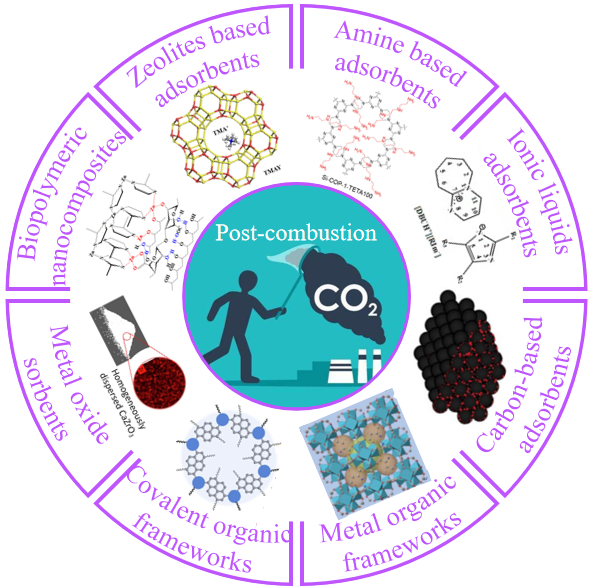
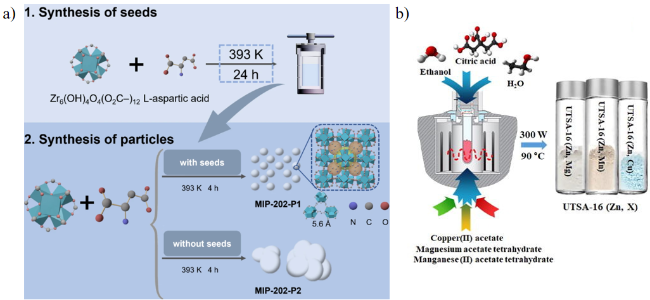
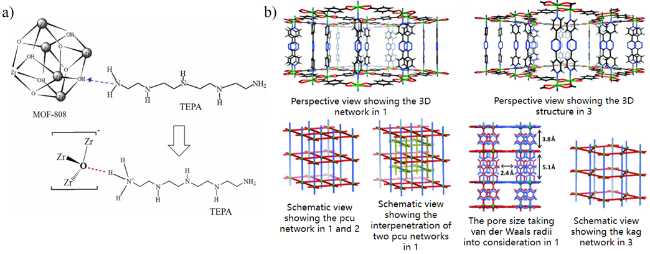
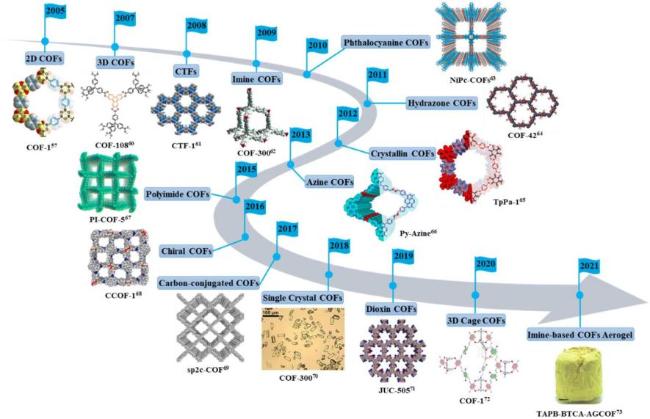
1 引言
1.1 CO2排放现状及其危害
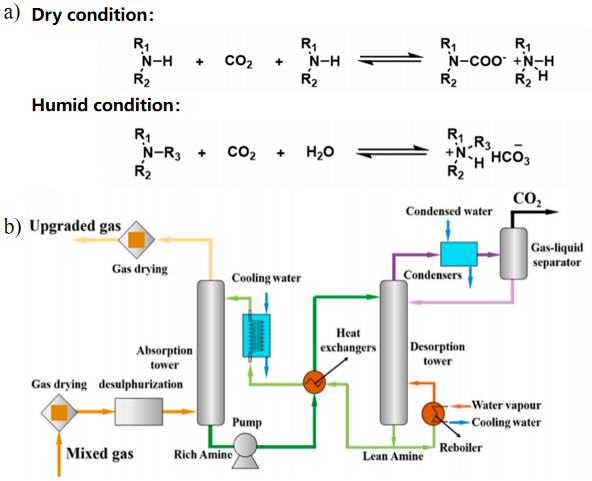
1.2 CO2捕获技术
表1 三种碳捕获技术的比较Table 1 Comparison of three carbon capture technologies |
| CO2 capture technology | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Pre-combustion capture | The concentration of CO2 is high which makes it easy to capture | Not applicable to existing power plants;high investment cost;a large amount of energy consumed for chemical solvent regeneration |
| Oxy-fuel capture | The concentration of CO2 is high which makes it easy to capture;avoids the requirement of chemicals | A large amount of pure oxygen needs to be provided;high investment cost;limited existing technical knowledge |
| Post-combustion capture | Suitable for large new and existing power plants,without the need for upgrades and renovations;convenient maintenance | High energy consumption of adsorbent regeneration;low CO2 concentration in flue gas |
1.3 设计CO2捕获材料的标准
2 CO2捕获材料
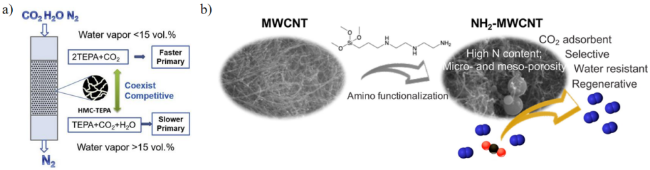
2.1 胺溶液吸收剂
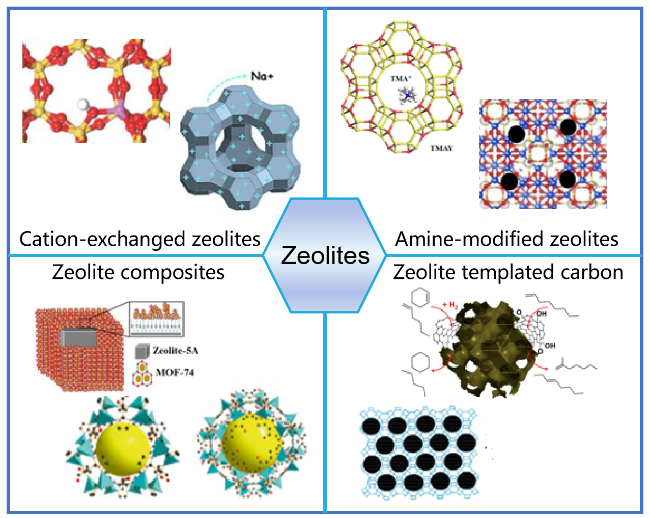
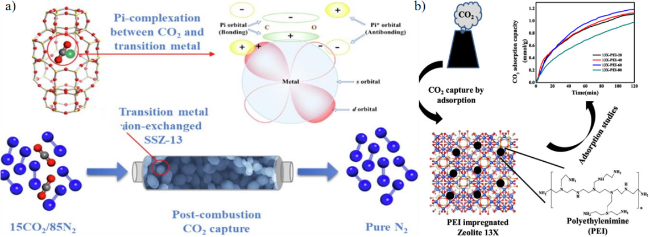
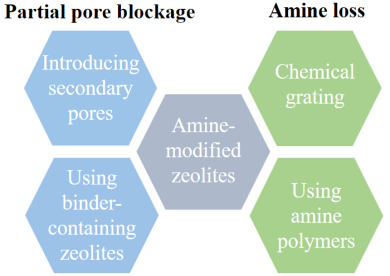
2.2 沸石基吸附剂
表2 部分沸石对于CO2捕获性能Table 2 CO2 capture performance of some zeolites |
| Zeolites | BET (m2/g) | Temperature (K) | Pore size (nm) | Capacity (mmol/g) | CO2/N2 selectivity | Qst (kJ/mol) | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SAPO-34 | 402.2 | 278 | 0.3~0.8 | 22.7 | 2.6 | 36.74 | 33 |
