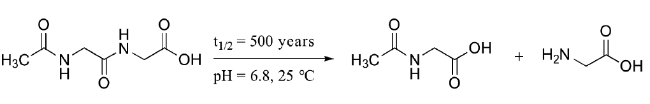1 引言
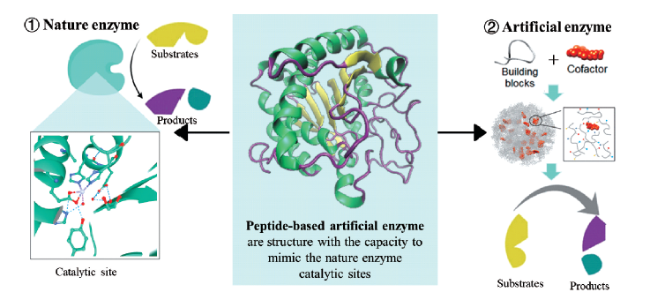
2 肽基水解模拟酶的活性来源
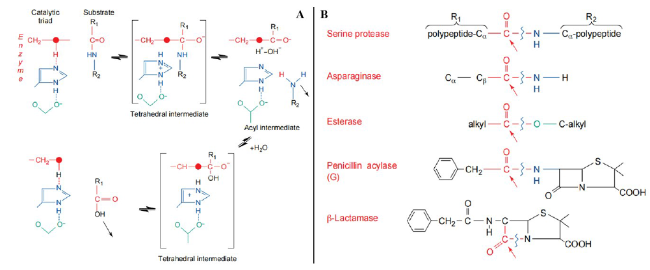
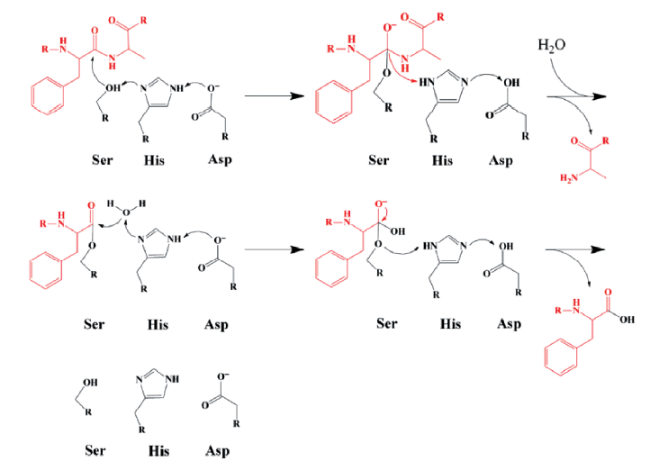
图1 (A) 催化三联体对肽键的亲核攻击作用,含亲核试剂的残基显示为红色,红点表示亲核原子,组氨酸和酸性残基分别用蓝色和绿色表示;(B) 常见天然酶催化降解的化学键,箭头表示亲核攻击的位置[26]Fig. 1 (A) Nucleophilic attack on the peptide bond by the catalytic triad. The nucleophile-bearing residue is shown in red; the red dot indicates the nucleophilic atom. The histidine and acidic residues are shown in blue and green, respectively. (B) The bonds are cleaved by various classes of enzymes. Arrows indicate the sites of nucleophilic attack[26] |
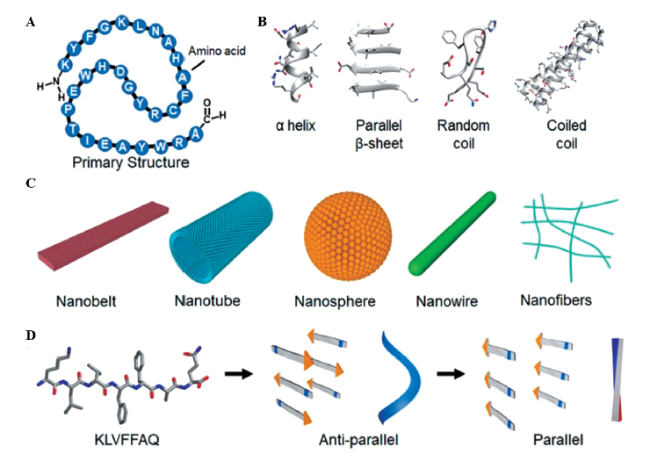
