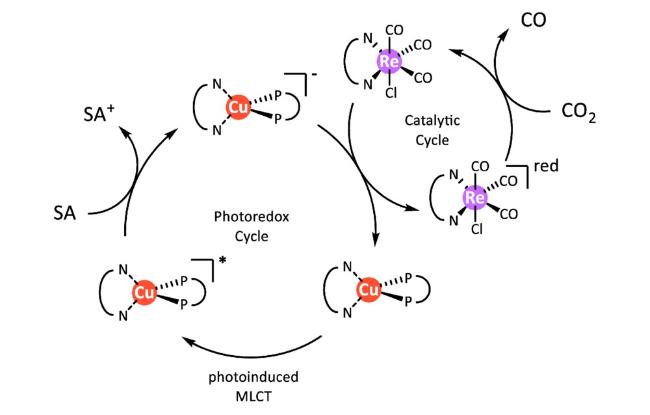
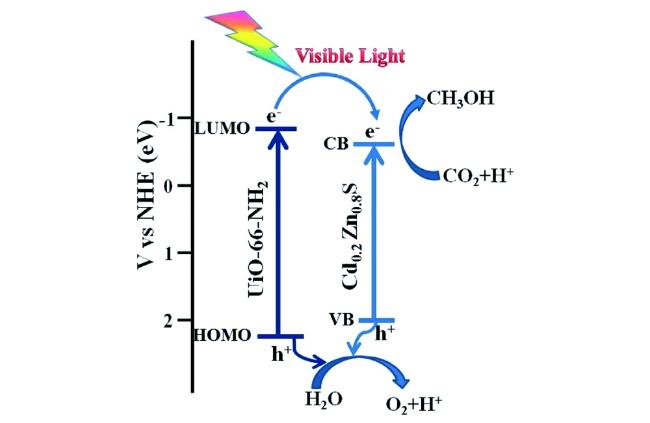
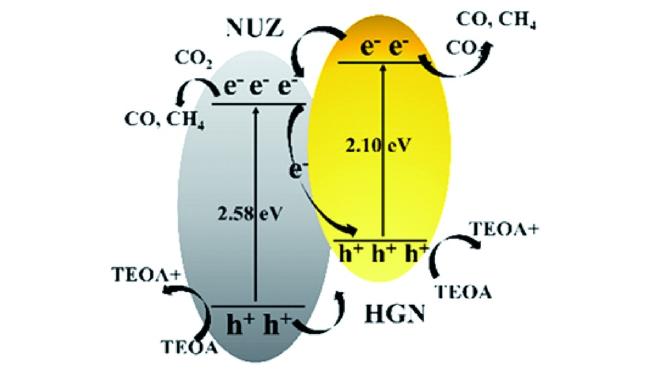
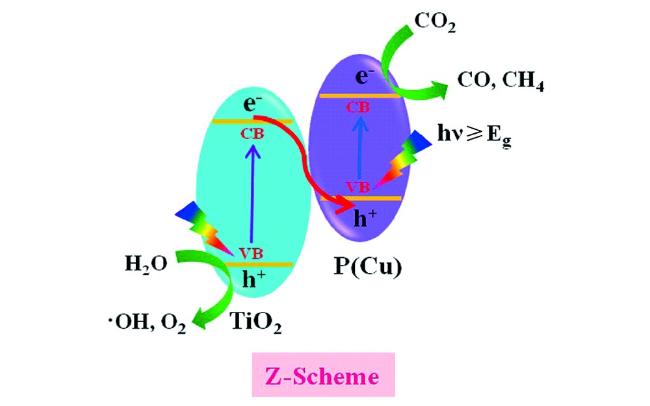
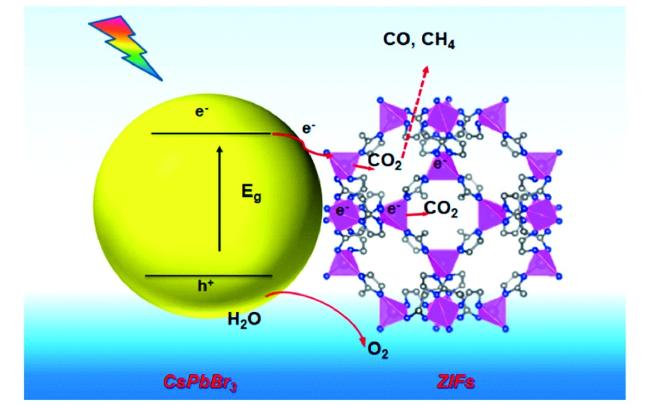
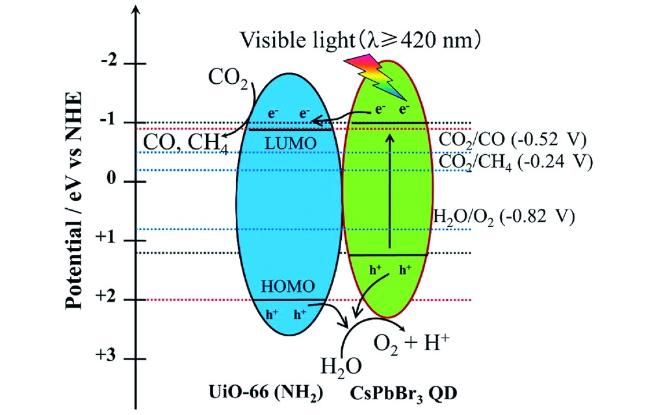
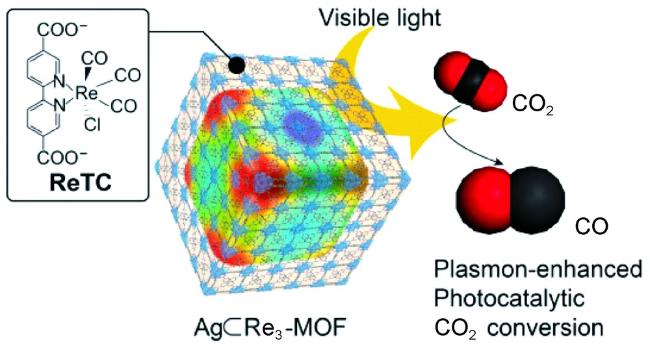
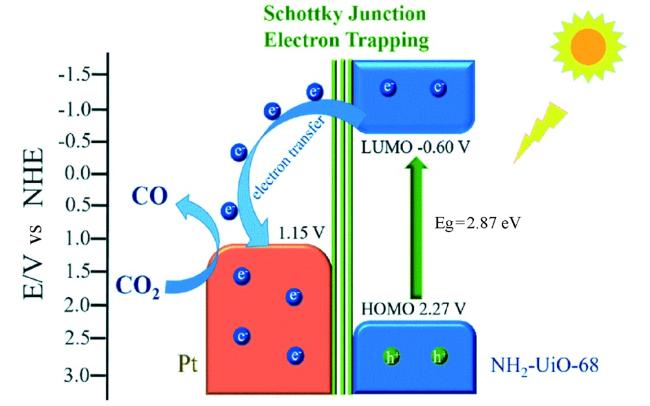
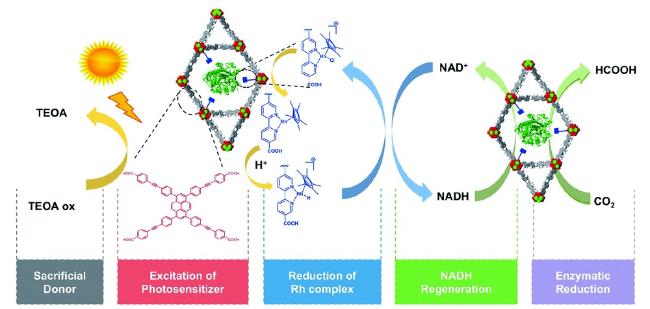
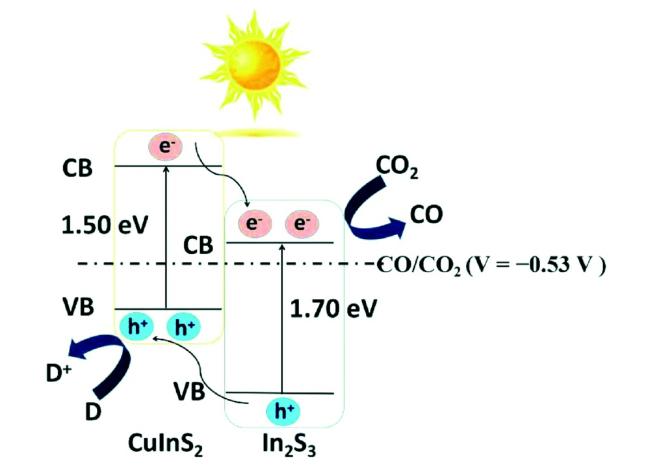
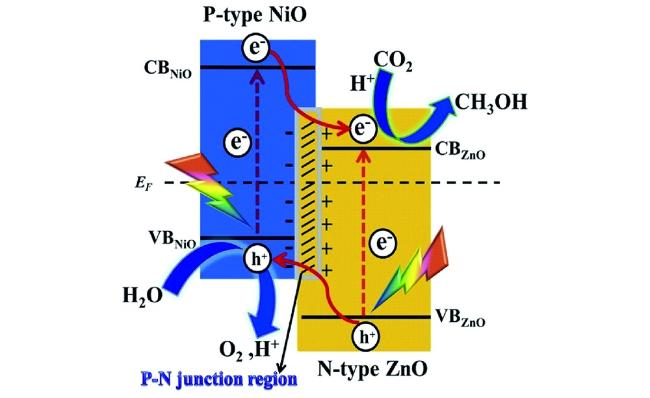
