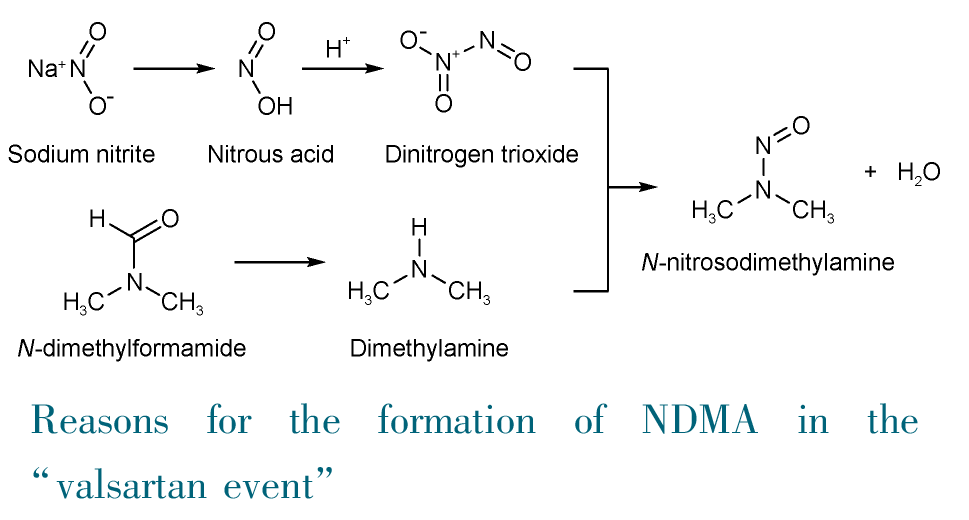
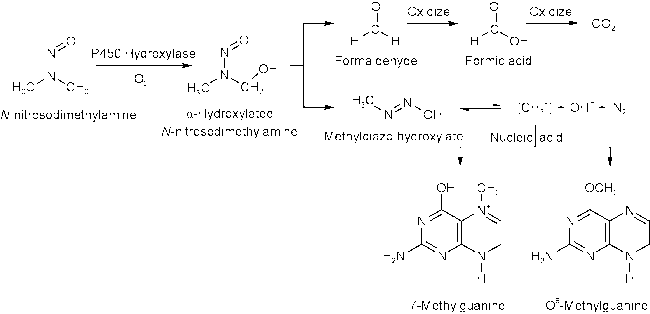
1 引言
2 药品中亚硝胺杂质的检测
表1 监管机构发布的检测方法Table 1 Testing methods issued by regulatory agencies |
| Regulatory agencies | Method | Extraction solvent | N-nitrosamine |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNMPA | GC-MS | Methanol (MeOH) | NDMA, NDEA |
| HS-GC-MS | N- Methylpyrrolidone (NMP) | NDMA, NDEA | |
| EDQM | LC-MS/MS | Methanol (MeOH) | NDMA, NDEA |
| LC-(APCI)MS/MS | Water (H2O) | NMBA | |
| HS-GC-MS | Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) | NDMA, NDEA, NEIPA, NDIPA | |
| U.S.FDA | GC-MS/MS | Dichloromethane (DCM) | NDMA, NDEA NEIPA, NDIPA, NDBA |
| LC-HRMS | Methanol (MeOH) | NDMA, NDEA, NEIPA, NDIPA, NDBA NMBA |
表2 文献报道药品中亚硝胺杂质的浓度水平Table 2 Concentration levels of N-nitrosamine impurities reported in pharmaceutical literatures |
| Pharmaceutical | Chemical formula | Structural formula | Applicable symptoms | Method & publication Year | Concentration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Valsartan | C24H29N5O3 | 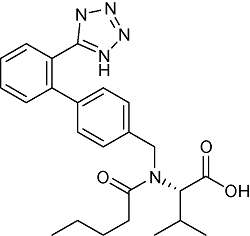 | Hypertension, congestive heart failure, posterior myocardial infarction | LC-HRMS 2019 | NDMA:Not detected ~20.19 μg/tablet[26] NDEA:Not detected ~1.31 μg/tablet[26] |
| UPLC-MS/MS 2021 | NDMA: Not detected[27] NIEA:0.090~0.241 μg/g[27] | ||||
| GC-MS/MS 2019 | Not detected[28] | ||||
| HPLC 2019 | Not detected[29] | ||||
| LC-MS/MS 2022 | Not detected[30] | ||||
| Irbesartan | C25H28N6O | 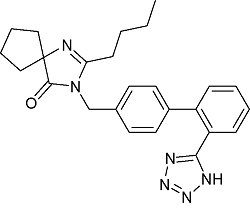 | Essential hypertension | GC-MS/MS 2020 | NDEA :0.11~0.54 μg/g[31] |
| UPLC-MS/MS 2022 | NDEA :0.016~0.024 μg/g NDBA:0.001~0.002 μg/g[32] | ||||
| Telmisartan | C33H30N4O2 | 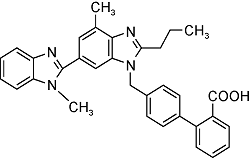 | Essential hypertension | GC-MS/MS 2023 | NDMA: n.d.~0.12μg/g[33] |
| Candesartan | C24H20N6O3 | 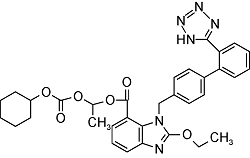 | Essential hypertension | GC-MS/MS 2023 | NDMA: n.d. NDEA: n.d.[34] |
| Ranitidine | C13H22N4O3S | 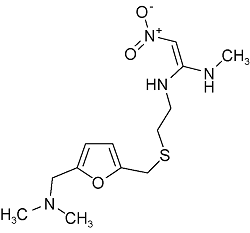 | Canker | LC -HRMS 2021 | NDMA:0.01~0.86 μg/g[35] |
| LC -MS 2021 | NDMA:0.01~0.17 μg/g[36] | ||||
| Metformin | C4H11N5 | 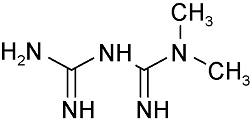 | Type 2 diabetes | LC- HRMS 2022 LC- HRMS 2020 | Not detected ~0.19 μg/g[37] Not detected[38] |
| HPLC-MS/MS 2022 | Not detected[39] | ||||