图2 小分子肽的结构:(A) 一级结构;(B) 二级结构;(C) 自组装纳米结构;(D) Aβ(16~22)的组装过程Fig. 2 Peptide structures. (A) Primary structure; (B) secondary structures; (C) higher-order self-assembled nanostructures; (D) model for the progressive transitions observed for Aβ(16~22) |
3 肽基水解模拟酶的催化反应类型
表1 具有催化酯键降解功能的肽基模拟酶Table 1 Ester bond hydrolase activity reported for peptide-based artificial enzymes |
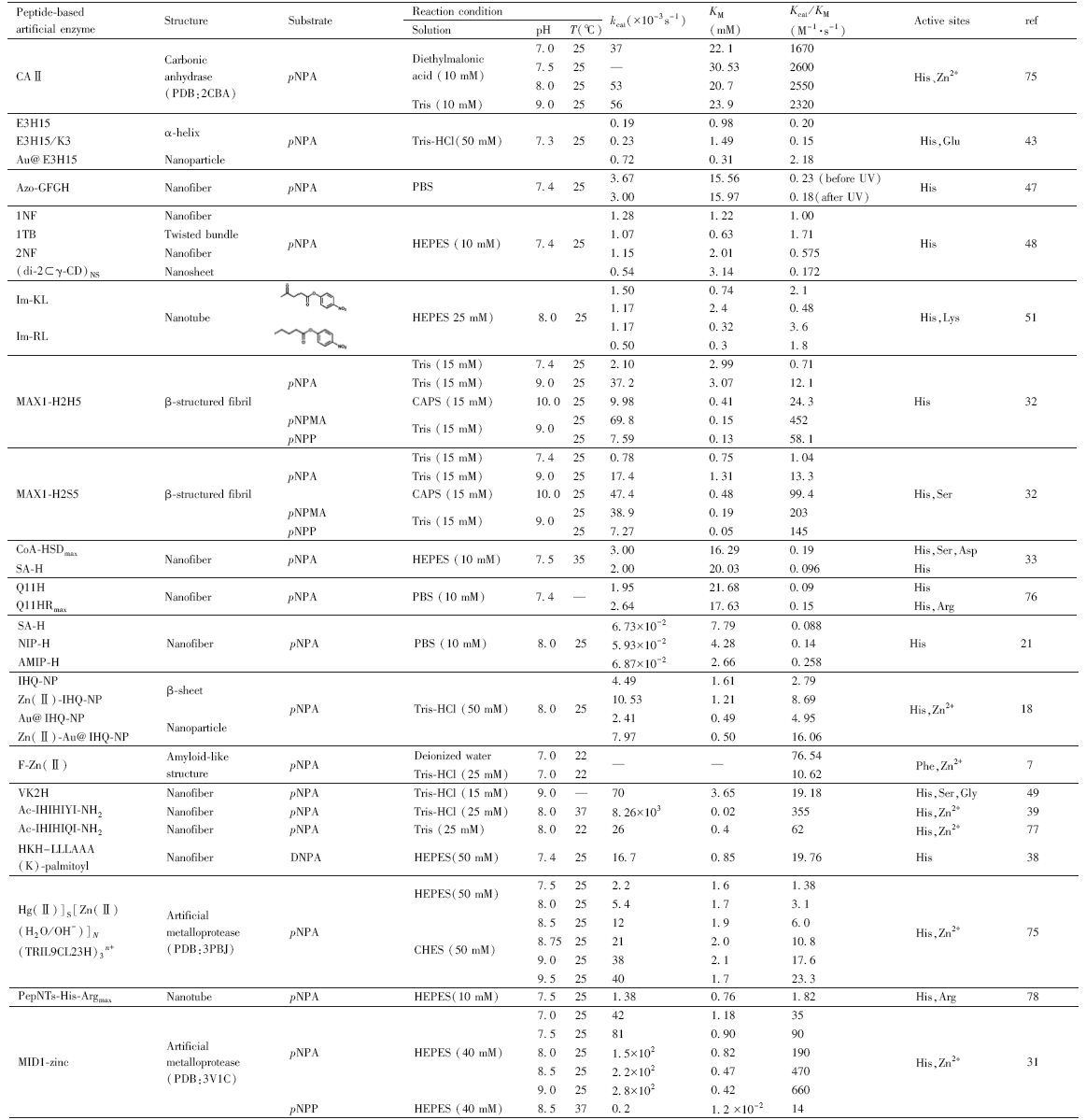 |
表2 具有催化肽键降解功能的肽基模拟酶Table 2 peptide bond hydrolase activity reported for peptide-based artificial enzymes |
| Peptide-based artificial enzyme | Structure | Substrate | Reaction condition | kcat or Reaction time | KM | Catalytic rate | Peptide sequence | ref | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | T/℃ | ||||||||
