Contents
1 引言
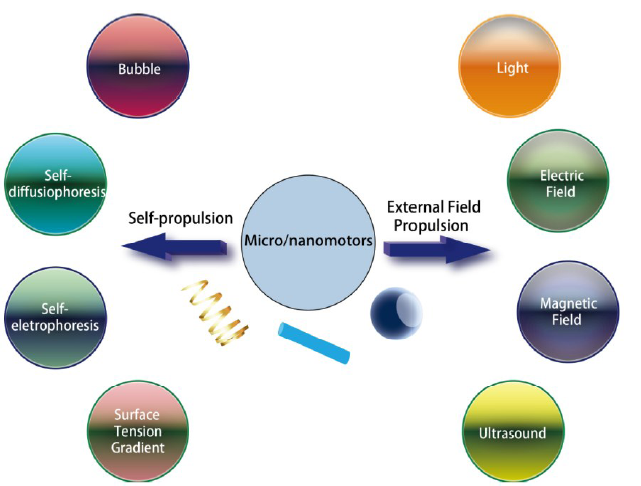
2 微纳米马达的驱动机理
2.1 自场驱动机理
2.2 外界场驱动机理
3 可用于药物递送的微纳米马达的基本结构
3.1 具有聚合物囊泡结构的马达
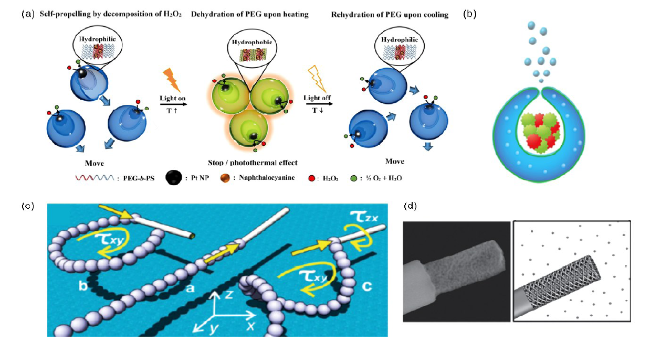
图2 (a)PEG44-b-PS141纳米囊泡马达系统示意图[9];(b)包裹有多种生物酶的囊泡状纳米马达示意图[30];(c)纳米管状马达不同的运动轨道示意图[31];(d)具有超高比表面积的多孔金纳米线马达[32]Fig.2 (a)Schematic representation of a light-guided nanomotor system using PEG44-b-PS141/naphthalocyanine(NC) and Pt nanoparticles(Pt-NPs)[9]. Copyright 2018, American Chemical Society; (b) Schematic representation of the assembly of the nanomotor with multiple enzymes entrapped inside the structure[30]. Copyright 2016, American Chemical Society; (c) Schematic of different nanotubes’ trajectories[31]. Copyright 2012, American Chemical Society; (d) Nanowire motors based on nanoporous gold segment[32]. Copyright 2014, John Wiley and Sons |
3.2 具有管状结构的马达
3.3 具有纳米线结构的马达
4 药物递送微纳米马达的运动控制
4.1 运动开-关控制
4.2 运动方向控制
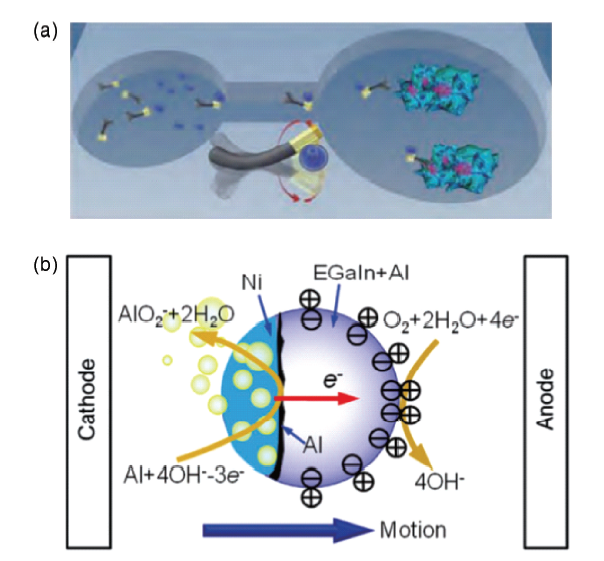
图3 (a)Ag/Ni纳米线马达在磁场控制下向癌细胞递送药物过程示意图[36];(b)在电场作用下,Ni/Al/EGaIn马达运动方向可控[7]Fig.3 (a)The drug delivery of Ag/Ni nanomotors towards cancer cells under magnetic field[36]. Copyright 2012, John Wiley and Sons; (b)The direction control of Ni/Al/EGaIn motor with an electrical field[7]. Copyright 2016, Royal Society of Chemistry |