| HPLC-MS/MS 2020 | NDMA:0.072~0.282 μg/g[40] | ||||
| Amoxicillin | C16H19N3O5S | 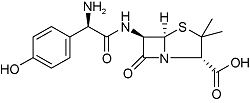 | Bacterial infection | GC-MS/MS 2021 | Not detected[41] |
3 亚硝胺的毒理学性质
3.1 基本特性
3.2 致癌机理
3.3 致癌效应因子
表3 常见亚硝胺的致癌效应因子Table 3 Carcinogenic effect factors of common N-nitrosamines |
| N-nitrosamines | English abbreviations | Carcinogen (mg/kg/d)-1 | IARC’s Carcinogen level |
|---|---|---|---|
| N-nitrosodimethylamine | NDMA | 51.0 | 2A |
| N-nitrosodiethylamine | NDEA | 150.0 | 2A |
| N-nitrosodiethylamine | NMEA | 22.0 | 2B |
| N-nitrosopiperidine | NPIP | 2.1 | 2B |
| N-nitrosopyrollidine | NPYR | 2.1 | 2B |
| N-nitrosodi-n-propylamine | NDPA | 7.0 | 2B |
| N-nitrosodi-n-butylamine | NDBA | 5.4 | 2B |
| N-nitrosodiphenylamine | NDPhA | 0.0049 | — |
3.4 药品亚硝胺的致癌风险评估
ADI=
CR=ADI×SF
表4 几种常用药品中亚硝胺类化合物暴露的致癌风险Table 4 Carcinogenic risks of exposure to N-nitrosamines in several commonly used pharmaceuticals |
| Pharmaceutical | N-nitrosamine | Crange (μg/ tablet) | (μg/ tablet) | (μg/ tablet) | (μg/ tablet) | C90% (μg/ tablet) | IR (mg/d) | EF (time/d) | AD (mg/kg/d) | SF((mg/kg/ d)-1) | C | C | C | C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Valsartan (320mg) | NDMA | Not detected ~20.19 | 3.86 | 0.0016 | 8.645 | 13.637 | 320 | 1 | 1.24 ×10-5 | 51 | 2.41 ×10-4 | 9.99 ×10-8 | 5.40 ×10-4 | 8.52 ×10-4 |
| NDEA | Not detected ~1.31 | 0.21 | 0.025 | 0.115 | 0.699 | 320 | 1 | 8.02 ×10-7 | 150 | 3.86 ×10-5 | 4.59 ×10-6 | 2.11 ×10-5 | 1.28 ×10-4 | |
| Total | 2.80 ×10-4 | 4.69 ×10-6 | 5.61 ×10-4 | 9.80 ×10-4 | ||||||||||
| Ranitidine (150mg) | NDMA | 0.01~0.86 | 0.177 | 0.110 | 0.200 | 0.452 | 150 | 2 | 1.07 ×10-6 | 51 | 2.21 ×10-5 | 1.37 ×10-5 | 2.50 ×10-5 | 5.65 ×10-5 |
| Metformin (250mg) | NDMA | Not detected ~0.19 | 0.016 | 0.005 | 0.01 | 0.048 | 250 | 1 | 1.63 ×10-7 | 51 | 9.99 ×10-7 | 3.12 ×10-7 | 6.24 ×10-7 | 3.00 ×10-6 |
Note:The calculation is based on the medication duration of 6 years, average body weight of 70 kg, and average life span of 70 years.Due to space constraints, only the average ADI values are shown in the table. |
4 流行病学调查
5 药品中亚硝胺杂质的来源
6 服药后亚硝胺的内源性生成
7 与其他外源暴露途径的比较
表5 不同国家和地区对食品和饮用水中亚硝胺的限量标准[73]Table 5 Maximum levels of N-Nitrosamines in food and drinking water in different countries and regions |