| Z4A | 39 | 273 | 4.7 | 3.77 | / | 32.45 | 34 |
| HZ4A-1-3 | 126 | 273 | 5.5 | 3.41 | / | 28.02 | 34 |
| CS-ZX | 561 | 298 | / | 4.23 | / | 10.4 | 35 |
| 3D-LTA | 9.00 | 273 | 4 | 1.99 | / | 21.49 | 36 |
| 2D-LTA | 12.66 | 273 | 4 | 2.31 | / | 44.52 | 36 |
| Co(II)/SSZ-13 | 786.75 | 273 | / | 4.49 | 52.55 | / | 26 |
| Ni(II)/SSZ-13 | 836.01 | 273 | / | 4.45 | 42.61 | / | 26 |
| NZL-500 | 670.11 | 298 | / | 5.56 | 619.99 | / | 37 |
| N-L | 427.2 | 298 | / | 2.85 | 198.6 | / | 38 |
| Modified Z-13X | 16.58 | 298 | 1.2 | 5.50 | / | 40.681 | 39 |
| KX | 720.14 | 298 | 1.944 | 4.90 | 152 | / | 40 |
| MCM41-450 | 259.10 | 298 | / | 2.275 | / | / | 41 |
| Na-ZK-4 | 687 | 273 | / | 4.86 | 49 | 40~45 | 42 |
| Li-LSX | 662.00 | 273 | 0.8~1.8 | 4.21 | 85.7 | / | 43 |
| ZSM-5-25 | 404 | 273 | 0.5 | 2.22 | 77~149 | / | 44 |
| HASM-5 | 417.63 | 298 | 2.647 | 4.27 | / | 54.27 | 45 |
| Calcined Beads@2.0-3.0mm | 586 | 273 | 5.4 | 4.5 | / | / | 46 |
| Zeolite X | 735.88 | 273(303) | 0.6 | 7.3(6.1) | / | / | 47 |
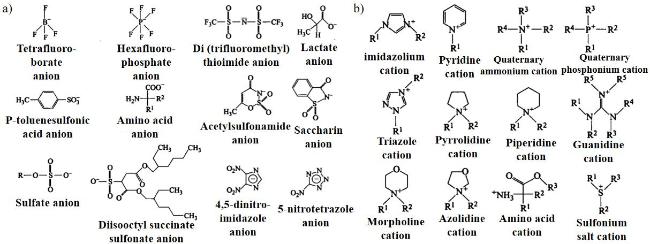
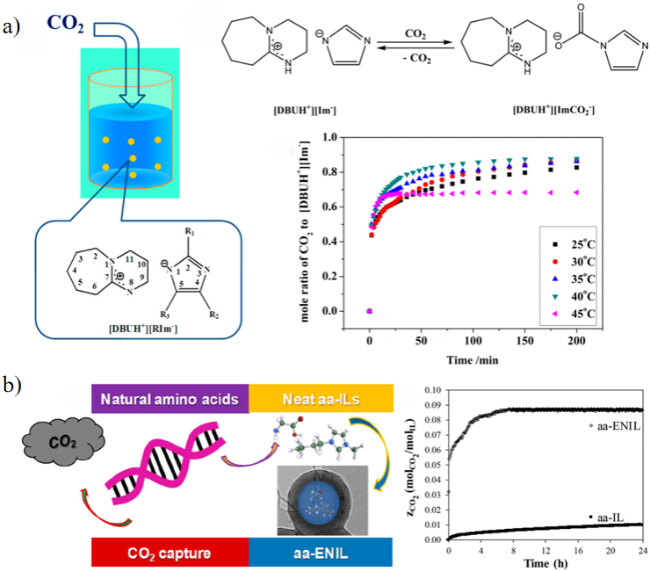
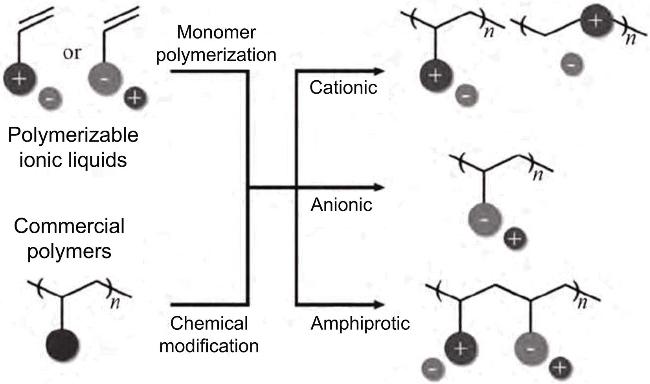
2.3 离子液体吸附剂
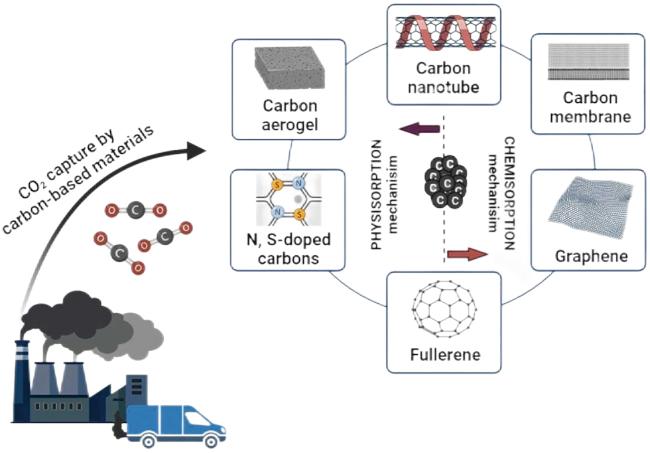
2.4 碳基吸附剂
表3 不同前驱体合成碳材料对于CO2捕获性能Table 3 CO2 capture performance of synthesized carbon materials with different precursors |
| Different precursors | Exemple | BET (m2/g) | Temperature (K) | Pressure (bar) | Capacity (mmol/g) | Qst (kJ/mol) | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Biomass-derived porous carbons | ANKO1 | 1894 | 273(298) | 1 | 7.18(4.81) | / | 63 |
