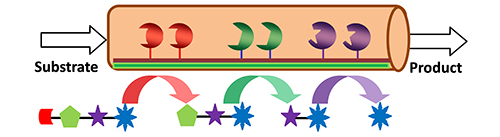
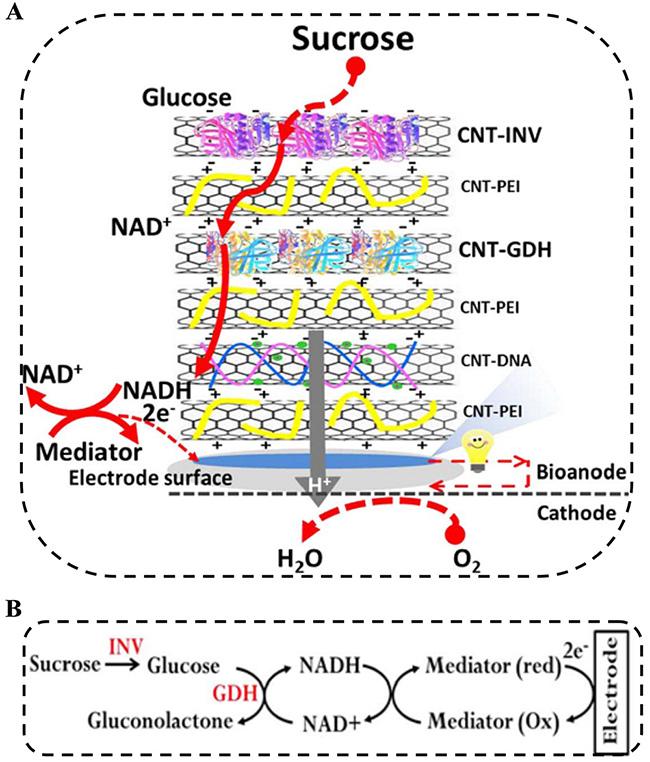
1 引言
2 固定化多酶级联反应的基本原理
3 固定化多酶级联反应器的制备
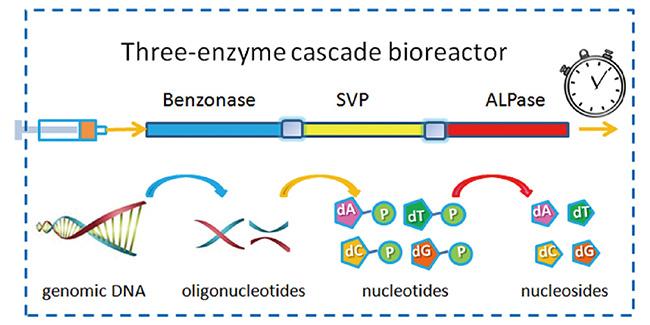
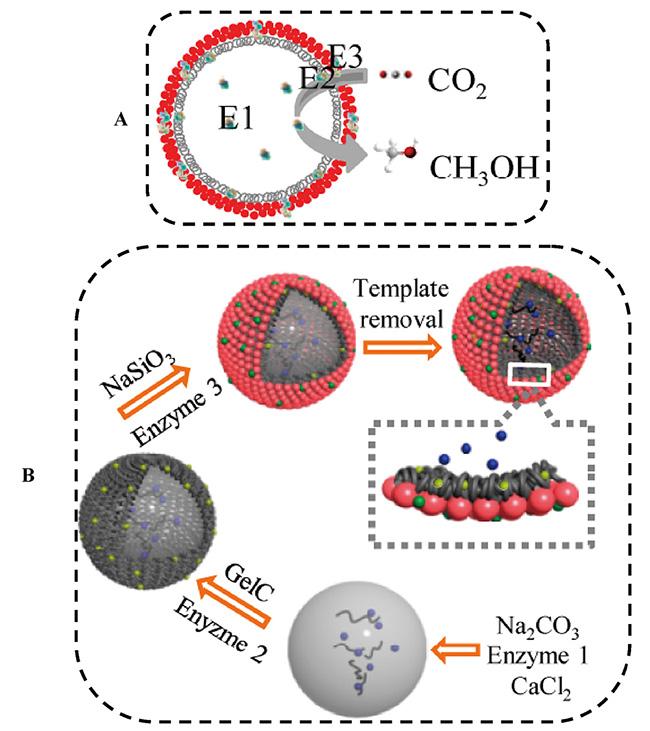
3.1 共固定法
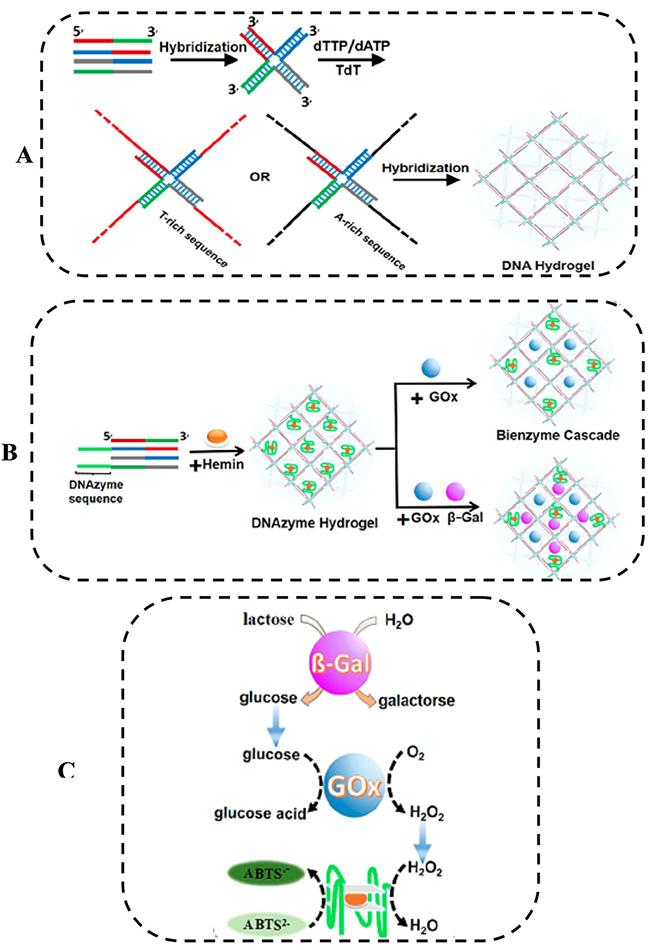
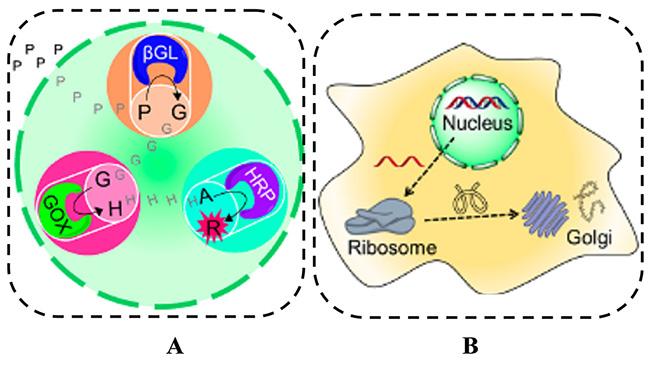
图2 DNA水凝胶多酶级联系统[24]:(A)DNA水凝胶的制备;(B)DNA水凝包埋的双酶或三酶的制备;(C)乳糖检测的β-半乳糖苷酶/GOx/DNAzyme三酶级联反应原理Fig. 2 Schematic illustration of multi-enzyme cascade reaction systems based on the DNA hydrogel[24]:(A) preparation of the DNA hydrogel by TdT-generated X-shaped polymers(X-DNA-An and X-DNA-Tn),(B) illustration of X-shaped polymers incorporated with DNAzyme sequences forming peroxidase-mimicking DNAzyme