1 引言
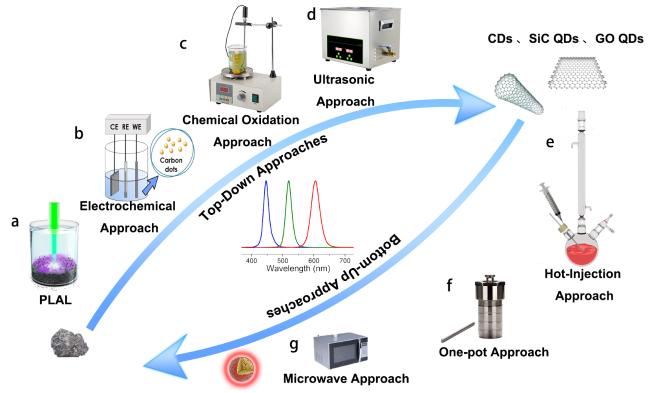
2 量子点合成方法
2.1 自上而下合成法
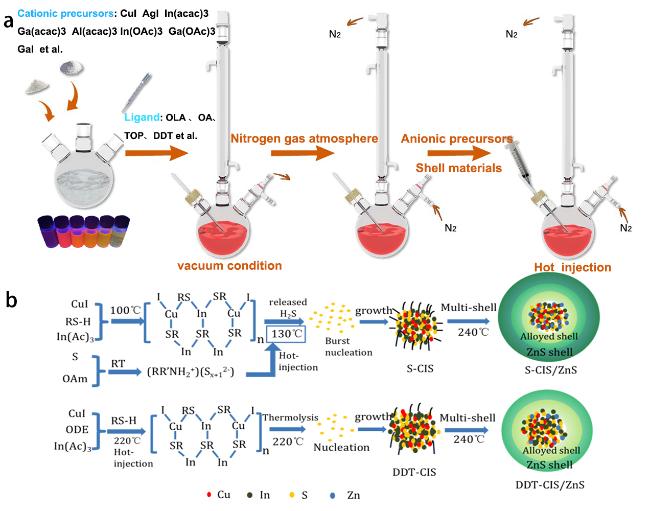
2.2 自下而上-热注入法
2.3 自下而上:一锅热法
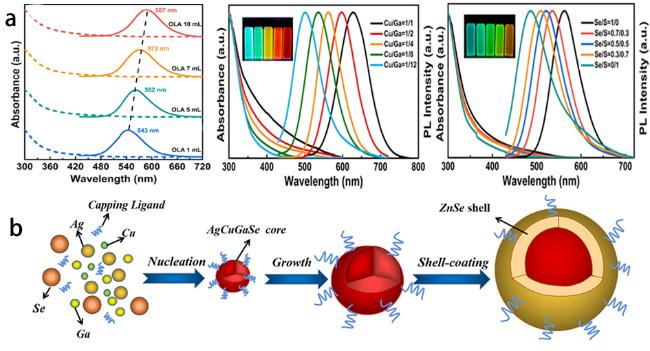
图3 (a)不同油氨剂量、前驱体比例、硫源掺杂CuGaSe2/ ZnSe量子点的紫外可见吸收光谱和光致发光谱[29];(b)Ag-Cu-Ga-Se多元量子点生长机理图[34]Fig 3 (a)UV-vis absorption spectra and photoluminescence spectra of CuGaSe2/ZnSe quantum dots doped with different oleoammonia doses, precursor ratios, and sulfur source[29]. (b)Ag-Cu-Ga-Se multiplexed quantum dot growth mechanism[34] |
3 Ⅰ-Ⅲ-Ⅵ2族量子点的研究现状
3.1 Ⅰ-Ⅲ-Ⅵ2族量子点的发光机制
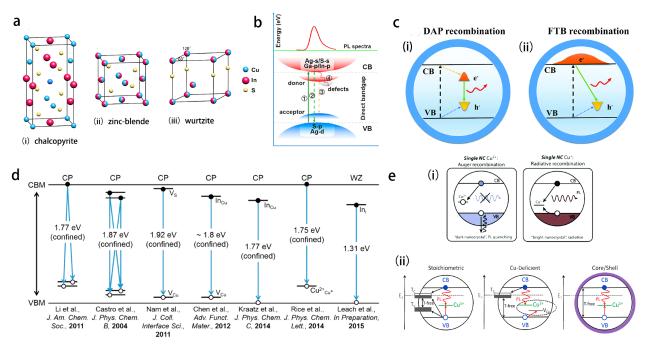
图4 (a)黄铜矿、闪锌矿和纤锌矿晶体结构[42];(b)Ⅰ-Ⅲ-Ⅵ2族量子点的电子能带结构和不同的重组或猝灭路径[37];(c)DAP重组和FTB重组示意图[14];(d)黄铜矿和纤锌矿CuInS2量子点的辐射衰变机制及观测到的能量[43];(e)俄歇复合导致Cu2+的PL猝灭,辐射复合导致Cu+的亮化;不缺铜和缺铜的CuInS2量子点以及CuInS2/ZnS 核壳结构的弛豫过程示意图[44,45]Fig. 4 (a)Crystal structures of chalcopyrite, sphalerite, and fibrillar zincite[42]. (b)Electronic energy band structures and different recombination or quenching paths of group Ⅰ-Ⅲ-Ⅵ2 quantum dots[37]. (c)Schematic diagrams of the DAP recombination and the FTB recombination[14]. (d)Overview of the radiative decay mechanisms of the CuInS2 quantum dots of chalcopyrite and fibrillar zincite and their observed energies[43]. (e)Rushes of composites leading to the PL burst of Cu2+ and radiative complexation leads to Cu+ brightening; schematic diagrams of the relaxation processes in Cu-less and Cu-deficient CuInS2 quantum dots as well as in the CuInS2/ZnS core-shell structure[44,45] |
3.2 Ⅰ-Ⅲ-Ⅵ2族量子点光学性能优化
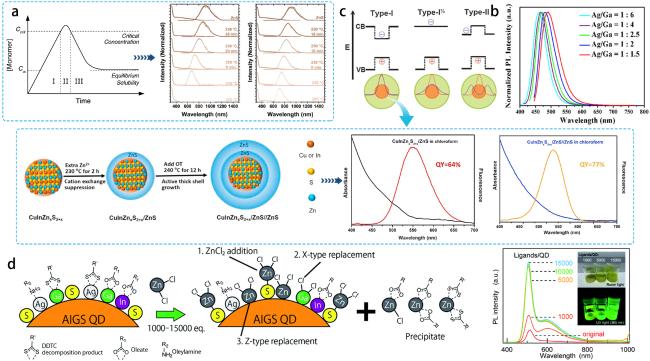