| SWC-derived AC | 1085 | 298 | 1 | 2.63 | 14 | 64 | |
| ACPS600-K-4 | 2437 | 273 | 1 | 5.79 | / | 65 | |
| Synthetic resin-derived porous carbons | NSOPC-1 | 1292 | 273(298) | 1 | 7.04(3.88) | / | 66 |
| UFC-600-3 | 1686 | 273(298) | 1 | 5.42(3.53) | 45 | 67 | |
| PPSC-650-2 | 1094 | 273(298) | 1 | 3.64(5.13) | 35~41 | 68 | |
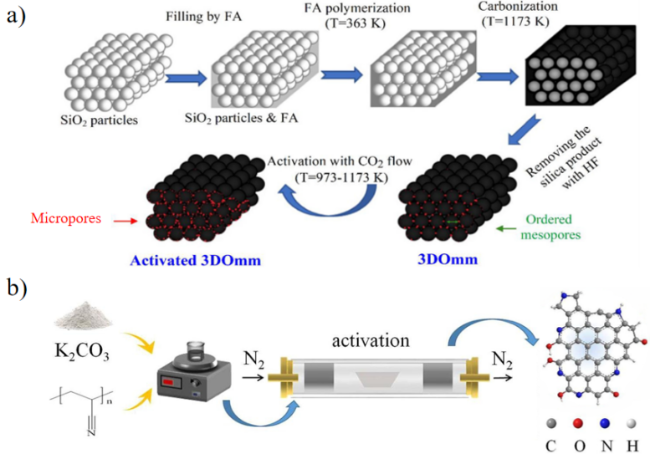
| Synthetic polymer-derived porous carbons | KOH-700 | 2155 | 273 | 1 | 6.23 | 26.5~29.2 | 69 |
| K2CO3-800 | 1143 | 273 | 1 | 5.47 | 37.1 | 69 | |
| 3DOmm | 1462 | 273(298) | 1 (20) | 3.19(11.18) | 18.9~29.2 | 57 | |
| Biopolymer-derived porous carbons | LBAU5 | 1134 | 273 | / | 4.06 | / | 70 |
| LHPC-700 | 1788 | 273(298) | 1 | 8.2(4.8) | 28.6 | 71 | |
| CHNH1∶2 | 2906 | 273 | 1 | 7.38 | 46.87 | 72 | |
| Graphene-derived porous carbons | CuBTC/GO | 1760 | 273(298) | 1 | 9.59(5.33) | 25.3~25.6 | 73 |
| a-RGO-950 | 1316 | 273 | 1 | 3.36 | 27.42 | 74 | |
| T-GU-700-6 | 1032 | 273(298) | 1 | 3.24(2.40) | 12~33 | 75 | |
| Fossil resources-derived porous carbons | IANC | 2186 | 298 | 1 (35) | 7.15(29.29) | / | 76 |
| A-rNPC | 2580 | 296 | 30 | 26.0 | 29.0 | 77 | |
| ARA | 1590 | 298 | 4 | 7.56 | 23.0 | 78 |
2.5 金属有机框架
表4 部分MOFs对于CO2捕获性能Table 4 Performance of some MOFs for CO2 capture |
| MOFs | BET (m2/g) | Temperature (K) | Pressure (bar) | Capacity (mmol/g) | CO2/N2 selectivity | Qst (kJ/mol) | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co-3-OADA | / | 273 | 1 | 2.02 | 48 | 34 | 89 |
| Zn-3-OADA | / | 273 | 1 | 1.91 | 43 | 25 | 89 |
| UTSA-16(Zn) | 786.61 | 298 | 1 | 4.71 | 118 | / | 90 |
