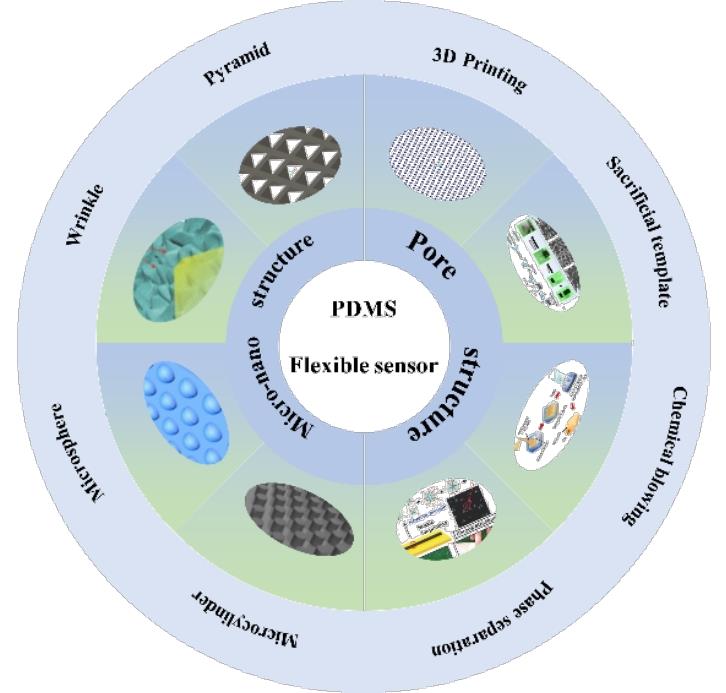
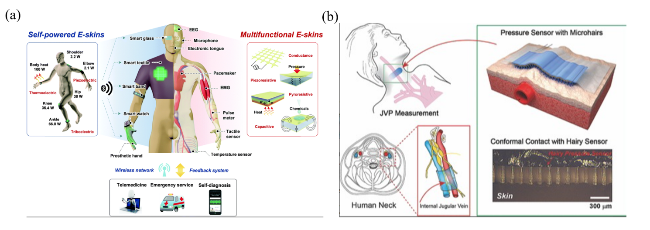
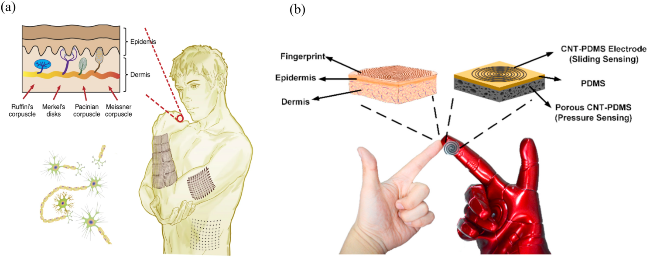
1 引言
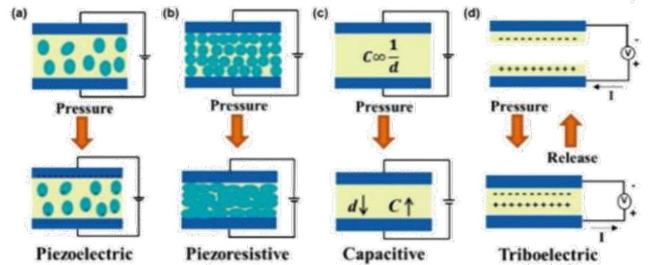
2 柔性压力传感器
表1 四种不同类型柔性压力传感器的工作原理及其优缺点Table 1 The working principle,advantages and disadvantages of four different types of flexible pressure sensors |
| Type | Operating principle | Conventional materials | Advantage | Disadvantage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resistive pressure sensor | Changes in resistance caused by changes in external forces (resistance effect) | Piezoresistive materials and conductive polymer composites | Simple structure Single signal Low power consumption | Easy affected by temperature and environment |
| Capacitive pressure sensor | The pressure input is converted to the capacitance change of the parallel plate capacitor | Dielectric material | Fast response speed Good stability High precision | Susceptible to outside interference |
| Piezoelectric pressure sensor | Piezoelectric effect | Piezoelectric materials | Self-electric High sensitivity | Easy to generate charge leakage problem Low output signal |
| Triboelectric pressure sensor | Triboelectric effect and principle of electrostatic induction | Flexible polymer materials such as PETPI and PMMA | No external power Easy to integrate High sensitivity | Limited measuring range |
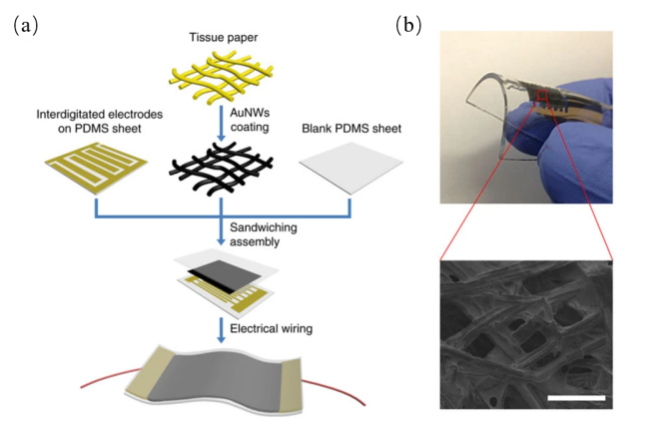
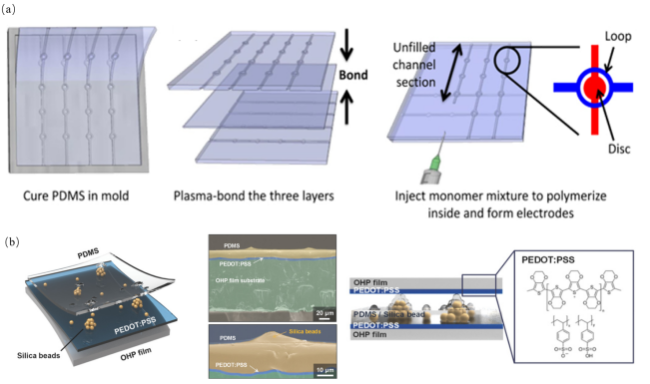
图3 (a)在模具中固化的PDMS以及其在电介质的顶部和底部形成的垂直通道和离子导电电极图像[36];(b)透明电容式压力传感器和传感器层的横截面SEM图像[37]Fig.3 (a) Images of PDMS solidified in the mold and the vertical channels and ionic conductive electrodes it forms on the top and bottom of the dielectric [36];(b) SEM image of transparent capacitive pressure sensor and cross section of sensor layer image [37] |