图5 (a)LaMer形核理论[62],CuInS2量子点吸光度和PL光谱演化[63];(b)不同Ag、Ga前驱体比例的PL光谱图[64];(c)核壳结构量子点中三种电荷载流子局域化机制的示意图[53], 多壳层CIZS/ZnS/ZnS量子点合成过程示意图和PL光谱[55];(d)配体交换机制的示意图[28]Fig 5 (a)LaMer shaped nucleus theory[62], CuInS2 quantum dots absorbance and PL spectral evolution[63]. (b)PL spectra of different Ag and Ga precursor ratios[64]. (c)Schematic representation of the three charge carrier localization mechanisms in the core-shell structured quantum dots[53]. Schematic representation of the synthesis process of the multi-shell CIZS/ZnS/ZnS quantum dots and PL spectra[55]. (d)Schematic representation of the ligand exchange mechanism[28] |
4 Ⅰ-Ⅲ-Ⅵ2族量子点发光器件
4.1 量子点发光显示器件
4.2 Ⅰ-Ⅲ-Ⅵ2族量子点QLED和WLED器件
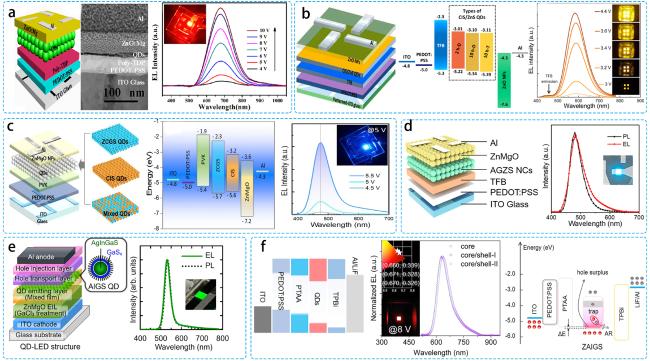
图6 (a)基于CuInS2/ZnS的QLED结构示意图,横截面TEM图像和器件的EL光谱随电压演化[85];(b)多壳层CuInS2/ZnS的QLED器件示意图,相应的能级图和器件的EL光谱随电压演化[86];(c)蓝光ZCGS、黄光CIS及其混合物的QLED结构,相应的能级图和器件的EL光谱随电压演化[58];(d)基于AGZS的QLED结构示意图结构和器件对应的EL光谱和PL光谱[59];(e)基于AIGS/GaS的QLED结构示意图,以及PL和EL光谱[88];(f)基于ZAIGS多元量子点的QLED结构示意图,核壳结构的EL光谱以及器件中载流子分布和复合的示意图[60]Fig. 6 (a)Schematic QLED structure based on CuInS2/ZnS, cross-sectional TEM image and EL spectra of the device evolving with voltage[85]. (b)Schematic QLED device based on multi-shell layer CuInS2/ZnS, corresponding energy level diagrams and EL spectra of the device evolving with voltage[86]. (c)QLED structure for blue ZCGS, yellow CIS and their mixtures, corresponding energy level diagrams and EL spectra of the devices evolving with voltage[58]. (d)Schematic structure of