| UTSA-16(Zn,Mn) | 810.43 | 298(333) | 1 | 5.28(3.76) | 135(95) | / | 83 |
| UTSA-16(Zn,Mg) | 825.19 | 298(333) | 1 | 5.56(3.95) | 141(97) | / | 83 |
| UTSA-16(Zn,Cu) | 817.40 | 298(333) | 1 | 5.13(3.60) | 131(92) | / | 83 |
| PAN/MIL-101 | 2657.7 | 343.96 | 1 | 2.48 | 38 | 31.88 | 91 |
| NBC@MOF-99 | 553.4 | 298~303 | 1 | 2.9 | / | / | 92 |
| MOF-74(Ni) | 1129 | 273(298) | 1 | 8.29(6.61) | 49 | 27~52 | 93 |
| Cu-OATA | / | 273(298) | 1 | 5.61(2.02) | 43.8 | 25 | 94 |
| CUT | 802 | 273 | 1 | 2.53 | 34.2 | 30.15 | 95 |
| Zr-MOF-808/NH2 | 2021 | 298 | 9 | 8.39 | / | 17.36 | 96 |
| Ni(3-ain)2 | 790.1 | 298 | 1 | 3.73 | 26.3 | 31.8 | 97 |
| CuBDC-NO2 | 523 | 298 | 1 | 2.40 | 28 | 20.2 | 98 |
| MC-HUN-4 | 523 | 298 | 1 | 1.90 | 13.02 | / | 99 |
| NaX | 17.39 | 273 | 1.13 | 4.34 | 89.2 | 37.9 | 100 |
| NUM-3a | 2111.2 | 273(298) | 1 | 4.56(3.35) | 82.8(64.8) | / | 101 |
2.6 共价有机框架
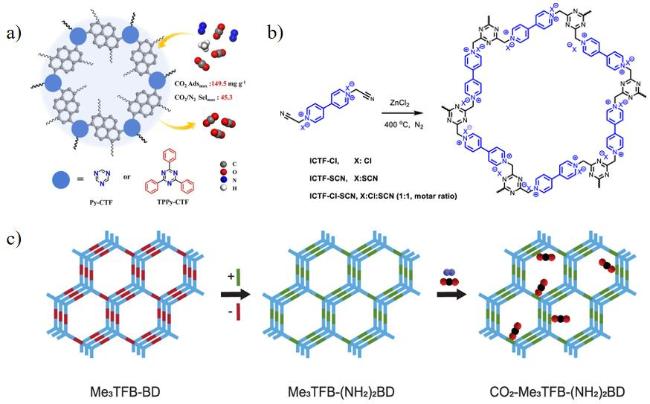
图16 (a) 1,3,6,8-四(4-氰苯)芘构建CTFs结构示意图[107],(b)微孔ICTF-Cl、ICTF-SCN和ICTF-Cl- SCN合成示意图,(c) COF (Me3TFB-(NH2)2BD)合成与CO2捕集示意图[111]Fig.16 (a) Schematic diagram of CTFs constructed from 1,3,6,8-tetrakis(4-cyanobenzene)pyrene[107],(b) Schematic diagram of the synthesis of microporous ICTF-Cl,ICTF-SCN,and ICTF-Cl- SCN,(c) Schematic of the synthesis of COF (Me3TFB-(NH2)2BD) and CO2 capture by COF[111] |
表5 部分COFs对于CO2捕获性能Table 5 Performance of some COFs for CO2 capture |
| COFs | BET (m2/g) | Temperature (K) | Pore size (nm) | Capacity (mmol/g) | CO2/N2 selectivity | Qst (kJ/mol) | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JUC-610 | 2072 | 273(298) | 1.5 | 2.26(1.44) | / | 21.9 | 112 |