| Trypsin | — | BAPNA | 7.4 | 37 | 1.33×103min-1 | 0.47 g·L-1 | 2.86×103 L·g-1·min-1 | — | 56 |
| AuNPs@POMD-8pep | Nanoparticle | ||||||||
| 1.31×105 min-1 | 0.16 g·L-1 | 8.26×105 L·g-1·min-1 | |||||||
| JAL-AK22 | Small peptide | MMP18-33 | 7.4 | 37 | — | 0.17 mM | 0.55 nmol/h | KYEGHWYPEKPYK GSGFRCIHI | 59 |
| MMP18-40 | 0.15 mM | 0.78 nmol/h | |||||||
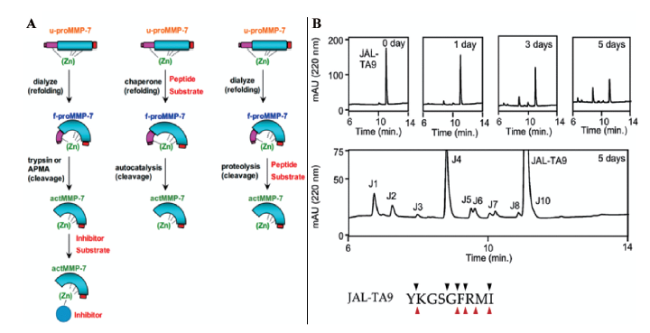
| JAL-TA9 | Small peptide | Aβ1-20 | 7.4 | 37 | — | 1.27 mM | 5.4 nmol/h | YKGSGFRMI | 59,63,66 |
| Aβ11-29 | 0.56 mM | 2.3 nmol/h | |||||||
| MMP18-33 | 7.4 | 37 | 4.58×10-4min-1 | 0.17 mM | 0.55 nmol/h | 64 | |||
| MMP18-40 | 6.5×10-4min-1 | 0.15 mM | 0.78 nmol/h | ||||||