QLED based on AGZS Schematic structure and corresponding EL spectra and PL spectra of the devices[59]. (e)Schematic structure of QLED structure based on AIGS/GaS, along with the PL and EL spectra[88]. (f)Schematic structure of QLED structure based on ZAIGS multiplexed quantum dots, EL spectra of the core-shell structure, and the device Schematic representation of carrier distribution and complexation in the device[60] |
图7 (a)CIS量子点器件正向电流相关EL光谱演化以及CIE白光颜色坐标[92]; (b)在20 mA的驱动电流下,基于绿色和红色QD/PAAm膜的LED的发射光谱和CIE色坐标[93]; (c)CGS和CIS量子点之间的不同重量比制造白光WLED的EL光谱、CRI、CCT和发光效率的变化[95]; (d)基于单一体系CGS核壳量子点的WLED器件结构图和能带图,EL光谱随电压演化[96]; (e)In掺杂Zn-Cu-Ga-S/ZnS的WLED器件结构图、CRI的比例变化[97]; (f)双体系CIS和CGS核壳量子点混合发光层的WLED器件EL光谱以及归一化光谱随电压演化[58]Fig. 7 (a)Forward current-dependent EL spectral evolution of CIS quantum dot devices and CIE white light color coordinates[92]. (b)Emission spectra and CIE color coordinates of LED based on green and red QD/PAAm films at a drive current of 20 mA[93]. (c)Variation of EL spectra, CRI, CCT and luminous efficiency of white WLED fabricated with different weight ratios between CGS and CIS quantum dots[95]. (d)Structural and energy band diagrams of WLED devices based on single-system CGS core-shell quantum dots, EL spectra evolution with voltage[96]. (e)Structure of In-doped Zn-Cu-Ga-S@ZnS WLED device, scale variation of CRI[97]. (f)EL spectra of WLED devices with dual-system CIS and CGS core-shell quantum dots hybrid light-emitting layers and normalized spectra evolution with voltage[58] |