| Cu-anPPCs | 2043 | 273(298) | 0.5 | 7.6 | / | 40.6 | 113 |
| UPC-6Li | 5974.80 | 298 | 16.37 | 8.95 | 308 | 38.75 | 114 |
| UPC-6Na | 5608.74 | 298 | 17.31 | 7.60 | 235 | 34.82 | 114 |
| UPC-6K | 3759.12 | 298 | 14.67 | 5.67 | 255 | 37.98 | 114 |
| Me3TFB-(NH2)2BD | 1624 | 273(295) | 2.7 | 1.12(0.72) | 47 | / | 111 |
| TpPa-NO2 | 398 | 273(298) | 1.5 | 2.38(1.83) | 125.23~34.87 | 36.26 | 115 |
| COF-300-SO3H | 428.42 | 298 | 5.29 | 6.23 | 393 | 39.71 | 116 |
| TMFPT-COF | 1407 | 273 | 1.86 | 1.54 | 19 | 34.1 | 117 |
| TAPT-BP2+-COF | 473.5 | 298 | 3.3 | 1.60 | 51.35 | 34.21 | 118 |
| 3D-TPB-COF-HQ | 842 | 273 | 0.52 | 3.77 | 40 | 23.5 | 119 |
| TBICOF | 1424 | 273(298) | 2.5 | 2.78(1.58) | 40.3 | 42.8 | 120 |
| CTF-TPM | 2002 | 273(298) | 1.13 | 4.84(2.87) | / | 26.9 | 121 |
| NH2-UiO-66@Br-COF | 966 | 273 | 2.5 | 3.86 | 24.08 | 117.2 | 122 |
| Py-CTF-400 | 1515 | 298 | 1.24(1.77) | 4.24 | 76.1 | 25.9 | 107 |
| Py-CTF-500 | 1564 | 298 | 1.24(2.20) | 3.49 | 61.5 | 23.1 | 107 |
| TPP-CTF | 1390 | 273(298) | 1.11 | 9.77(5.02) | 19 | / | 123 |
| 3D-ceq-COF | 1148.6 | 273(298) | 1.0(1.6) | 3.69(2.02) | 27.5 | 50.0 | 124 |
| JUC-568 | 1433 | 273(298) | 1.92 | 3.96(3.27) | / | / | 125 |
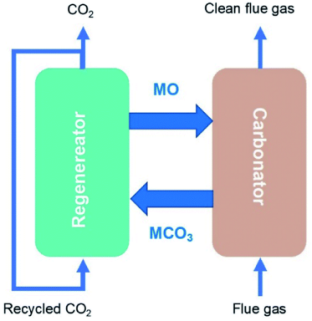
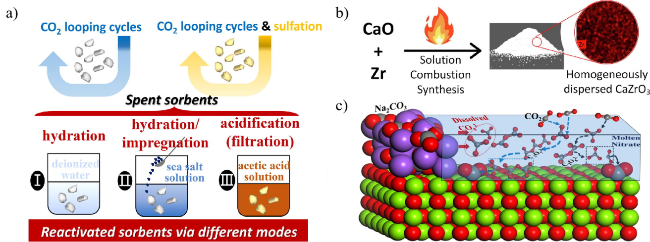
2.7 金属氧化物材料
图18 (a) 废吸附剂再活化过程[132],(b) 锆稳定氧化钙吸附剂合成及吸附剂循环捕获能力测定[133],(c) MgO-Na2CO3-KNO3吸附剂捕获CO2[139]Fig.18 (a) Reactivation process of spent adsorbent[132],(b) Synthesis of zirconium-stabilized calcium oxide adsorbent and determination of adsorbent cyclic capture capacity[133],(c) CO2 capture by MgO-Na2CO3-KNO3 adsorbent[139] |