| Category | Food(μg/kg) | Drinking water(ng/L) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Meat | Aquatic product | Beer | NDMA | NDEA | NDPA | |||||||
| NDMA | NDEA | NDMA | NDEA | NDMA | ||||||||
| Austria | 0.5 | |||||||||||
| Australia | 100 | |||||||||||
| Ontario, Canada | 9 | |||||||||||
| Canada | 1.5 | 40 | ||||||||||
| China | 3 | 4 | 3 | 100* | ||||||||
| Germany | 0.5 | 10 | ||||||||||
| Japan | 5 | |||||||||||
| Russia | 2(total nitrosamine) | 3(total nitrosamine) | 3 | |||||||||
| Iceland | 10(total nitrosamine) | 7(total nitrosamine) | ||||||||||
| Ukraine | 2(total nitrosamine) | 3(total nitrosamine) | 3 | |||||||||
| Massachusetts, USA | 10 | |||||||||||
| California, USA | 10 | 10 | 10 | |||||||||
| USA | 5 | ** | ||||||||||
| WHO | 100 | |||||||||||
* Listed in the appendix of “Standards for drinking water quality” (GB5749-2022) of China | |
** Listed in the “Drinking Water Standards and Health Advisory” of the United States, with no limit value set |
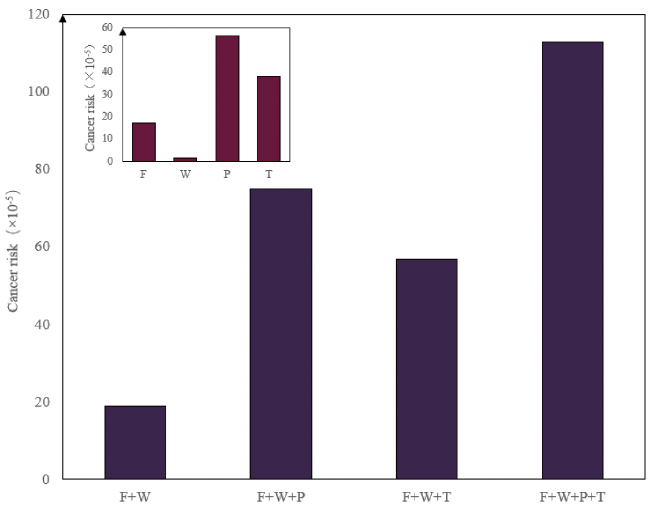
图3 四种不同生活方式导致的外源摄入亚硝胺致癌风险比较。注:药品导致的致癌风险按照U.S.FDA报道的缬沙坦中NDMA和NDEA的75百分位浓度值计算;F表示食品,W表示饮用水,P表示药品,T表示烟草Fig. 3 Comparison of carcinogenic risks of exogenous intake of nitrosamines caused by four different lifestyles.Note: The carcinogenic risk caused by pharmaceuticals is calculated based on the 75th percentile concentration values of NDMA and NDEA in valsartan reported by the U.S.FDA;F means Food, W means Water, P means Pharmaceutical, T means Tobacco |
8 药品监管措施
表6 遗传毒性杂质监管文件Table 6 Regulatory documents for genotoxic impurities |
| Stage | Time | Issuing agency | Document |
|---|---|---|---|
| Regulatory gaps | 2000 | EDQM | Essay:“Enquiry: Alkyl mesilate (methane sulfonate) impurities in mesilate salts” |
| Completely avoid | 2004 | EMA | “Draft guidelines for limits genotoxic impurities” |
| 2006 | EMA | “Final guide to the limits of genotoxic impurities” | |
| 2008 | U.S.FDA | “Recommended methods for genotoxic and carcinogenic impurities in raw materials and finished pharmaceuticals” | |
| Reasonable reduction | 2014 | ICH | ICH M7“Evaluation and control ofDNA reactive (mutagenic) impurities in pharmaceuticals to limit potential carcinogenic risks” |
| 2019 | Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission | “Guidelines for the control of genetically toxic impurities (draft for comments)” | |