| hPrP180-192 | 7.5 | 37 | 3 days | — | — | 63 | |||
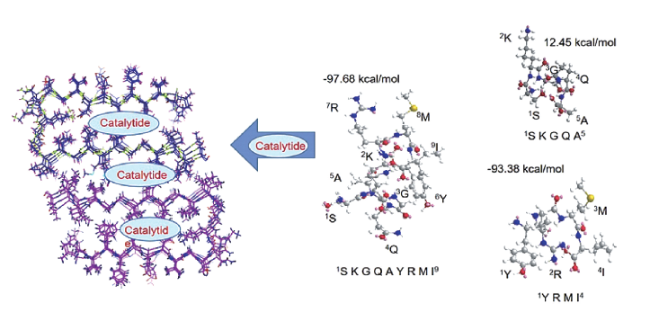
| ANA-TA9 | Small peptide | Aβ11-29 | 7.4 | 37 | 1.23×10-3 min-1 | 0.32 mM | 1.47 nmol/h | SKGQAYRMI | 60⇓~62 |
| ANA-SA5 | Small peptide | Aβ11-29 | 7.4 | 37 | 4.75×10-4 min-1 | 0.13 mM | 0.57 nmol/h | SKGQA | 60 |
| ANA-YA4 | 6.67×10-4min-1 | 0.15 mM | 0.80 nmol/h | YRMI | |||||
| GSGFR | Small peptide | Aβ1-20 Aβ11-29 | 7.4 | 37 | 2 days | — | — | GSGFR | 65 |
| GSGYR | GSGYR | ||||||||
| GQAYR | GQAYR | ||||||||
| GQAFR | GQAFR | ||||||||
| [GADV]-P30 | Small peptide mixture | BSA | — | 37 | 6 days | — | — | — | 58 |
| Gly-pNA | 7 days | ||||||||
| BSA | 4 days | ||||||||
| [GADV]- octapeptides | |||||||||
