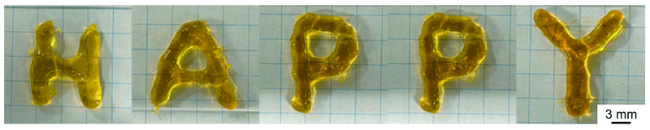
1 引言
图1 (a) 由聚四氟乙烯粉末制备的液体弹珠[38];(b) 利用界面颗粒堵塞得到的非球形气泡 (i) 和油滴 (ii)[41];(c) 利用液体弹珠凝并得到的哑铃形液体橡皮泥[42];(d) 利用镀膜工具挤压液滴得到的液体橡皮泥[43];(e) 诱导液体橡皮泥凝并的过程;(f) 基于多重凝并拼接而得到的复杂形状液体橡皮泥[44]Fig. 1 (a) Image of a polytetrafluoroethylene LM[38]; (b) Non-spherical bubble (i) and oil droplet-in-water (ii) obtained by interfacial jamming[41]; (c) A dumbbell-shaped LP produced by coalescing two LMs[42]; (d) LPs produced by squeezing particles onto droplet surfaces[43]; (e) A typical process for coalescing two LPs; (f) Demonstration of LPs produced by the coalescence-based joining strategy[44] |
2 单层纳米颗粒结构(mNPc)液体橡皮泥
2.1 单层纳米颗粒覆盖的液面
2.2 mNPc液体橡皮泥的制备及原理
图3 (a)通过局部挤压使液体橡皮泥进一步形变的过程;(b) 经多次挤压、摩擦而得到的典型液体橡皮泥[43];(c) 挤压液滴引起的单层颗粒转移以及界面堵塞示意图;(d)利用激光共聚焦技术观察到的液体橡皮泥表面,其中蓝色部分为颗粒;(e) 液体表面两个颗粒之间的相互作用能与颗粒间距的关系,其中α = h/2r; (f) 注液、抽液引起的液滴形态演变[44]。Fig. 3 (a) Shaping a LP by local squeezing; (b) Typical LPs obtained by multiple squeezing and rubbing[43]; (c) Schematic of transfer and jamming of monolayer NPs by squeezing; (d) Laser confocal image of a LP surface with the blue areas representing NPs. (e) Interaction energy between two NPs on liquid surface versus their distance, where α = h/2r; (f) Liquid addition and extraction-induced evolutions of droplet shape[44] |
图4 (a) 液饼表面堵塞前后形态变化;五角星形液体橡皮泥制备过程示意图 (b) 及产品实物图 (c);(d) 环形液体橡皮泥在加液过程中的形态演变;(e) 复杂汉字型液体橡皮泥;(f) 由若干个堵塞态液饼拼接得到的超大尺寸液饼 (i),以及通过对该液饼塑形得到的管道网络型液体橡皮泥 (ii)[45]Fig. 4 (a) Shape change of a liquid pancake induced by surface jamming; Schematic illustrating the cutting strategy for liquid shaping (b) and real image of a star-shaped LP (c); (d) Shape evolution of a ring-shaped LP during liquid addition; (e) A Chinese character dragon-shaped LP; (f) A large pancake produced by joining several jammed pancakes (i), and the resulting network-shaped LP (ii)[45] |
2.3 mNPc液体橡皮泥的应用
