1 引言
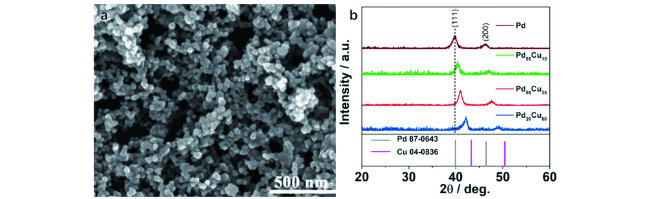
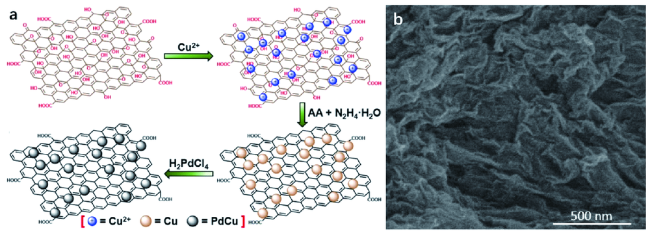
2 钯铜纳米电催化剂的结构及制备方法
2.1 多孔纳米结构
2.2 枝状纳米结构
2.3 中空结构纳米笼
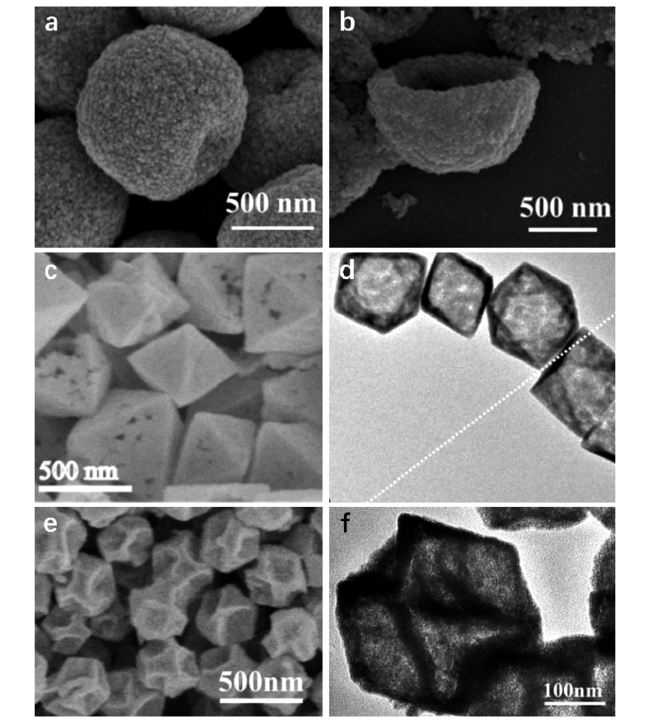
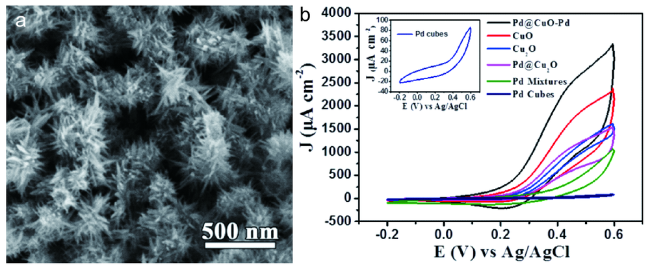
图5 (a)苹果状、(b)碗状PdCu合金空心微粒SEM图像[13];多孔八面体PdCu纳米笼的(c)SEM与(d)TEM图像[32];PdCu花状合金纳米笼的(e)SEM与(f)TEM图像[33]Fig. 5 SEM images of apple-like (a), bowl-like (b) PdCu alloy hollow microparticles[13]. SEM (c) and TEM (d) images of porous octahedral PdCu nanocages[32]. SEM (e) and TEM (f) images of PdCu alloy flower-like Nanocages[33] |
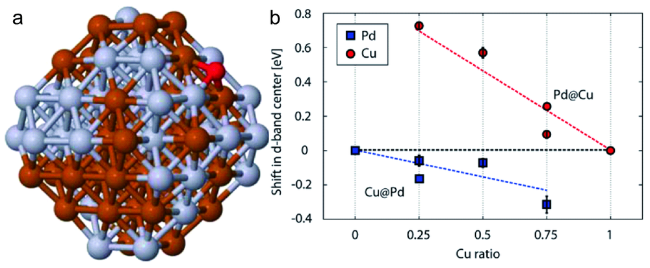
2.4 核壳纳米结构
2.5 球形纳米合金颗粒
2.6 钯铜单原子分散电催化剂
3 钯铜纳米电催化剂在有机小分子氧化反应中的应用
3.1 甲醇氧化反应(MOR)
图9 (a)直接甲醇燃料电池结构示意图[9];不同原子比例IL/PdCu和Pd/C在1 mol/L KOH和1 mol/L甲醇中的(b)循环伏安(CV)曲线、(c)比活性和质量活性直方图[9]Fig. 9 (a) Schematic illustration of direct methanol fuel cell[9]; CV curves (b) and histogram of specific and mass activities (c) of IL/PdCu and Pd/C with different atomic ratios in 1 mol/L KOH containing 1 mol/L methanol[9] |
3.2 乙醇氧化反应(EOR)
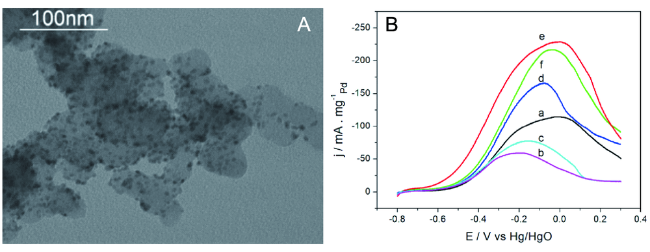