hydrogel, the bienzyme cascade, and the trienzyme cascade,(C) activation of the β-gal/GOx/DNAzyme cascade. Copyright 2016, ACS |
3.2 依序固定法
3.3 分区固定法
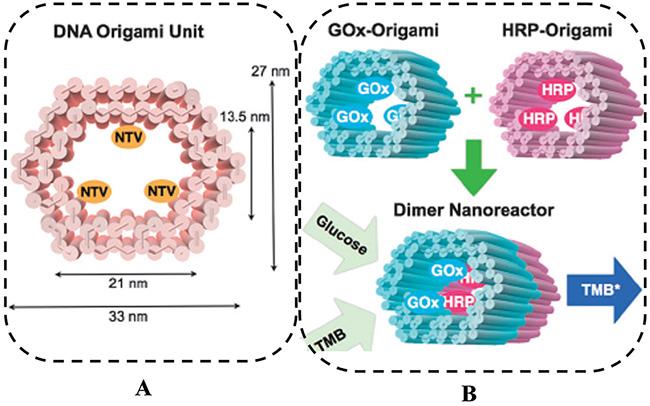
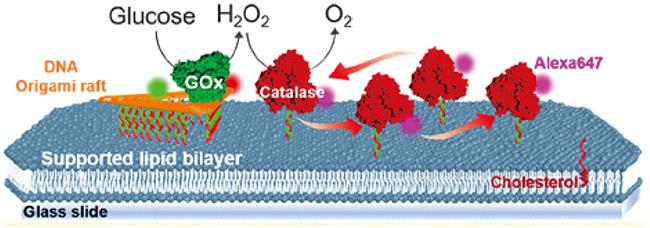
3.4 可寻址固定法
4 影响固定化多酶级联反应效率的因素
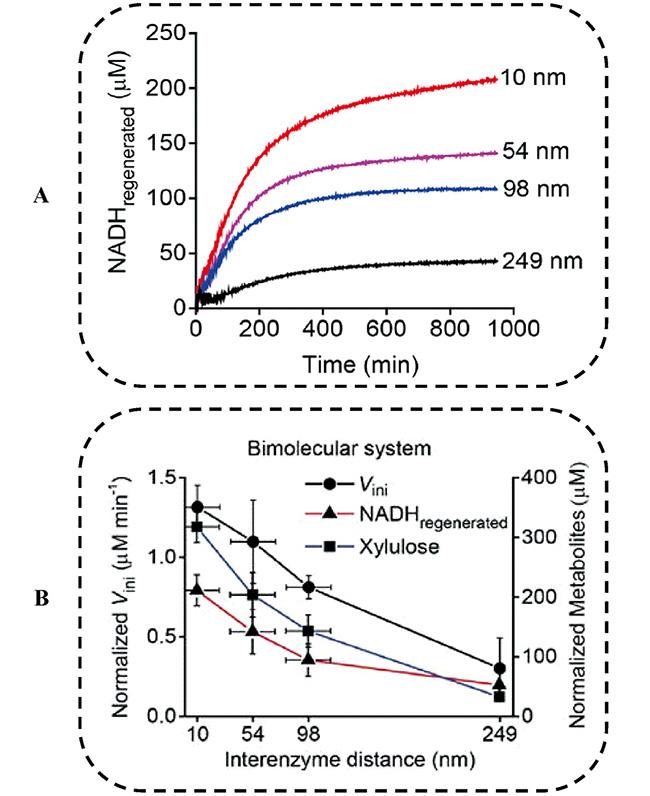
图8 反应效率和酶间距的关系[66].(A) ZS-XR/G-XDH双酶体系中不同酶间距(10, 54, 98, 298 nm)下NADH产物量随时间的变化曲线;(B) 反应16 h后, NADH的初始生成速率、产量,及木糖产量和酶间距的关系Fig. 8 Distance-dependent effect of assembled ZS-XR/G-XDH pairs[66].(A) Time-course profiles of the amount of NADH regenerated by G-XDH when the enzymes were coassembled with interenzyme distances of 10, 54, and 98 nm, and for the free diffusion system with that