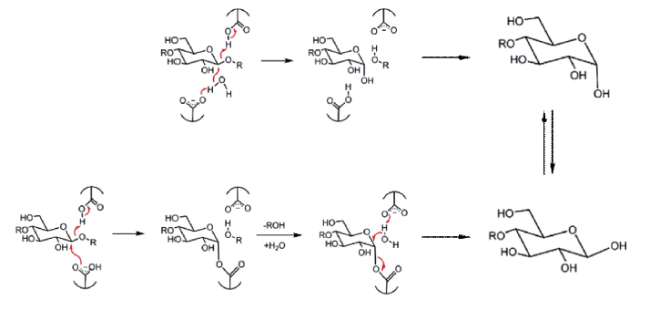
表3 具有催化糖苷键降解功能的肽基模拟酶Table 3 Glycosidic bond hydrolase activity reported for peptide-based artificial enzymes |
| Peptide-based artificial enzyme | Structure | Substrate | Reaction condition | Reaction time | Catalytic activity or Product quantity | Active sites | Peptide sequence | ref | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | T(℃) | ||||||||||
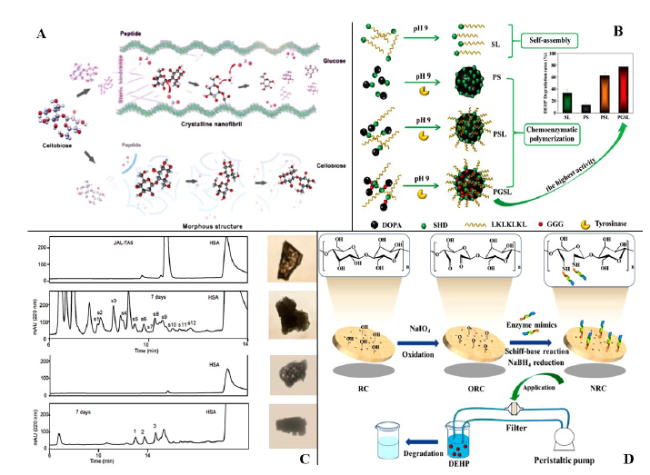
| GO-PNFs | Nanofiber | Cellobiose Cellopentose | 7.0 | 30 | 48 h | 280.19 μmol/h/mg 69.18 μmol/h/mg | Glu | — | 29 | ||
| PNF 1 PNF 2 PNF 3 PNF 4 | Nanofiber | Cellobiose | 5.0 7.0 | 30 30 | 48 h | 0.27 mM 0.57 mM 0.36 mM 1.18 mM | Glu | Fmoc-IEIEIEI-CONH2 Fmoc-IIIIEEE-CONH2 Fmoc-AEAEAEA-CONH2 Fmoc-AAAAEEE-CONH2 | 29 | ||