3 柔性传感器的性能改进制备工艺
3.1 孔隙结构
表2 PDMS材料引入孔隙结构的制造技术和其优缺点Table 2 Manufacturing technology,advantages and disadvantages of PDMS materials introduced into pore structure |
| Manufacturing method | Aperture | Advantage | Disadvantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3D Printing | Submicron scale | Complex structure preparation Precise control of aperture | High cost Low efficiency |
| Phase separation technique | Ten-micron scale | Easy to prepare Easy to control aperture | Organic solvents can be harmful |
| Chemical foaming process | Micrometer scale | Simple process Low cost | Aperture control is difficult |
| Template removal method | Hundred-micron scale | The aperture size is adjustable Porosity control Easy to prepare | The template limits the preparation of the aperture Aperture distribution is not easy to control |
3.1.1 3D打印技术
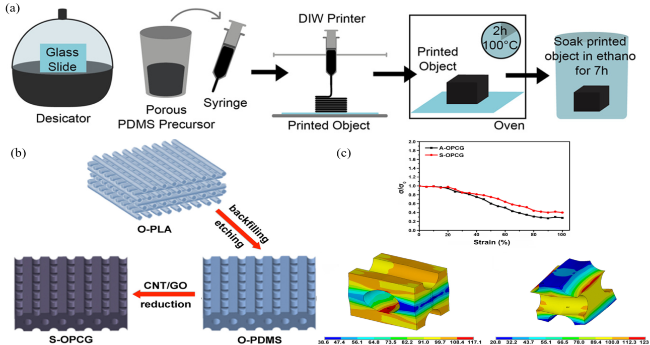
图4 (a)多孔PDMS前驱体的制备和印刷的分步过程[48];(b)S-OPCG制备示意图;(c)S-OPCG和A-OPCG的归一化电导率随拉伸应变的变化,以及100%拉伸下对齐O-PDMS分层O-PDMS模型的应变分布[49]Fig.4 (a) The step-by-step process of preparation and printing of porous PDMS precursors[48];(b) Schematic diagram of S-OPCG preparation;(c) The change of normalized conductivity of S-OPCG and A-OPCG with tensile strain,and the strain distribution of aligned O-PDMS stratified O-PDMS models at 100% tensile[49] |
3.1.2 相分离技术
图5 (a)将MWNT、RMS和PDMS混合,在超声下分散并搅拌混合过程的示意图[54];(b)PDMS和四氢呋喃溶液的制备和成型[55];(c)多孔PDMS-CNT纳米复合材料的制备过程与PDMS-CNT纳米复合材料的示意图[56]Fig.5 (a) Schematic diagram of mixing MWNT,RMS and PDMS,dispersing under ultrasound and stirring [54];(b) Preparation and molding of PDMS and tetrahydrofuran solution [55];(c) Preparation process of porous PDMS-CNT nanocomposites and schematic diagram of PDMS-CNT nanocomposites [56] |