of 298 nm;(B) Plots of the normalized V ini, the normalized amount of regenerated NADH, and the normalized amount of xylulose produced after 16 h against the interenzyme distances. Copyright 2016, ACS |
5 固定化多酶级联器的应用
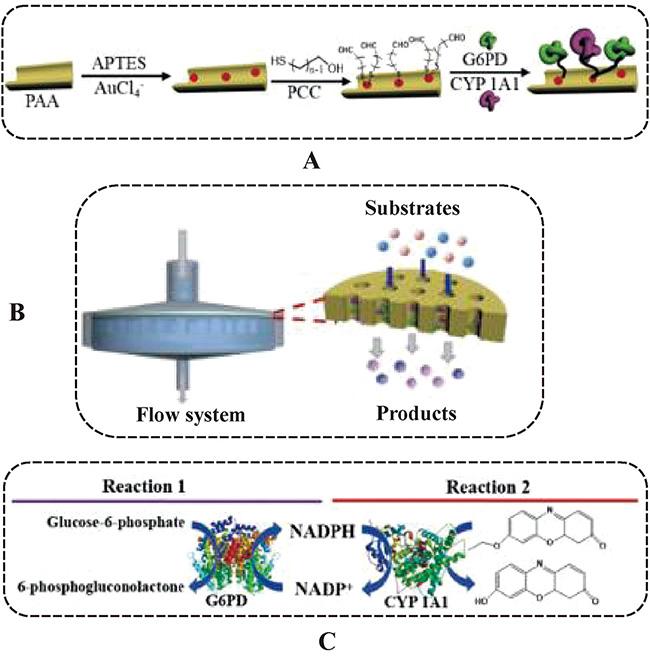
图10 模拟体内药物CYP酶代谢通道级联系统示意图[82]:(A) G6PD 和 CYP1A1在PAA纳米通道内的固定过程;(B)模拟代谢区室流通系统;(C)酶级联反应原理Fig. 10 Schematic illustration of an artificial metabolon confined inside PAA nanochannels to mimic the natural enzyme complex systems[82]:(A) the immobilization of bi-enzymes inside the PAA nanochannels,(B) flow system of the artificial metabolon,(C) the cascade enzymatic reaction cycles catalyzed by G6PD and CYP1A1. Copyright 2017, RSC |