2.3.1 纳米金的电泳
2.3.2 低速化学微反应器
2.3.3 多功能气体传感器
图7 (a) 由酚酞溶液制成的条形液体橡皮泥;(b) 加入氨水液滴后的最终现象;(c) 不同氨水体积条件下液体橡皮泥颜色随氨气挥发时间的演变;(d) 颜色前沿的行进速度;(e) 氨气扩散速度拟合曲线及拟合得到的扩散前沿浓度c0[46]Fig. 7 (a) Rod-shaped mNPc LP consisting of phenolphthalein; (b) The final phenomenon after introducing an ammonia droplet; (c) The color evolution of the LP versus the volatilization time of ammonia gas; (d) The forward velocity of the color frontier; (e) The fitting curve of velocity and the fitted gas concentration at the color frontier[46] |
2.3.4 蛋白质分离、分析平台
图8 (a) 液体橡皮泥-等电聚焦蛋白分析系统;(b) 蛋白分离示意图;(c) 蛋白分离后成像时的颜色分布;(d) 切割液体橡皮泥得到液体弹珠以及从液体弹珠中加入或提取物质的实例[47]Fig. 8 (a) LP-Isoelectrofocusing (IEF) system for protein analysis; (b) Schematic for protein separation; (c) Color distribution after protein separation; (d) LP-derived LMs and available manipulations for subsequent analysis[47] |
3 其他类型液体橡皮泥
3.1 纳米级粉末颗粒包裹的液体橡皮泥
3.2 单层毫米级多边形薄片包裹的液体橡皮泥
图10 由毫米级反光薄片制得的 (a) 多面体液体弹珠和 (b) 液体橡皮泥;(c) 利用透明薄片制成的液体橡皮泥[52];(d) 不同尺寸薄片(i: 2 mm, ii: 1 mm, iii: 0.2 mm)对应的转角结构实例[53]Fig. 10 Polyhedral LMs (a) and LP (b) produced with mm-sized hydrophobic sheets; (c) LPs produced with transparent sheets[52]; (d) Illustration of the angular parts of LPs with different sheet sizes (i: 2 mm, ii: 1 mm, iii: 0.2 mm)[53] |
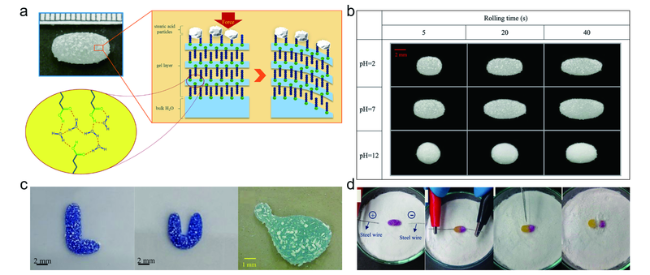
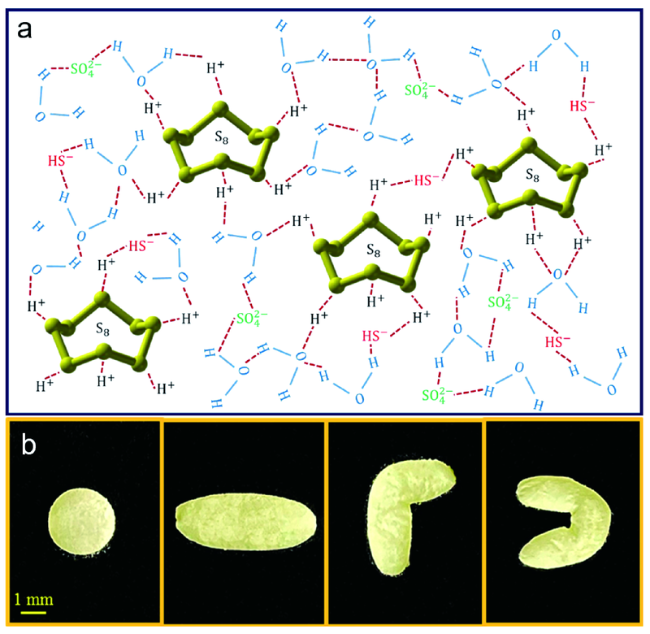
3.3 硬脂酸粉末颗粒包裹的液体橡皮泥
图11 (a) 液滴在硬脂酸粉末上滚动后的形态及表面凝胶化示意图;(b) pH值、体积、滚动时间对液滴滚动后形态的影响;(c) 复杂形状硬脂酸液体橡皮泥;(d) 利用液体橡皮泥的管道结构和可分割性获得不同颜色液体弹珠的过程[50]Fig. 11 (a) Image of a LP formed by rolling a droplet on the stearic acid powder and the schematic depicting the surface gelation mechanism; (b) Liquid shapes under different pH values, volumes, and rolling durations; (c) Stearic acid LPs with complex shapes; (d) A process for getting two LMs with different colors, based on the channel structure and the cuttable property of the LP[50] |