3.1.3 去除模板法
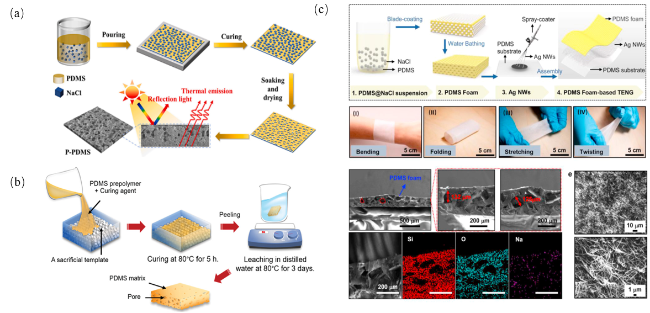
图6 (a)以NaCl为去除模板的多孔PDMS制备示意图;(b)多孔PDMS海绵制备示意图[62-63];(c)PDMS泡沫和柔性和可拉伸的摩擦电纳米发电机的制造过程示意图、薄PDMS泡沫在不同机械变形下的光学图像、PDMS泡沫的横截面SEM图像和用200 μm的比例尺对PDMS泡沫的Si、O和Na元素进行能量色散谱图[64]Fig.6 (a) Schematic diagram of preparing porous PDMS with NaCl as the removal template;(b) Preparation diagram of porous PDMS sponge[62-63];(c) Manufacturing process diagram of PDMS foam and flexible and stretchable triboelectric nanogenerators,optical images of thin PDMS foam under different mechanical deformation,SEM images of cross section of PDMS foam and energy dispersion spectra of Si,O and Na elements of PDMS foam with a scale of 200 μm[64] |
3.1.4 化学发泡法
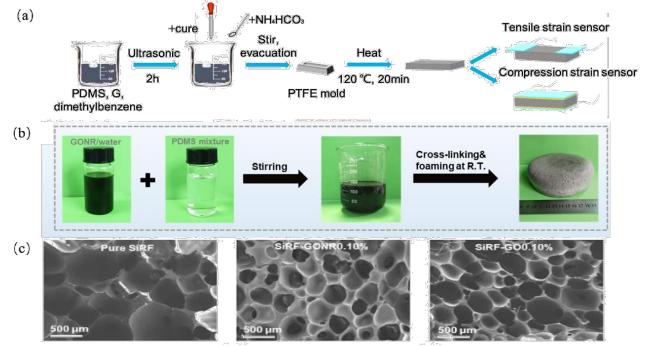
图8 (a)多孔石墨烯/PDMS复合材料的制备方法和两种传感器的组装示意图[68];(b)硅橡胶泡沫(SiRF)纳米复合材料的制备工艺和示意图;(c)纯SiRF、SiRF-GONR0.10%和SiRF-GO0.10%的SEM图像[69]Fig.8 (a) The preparation method of the porous graphene /PDMS composite and the assembly diagram of the two sensors[68];(b) Preparation process and schematic diagram of silicone rubber foam (SiRF) nanocomposites;(c) SEM images of pure SiRF,SIRF-GONR0.10% and SIRF-GO0.10% [69] |
3.2 表面微纳结构
3.2.1 微金字塔结构
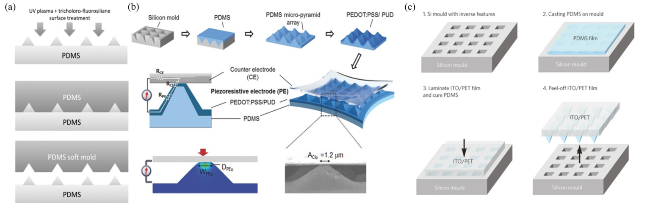
图9 (a)软PDMS模具的工艺示意图[80];(b)在金字塔表面涂覆PEDOT:PSS/PUD薄膜以及对传感器传感原理进行有限元分析示意图[81];(c)微纳结构PDMS薄膜的制备示意图[79]Fig.9 (a) Process diagram of the soft PDMS mold [80];(b) Coating the pyramid surface with PEDOT: PSS/PUD film and finite element analysis of the sensor sensing principle [81];(c) Schematic diagram of preparation of micro-nano PDMS films [79] |
3.2.2 微褶皱结构
3.2.3 微圆柱体结构
3.2.4 微球体结构
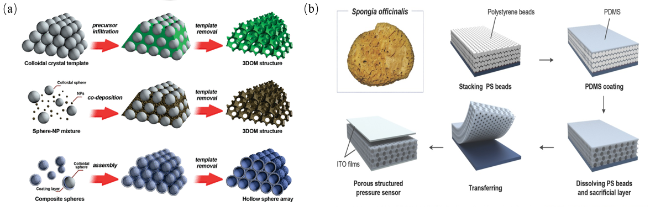
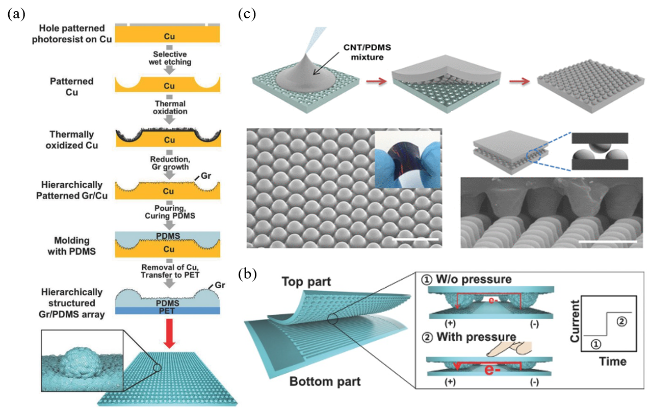