| 2020 | U.S.FDA | “Control of nitrosamine impurities in human pharmaceuticals” | |
| 2020 | CNFDA | “Technical guidelines for nitrosamine impurities in chemical pharmaceuticals (trial)” |
表7 药品中有害杂质的可接受摄入量Table 7 Acceptable intake of harmful impurities in pharmaceuticals |
| Treatment period | ≤ 1 month | >1~12 months | >1~10 years | >10 years to lifetime |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Daily intake of single impurity(μg/d) | 120 | 20 | 10 | 1.5 |
| Daily intake of multiple impurities(μg/d) | 120 | 60 | 30 | 5 |
表8 ICH M7对药品中有害杂质的分类和控制策略Table 8 ICH M7 classification and control strategy for hazardous impurities in pharmaceuticals |
| Category | Definition | Control strategy |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Known mutagenic and carcinogenic | Control not to exceed specific acceptable limits of the compound itself |
| 2 | Known mutagen with unknown carcinogenicity (bacterial mutagenicity positive*, but no rodent carcinogenicity data) | Control not to exceed acceptable limits (appropriate TTC) |
| 3 | There is a warning structure, but it is not related to the structure of the pharmaceuticals substance, and there is no mutagenicity data | Control not to exceed acceptable limits (appropriate TTC) or testing bacterial mutagenicity; If there is no mutagenicity, it is classified into 5 categories; If there is mutagenicity, it is classified into category 2 |
| 4 | Having a warning structure, or having the same warning structure as the pharmaceuticals substance and its related compounds (e.g., process intermediates), but tested without mutagenicity | Controlled by non mutagenic impurities |
| 5 | There is no warning structure, or there is sufficient data to prove that there is no mutagenicity or carcinogenicity despite the warning structure | Controlled by non mutagenic impurities |
表9 药品中N-亚硝胺类杂质的限度Table 9 Limits of N-nitrosamines impurities in pharmaceuticals |
| Chinese name | English abbreviations | English name | Limit |
|---|---|---|---|
| N-亚硝基二甲胺 | NDMA | N-nitrosodimethylamine | 96 ng/d |
| N-亚硝基二丁胺 | NMBA | N-nitrosodibutylamine | 96 ng/d |
| N-亚硝基二乙胺 | NDEA | N-nitrosodiethylamine | 26.5 ng/d |
| N-亚硝基乙基异丙胺 | NEIPA | N-Ethyl-N-isopropylnitrous amide | 26.5 ng/d |
| N-亚硝基二异丙胺 | NDIPA | N-Isopropyl-N-nitroso-2-propanamine | 26.5 ng/d |