图10 (A)富氧化物Pd0.9Cu0.1/C的TEM图像;(B)在1 M乙醇、1 M氢氧化钠溶液中,使用10 mV/s扫描速率测得的LSV曲线,(a) Pd/C 、(b) 富氧化物Pd0.6Cu0.4/C 、(c) 富氧化物Pd0.7Cu0.3/C、(d) 富氧化物Pd0.8Cu0.2/C、 (e) 富氧化物Pd0.9Cu0.1/C、(f) 富氧化物Pd0.95Cu0.05/C[50]Fig. 10 (A) TEM image of oxide-rich Pd0.9Cu0.1/C. (B) Linear sweep voltammetry (LSV) curves of: (a) Pd/C; (b) oxide-rich Pd0.6Cu0.4/C; (c) oxide-rich Pd0.7Cu0.3/C; (d) oxide-rich Pd0.8Cu0.2/C; (e) oxide-rich Pd0.9Cu0.1/C; and (f) oxide-rich Pd0.95Cu0.05/C in deaerated 1 M NaOH containing 1 M C2H5OH. Scan rate: 10 mV/s[50] |
3.3 甲酸氧化(FAOR)
3.4 葡萄糖氧化
4 钯铜纳米电催化剂在无机小分子还原反应中的应用
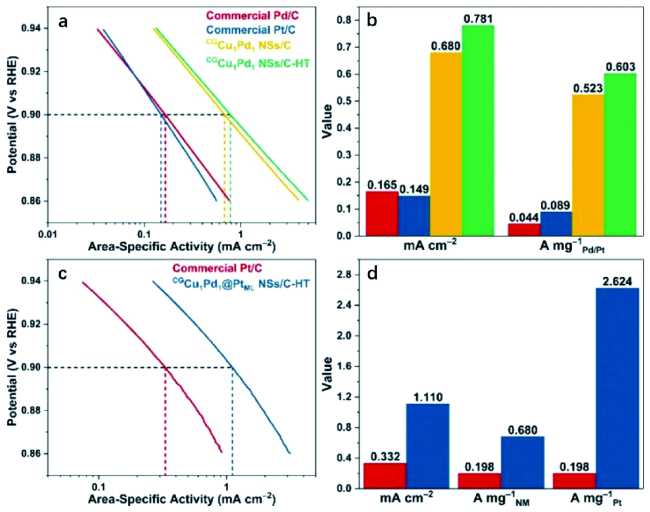
4.1 氧还原反应(ORR)
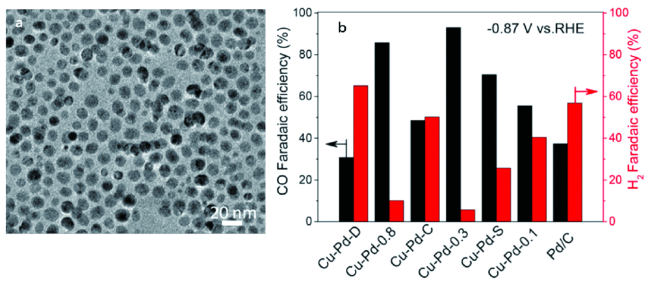
4.2 CO2电化学还原反应
4.3 N2还原制氨、一氧化二氮还原及电解水析氢反应(HER)
图18 PdCu/NC的(a)原子分辨率HAADF-STEM图像;(b)a中黄框区域的放大图像;PdCu/NC、Pd/NC和Cu/NC的(c)NH3产率和(d)法拉第效率[46]Fig. 18 (a) Atomic-resolution HAADF-STEM image; (b) Magnified atomic-resolution HAADF-STEM image of the yellow-frame area in (a). NH3 yield rates (c) and Faradaic efficiencies (d) of PdCu/NC, Pd/NC and Cu/NC[46] |