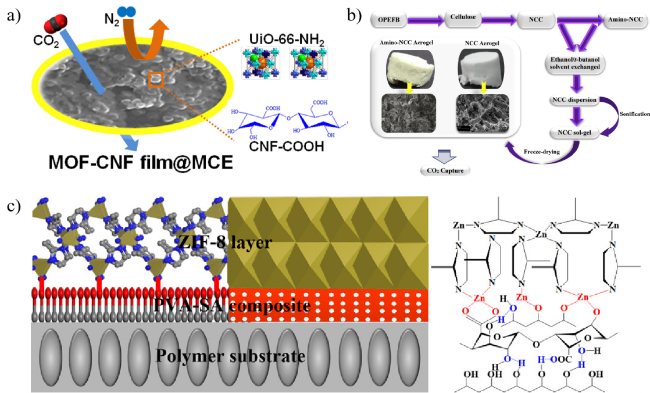
2.8 生物聚合物纳米复合材料
图19 (a) UiO-66-NH2与CNF-COOH结合生成复合膜用于CO2/N2分离[144],(b) NCC及氨基-NCC气凝胶制备与应用[145],(c) ZIF-8/PES复合膜结构示意图Fig.19 (a) UiO-66-NH2 combined with CNF-COOH to generate composite membranes for CO2/N2 separation[144],(b) Preparation and application of NCC and amino-NCC aerogels[145],(c) Schematic structure of ZIF-8/PES composite membrane |
3 捕获材料的比较与展望
表6 各类CO2捕获材料的优缺点Table 6 Advantages and disadvantages of various kinds of CO2 capture materials |
| Materials | Advantages | Disadvantages | Applicability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amine solution absorbents | High solubility and selectivity;high mass transfer coefficient;stable adsorption in humid environment;the techology is mature | High volatility;high cost;high energy consumption;causing corrosion to equipment | Suitable for most power plants and factories with high CO2 emission concentrations at present |
| ILs | Negligible vapor pressure;high thermal stability;relatively non flammable;strong designability | High viscosity;poor permeability;difficult exposure of active sites | Suitable for environments with high flue gas temperatures |
| Carbon-based adsorbents | High specific surface area;adjustable structure;high thermal stability;low adsorption heat;less affected adsorption performance under humid conditions | Low adsorption capacity;poor adsorption selectivity;high energy consumption during the regeneration process | Can function in low or medium low pressure environments |