| Glu/CNTs | Nanotube | Sucrose、 Lactose、 Maltose、 Cellobiose | 3.5~4.5 | 25 | 24 h | < 6.00 μg/mL | Glu、Asp | — | 79 | ||
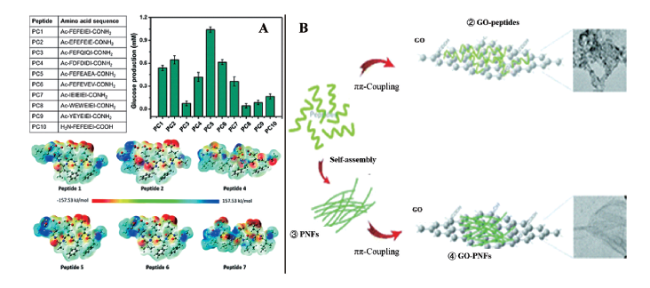
| PC1 PC2 PC4 PC5 PC6 PC7 | Nanofiber | Cellobiose | 3.0 | 25 | 24 h | 0.54 mM 0.64 mM 0.42 mM 1.04 mM 0.61 mM 0.36 mM | Glu | Ac-FEFEIEI-CONH2 Ac-EFEFEIE-CONH2 Ac-FDFDIDI-CONH2 Ac-FEFEAEA-CONH2 Ac-FEFEVEV-CONH2 Ac-IEIEIEI-CONH2 | 70 | ||
| [GADV]-P30 | Peptide mixture | MetU-Gal | — | 37 | 6 days | — | — | — | 58 | ||
3.1 酯键水解模拟酶
3.1.1 组氨酸为活性中心构建肽基模拟酶
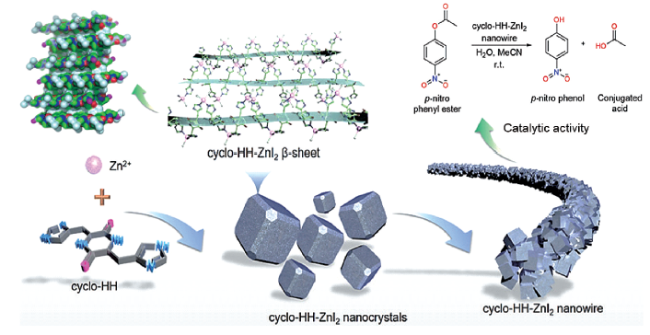
3.1.2 小分子肽结合金属离子构建肽基模拟酶
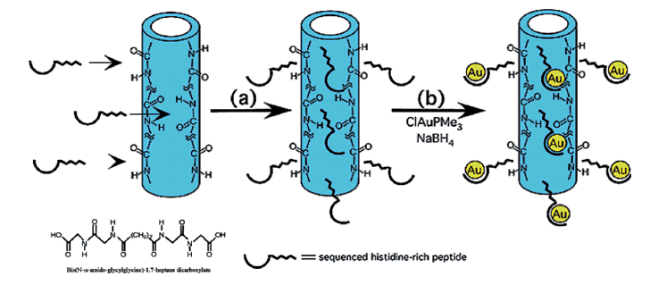
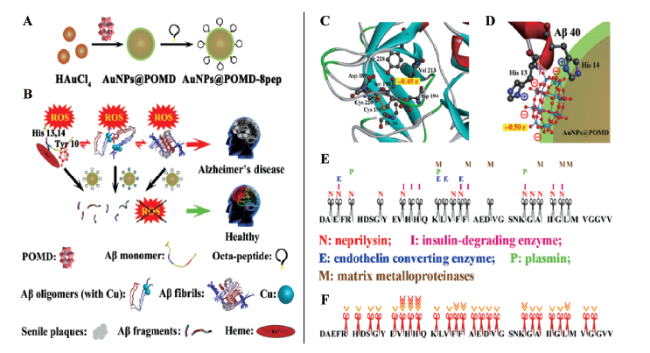