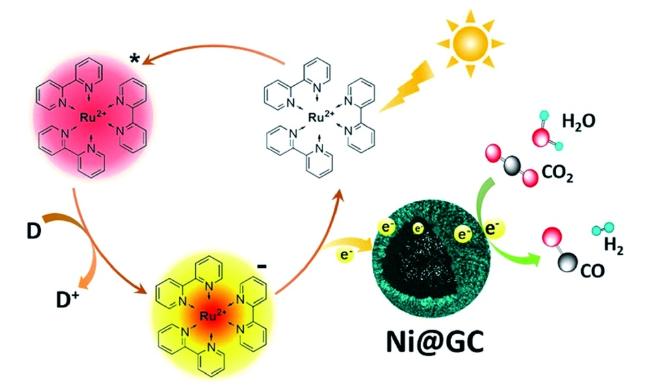
Guo等
[75]通过对不同纳米尺寸(80~800 nm)的MIL-101(Cr)-Ag催化性能的研究发现,随着催化剂尺寸的减小,光还原CO
2的催化性能逐渐增强。当粒径减小到80 nm时,复合催化剂表现出最高的催化活性,可见光照射下,CO和CH
4的生成速率能够达到808.2和427.5 μmol·g
-1·h
-1,分别是粒径为800 nm催化剂的23和18倍。由扩展X射线吸收精细结构(EXAFS)光谱的分析结果可知,粒径为80 nm催化剂中Ag的配位数(
N=8.95)要高于Ag NPs(
N=5.71),这意味着催化剂中Ag颗粒表面的缺陷状态较少,而缺陷位处容易发生电子空穴对的复合,因此,光生电荷的分离效率显著提高。而小尺寸催化剂的边和拐角处晶胞密度更大,更有利于电子的迁移,在光电流测试中粒径为80 nm催化剂的光电流强度最大。他们通过Mott-Schottky测试进一步阐述了MIL-101(Cr)-Ag光催化还原CO
