1 引言
2 抗菌微纳米机器人的驱动方式
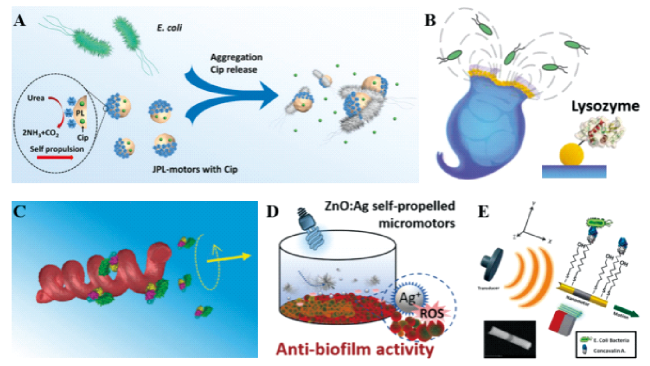
图1 (A)酶催化驱动的Janus血小板微米马达[25];(B)海洋轮虫驱动的溶菌机器人[32];(C)磁驱动的螺旋纳米机器人[44];(D)光催化驱动的ZnO:Ag微米马达[39];(E)超声驱动的金纳米线马达[42]Fig.1 (A) Urease-powered Janus platelet micromotors[25]. Copyright 2020, The American Association for the Advancement of Science; (B) rotifer based microrobots for enzymatic biodegradation of E. coli[32]. Copyright 2019, John Wiley and Sons; (C) magnetic powered helical nanorobots[44]. Copyright 2017, John Wiley and Sons; (D) light-driven ZnO:Ag micromotors[39]. Copyright 2021, John Wiley and Sons; (E) ultrasound-driven gold nanowire motors[42]. Copyright 2013, American Chemical Society |
3 微纳米机器人的抗菌应用
3.1 抗菌剂递送
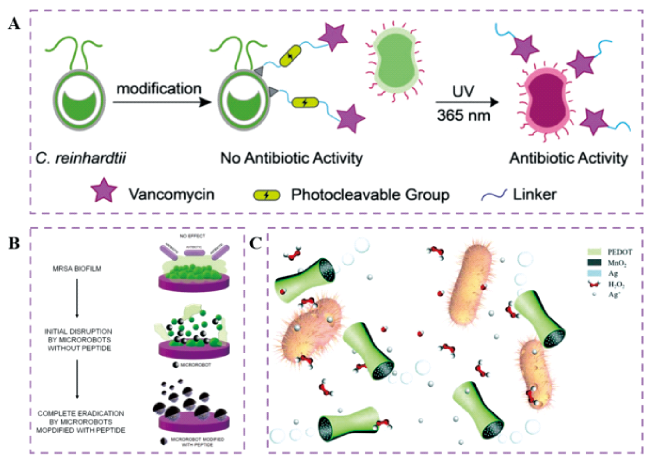
图2 (A)微藻机器人用于主动递送抗生素[30];(B)抗菌肽修饰的微型机器人用于去除MRSA生物膜[45];(C)PEDOT/MnO2管状微米马达用于增强的抗菌[26]Fig.2 (A) Microalgea robots for antibiotic delivery[30]. Copyright 2020, John Wiley and Sons; (B) antimicrobial peptide-modified microrobots for the eradication of MRSA biofilms[45]. Copyright 2022, John Wiley and Sons; (C) PEDOT/MnO2 tubular micromotors for enhanced antibacterial[26]. Copyright 2020, The Royal Society of Chemistry |
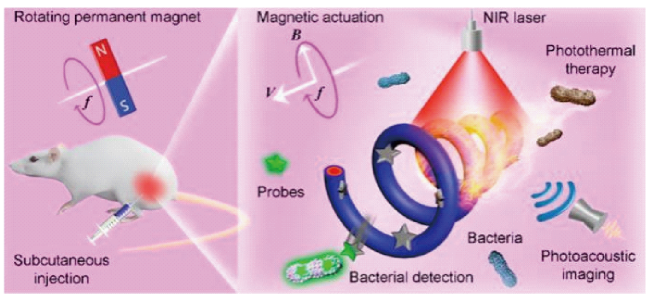
3.2 增强的光热治疗
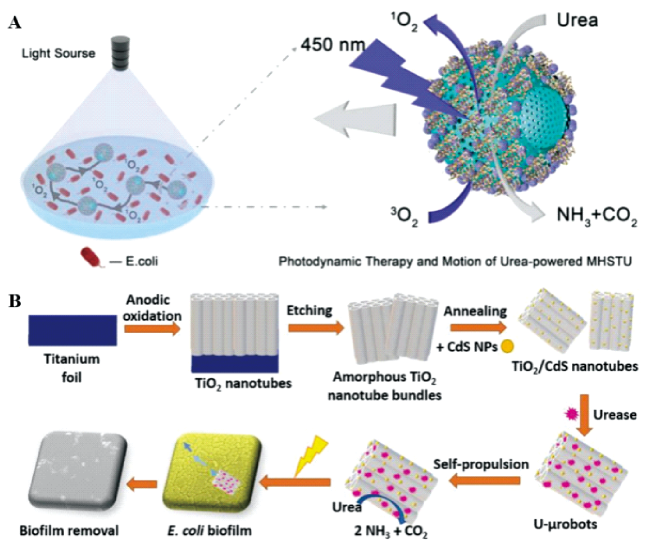
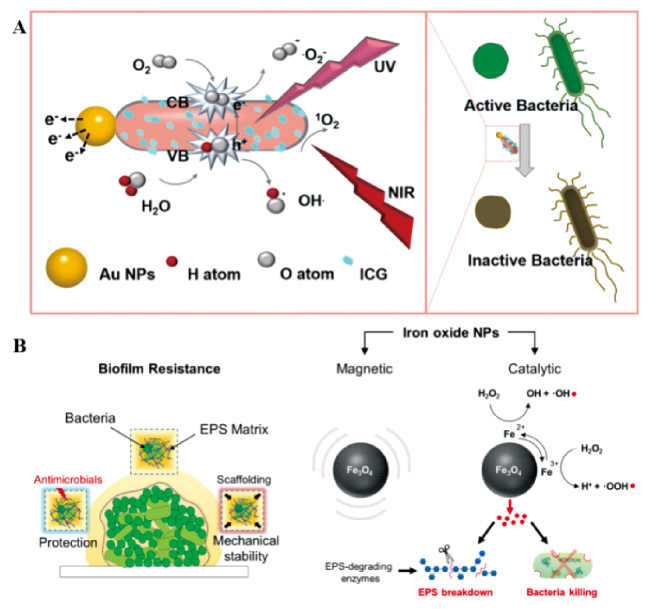
3.3 增强的光动力治疗
3.4 机械力杀伤
3.5 协同治疗
图6 (A)光热和光动力协同抗菌的 Janus纳米马达[63];(B)机械力协同ROS,药物清除生物膜的磁性抗菌机器人[64]Fig.6 (A) Janus nanomotors for killing bacteria with PTT and PDT[63]. Copyright 2022, The Royal Society of Chemistry; (B) magnetic antibacterial robots for removal of biofilm with mechanical force in collaboration with ROS and drug[64]. Copyright 2019, The American Association for the Advancement of Science |