图12 (a)微球体弹性层整体制造过程示意图;(b)由分层石墨烯/PDMS阵列组成的压力传感器的传感器组装和工作原理示意图[86];(c)具有微球阵列的CNT复合弹性体的制造过程与复合弹性体的SEM图像[87]Fig.12 (a) Schematic diagram of the overall manufacturing process of the microsphere elastic layer;(b) Schematic diagram of sensor assembly and working principle of a pressure sensor consisting of a layered graphene /PDMS array [86];(c) Fabrication process of CNT composite elastomer with microsphere array and SEM images of the composite elastomer [87] |
表3 不同结构的PDMS柔性压力传感器的性能Table 3 Performance of PDMS flexible pressure sensors with different structures |
| Basal material | Preparation technique | Sensitivity/kPa-1 | Detection range/kPa(Detection limit/Pa) | Response time/ms | Cycle stability/times | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Graphene/PDMS | Pore structure (chemical foaming method) | 68,770 | / | ~200 | 1000 | 64 |
| MWCNT/PDMS | Pore structure (direct sacrifice template method) | 2.155 | 0~500(50) | / | 2500 | 68 |
| Ag/PDMS | Surface micro-nano structure (Micropyramid) | 259.32 | 0~54(0.36) | ~0.2 | / | 69 |
| CNT/PDMS | Surface micro-nano structure (micro-fold) | 90,657 | 0~26 | ~12 | 1000 | 70 |
| Au/PDMS | Surface micro-nano structure (microspheres) | 196 | 0~100(0.5) | ~26 | 10 000 | 71 |
| Au/PDMS+PET/CPAn | Surface micro-nano structure (microcylinder) | 2.0 | 0~0.22(15) | ~50 | 10 000 | 72 |
| CNT/PDMS | Surface micro-nano structure (microsphere) + pore structure (sacrificial template method) | 15. | 0~30(0.2) | ~40 | / | 73 |
| PEDOT/PDMS | Surface micro-nano structure (Micropyramid) | 10.3 | 0~8(23) | / | / | 77 |
| AgNWs/PDMS | Surface micro-nano structure (microsphere) + pore structure (sacrificial template method) | 3788.2 | 0~220(0.83) | ~100 | 22 000 | 89 |
| MWCNT/PDMS | Surface micro-nano structure (micropyramid) + pore structure (sacrificial template method) | 83.9 | 0~10(0.5) | ~170 | 28 000 | 95 |