3.1.3 小分子肽结合金纳米颗粒构建肽基模拟酶
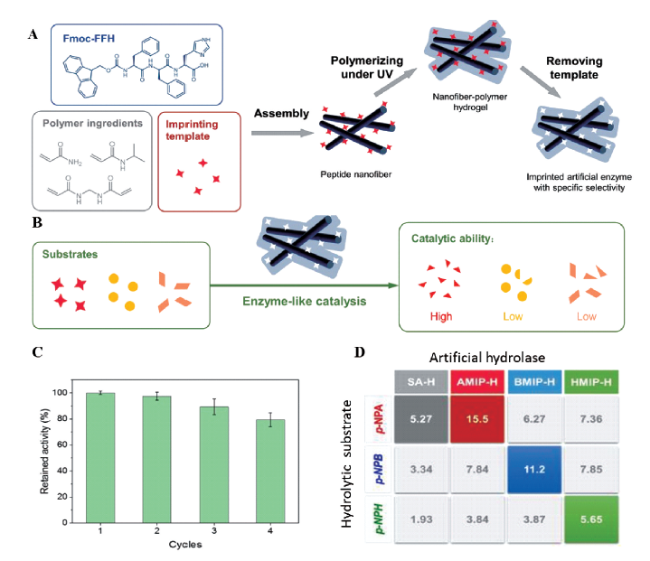
3.1.4 分子印迹法构建肽基模拟酶
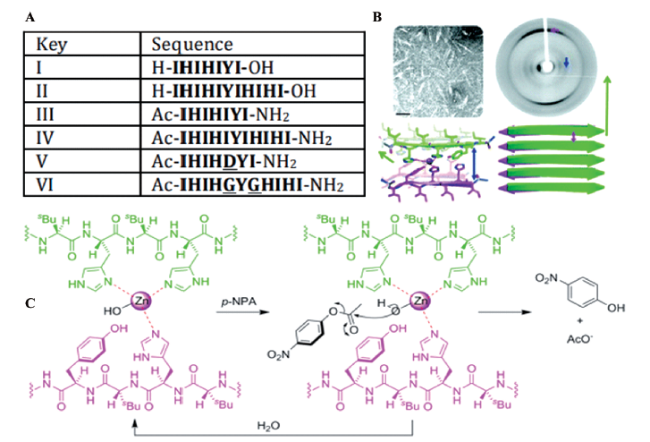
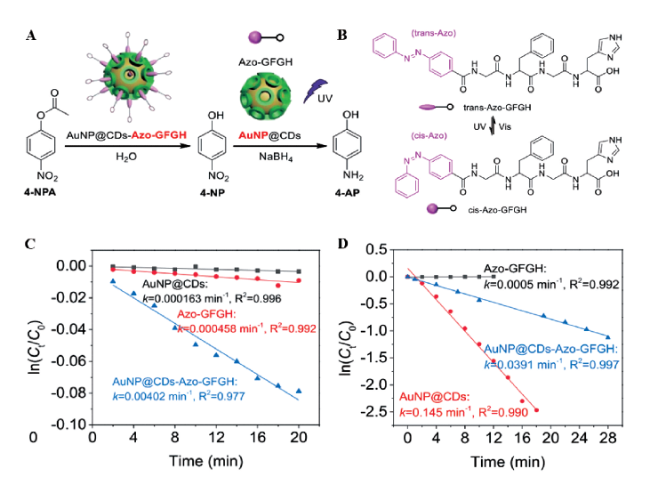
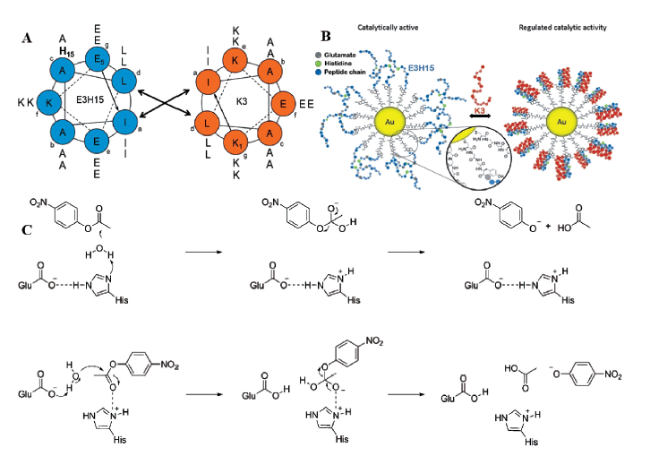
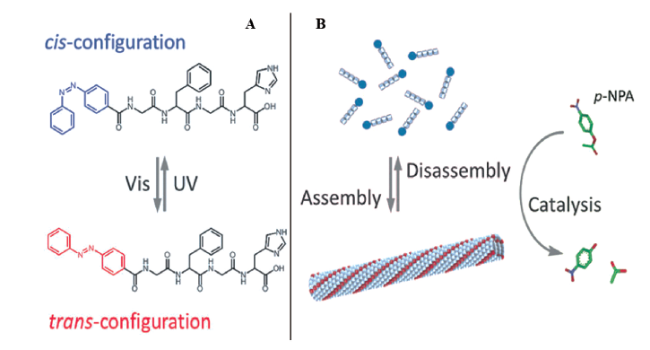
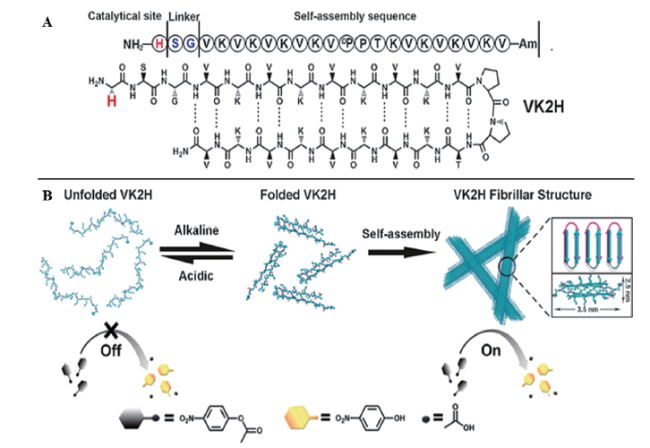
3.1.5 催化活性可调节肽基模拟酶
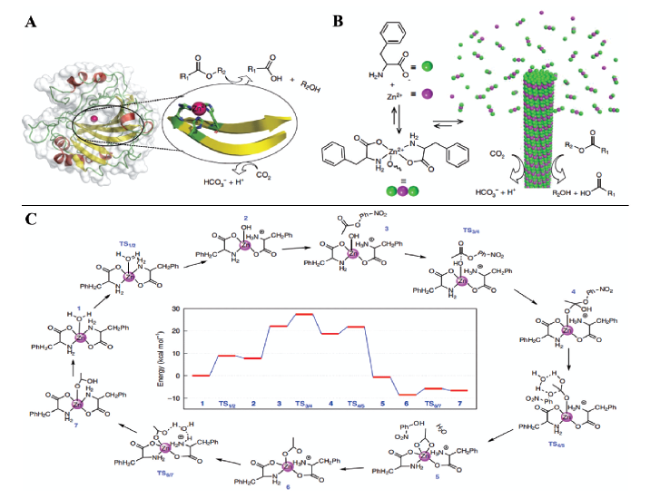
3.1.6 单一氨基酸自组装构建肽基模拟酶
图12 单个苯丙氨酸与锌离子通过自组装形成酯键降解模拟酶;(A) 天然碳酸酐酶;(B) 苯丙氨酸模拟酶催化过程;(C) 苯丙氨酸模拟酶催化机理[50]Fig. 12 Single phenylalanine and zinc ions form an ester bond degradation artificial enzyme by self-assembly. (A) Natural carbonic anhydrase; (B) phenylalanine artificial enzyme catalytic process; (C) phenylalanine artificial enzyme catalytic mechanism[50] |