| Zeolites based adsorbents | High specific surface area;adjustable pore design;high recyclability at low temperatures;low cost | Low gas selectivity;significant reduction in CO2 adsorption at high temperatures;poor adsorption performance under humid conditions;average regeneration performance | Can function under harsh conditions,such as low temperature environments;suitable for rapid adsorption |
| MOFs | High specific surface area;high CO2 selectivity;large pore volume;high porosity | Poor CO2 adsorption capacity under low pressure conditions;unstable adsorption under humid conditions;poor stability | Suitable for stable environments and appropriately high ambient temperatures |
| COFs | High specific surface area;high thermal and chemical stability;strong functional group adaptability;high CO2 selectivity | Avergy regeneration performance;poor adsorption performance under humid conditions | Suitable for CO2 capture under high pressure;maintaining stability in acidic,alkaline or high-temperature environments |
| Metal oxide sorbents | Superior adsorption effect;low cost of raw materials;synergistic effects can be produced when mixed with other materials | High difficulty of regeneration;average effect of recycling;average thermal stability | Further clarification is needed |
| Biopolymeric nanocomposites | Polymer raw materials are easily available;low energy consumption;strong structural designability;high specific surface area and porosity | Avergy stability and durability;high costs of nanomaterials;poor selectivity | Further clarification is needed |