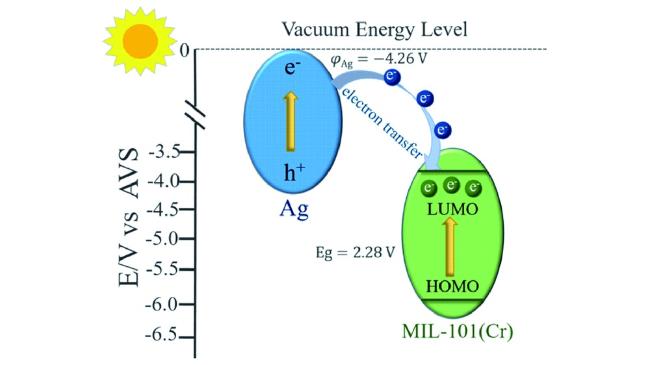
2的过程,计算可知MIL-101(Cr)的LUMO和HOMO电位分别为-3.76和6.04 V(vs AVS),Ag的功函数为-4.26 V(vs AVS),如
图18所示,在可见光照射下,Ag表面激发的电子将会迁移到MIL-101(Cr)的LUMO,同MIL-101(Cr)的光生电子一起还原CO
2。
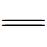 O双键的键能高达750 kJ·mol-1,具有很高的热力学稳定性,C
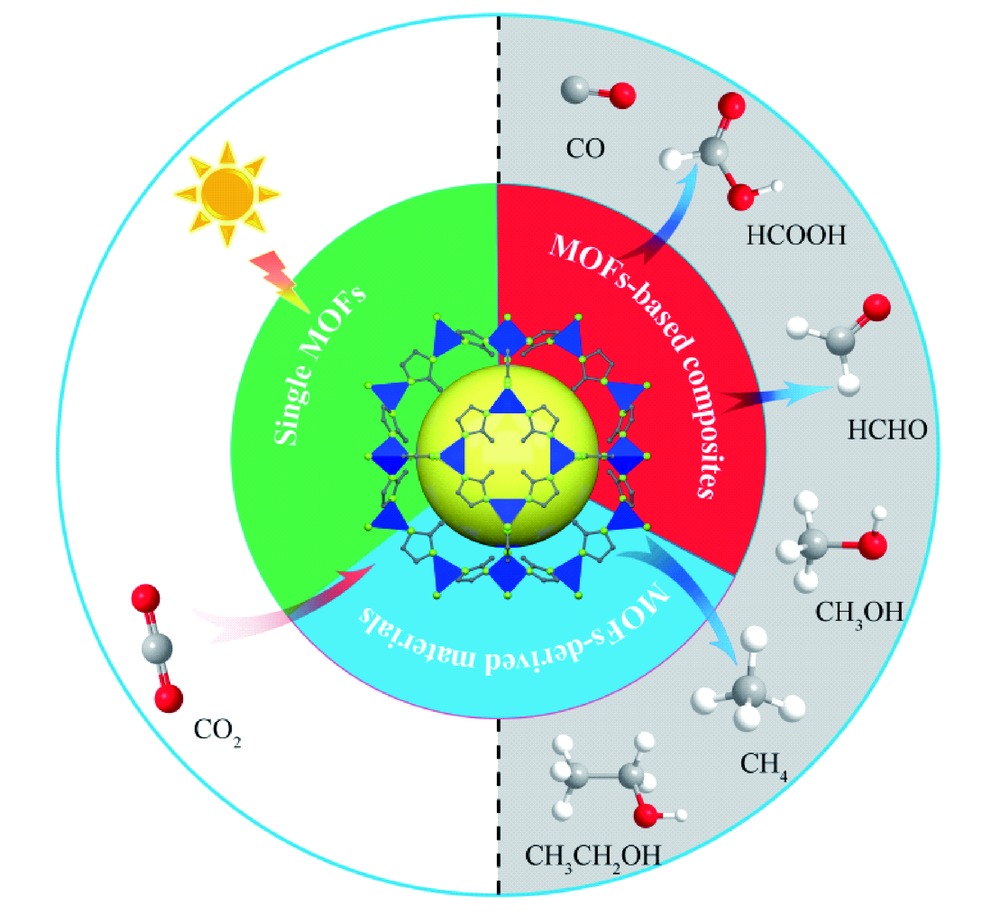
O双键的键能高达750 kJ·mol-1,具有很高的热力学稳定性,C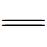 O键的断裂需要较高能量。根据转移电子数(n=2、4、6、8、12甚至更多的电子)的不同,CO2的还原产物主要有CO、HCOOH、HCHO、CH3OH、CH4、C2H5OH等,当反应体系中有水存在时还可能生成H2。CO2在水中的部分还原过程及其氧化还原电势(vs NHE, pH=7)如反应式(1)~(8)所示[4,5,6]。要使CO2光还原半反应能够顺利进行,半导体催化剂的导带(CB)必须比CO2还原半反应的还原电势更负。
O键的断裂需要较高能量。根据转移电子数(n=2、4、6、8、12甚至更多的电子)的不同,CO2的还原产物主要有CO、HCOOH、HCHO、CH3OH、CH4、C2H5OH等,当反应体系中有水存在时还可能生成H2。CO2在水中的部分还原过程及其氧化还原电势(vs NHE, pH=7)如反应式(1)~(8)所示[4,5,6]。要使CO2光还原半反应能够顺利进行,半导体催化剂的导带(CB)必须比CO2还原半反应的还原电势更负。