1 引言
2 MXenes的制备
表1 常见的二维MXenes制备工艺条件Table 1 The preparation process conditions for common 2D MXenes |
| Precursor | MXenes | Etchant | Concentration | T ( ℃) | Time (h) | Yield | ref | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ti2AlC | Ti2CTx | HF | 10 wt% | RT | 10 | 60% | 30 | |
| V2AlC | V2CTx | HF | 50 wt% | RT | 90 | 60% | 31 | |
| Nb2AlC | Nb2CTx | HF | 40 wt% | 60 | 72 | NA | 32 | |
| Mo2Ga2C | Mo2CTx | HF | 48wt%~51 wt% | 55 | 160 | NA | 33 | |
| Mo2Ga2C | Mo2CTx | HF | 48 wt% | 140 | 96 | NA | 34 | |
| Ti2AlN | Ti2NTx | HF | 5 wt% | RT | 24 | NA | 17 | |
| Ti3AlC2 | Ti3C2Tx | HF | 10 wt% | RT | 24 | NA | 35 | |
| Ti3AlC2 | Ti3C2Tx | HF | 50 wt% | RT | 2 | 100% | 23,30 | |
| Ti3AlCN | Ti3CNTx | HF | 30 wt% | RT | 18 | 80% | 30 | |
| Zr3Al3C5 | Zr3C2Tx | HF | 50 wt% | RT | 60 | NA | 36 | |
| Hf3Al(Si)4C6 | Hf3C2Tx | HF | 35 wt% | RT | 60 | 73% | 37 | |
| Mo2TiAlC2 | Mo2TiC2Tx | HF | 50 wt% | RT | 48 | 100% | 38 | |
| Mo2ScAlC2 | (Mo2Sc)C2Tx | HF | 48 wt% | 50 | 16 | NA | 39 | |
| V4AlC3 | V4C3Tx | HF | 40 wt% | RT | 165 | NA | 40 | |
| Nb4AlC3 | Nb4C3Tx | HF | 50 wt% | RT | 96 | 77% | 41 | |
| Ta4AlC3 | Ta4C3Tx | HF | 50 wt% | RT | 72 | 90% | 30 | |
| Mo2Ti2AlC3 | Mo2Ti2C3Tx | HF | 50 wt% | 55 | 90 | 100% | 38 | |
| Ti2AlN | Ti2NTx | HCl-KF | 6 M HCl-7.0 mol KF | 40 | 1 | 87% | 17 | |
| V2AlC | V2CTx | HCl-NaF | 12 M HCl-3.4 mol NaF | 90 | 72 | > 90% | 42 | |
| Nb2AlC | Nb2CTx | HCl-NaBF4 | 12 M HCl-3.1 mol NaBF4 | 180 | 20 | NA | 32 | |
| Mo2Ga2C | Mo2CTx | HCl-LiF | 12 M HCl-3 mol LiF | 35 | 384 | NA | 43 | |
| Ti3AlCN | Ti3CNTx | HCl-LiF | 6 M HCl-7.5 mol LiF | 30 | 12 | NA | 44 | |
| Cr2TiAlC2 | Cr2TiC2Tx | HCl-LiF | 6 M HCl-5 mol LiF | 55 | 42 | 80% | 38 | |
| Ti3AlC2 | Ti3C2Tx | HCl-LiF | 6 M HCl-5 mol LiF | 35 | 24 | NA | 45 | |
| Ti3AlC2 | Ti3C2Tx | HCl-LiF | 6 M HCl-7.5 mol LiF | 35 | 24 | NA | 45 | |
| Ti3AlC2 | Ti3C2Tx | HCl-LiF | 9 M HCl-7.5 mol LiF | 35 | 24 | NA | 46 | |
| Ti3AlC2 | Ti3C2Tx | HCl-LiF | 9 M HCl-5 mol LiF | 35 | 24 | NA | 47 | |
| Ti3AlC2 | Ti3C2Tx | HCl-LiF | 6 M HCl-10 mol LiF | 35 | 24 | NA | 48 | |
| Ti3AlC2 | Ti3C2Tx | HCl-LiF | 9 M HCl-12 mol LiF | 35 | 24 | NA | 14 | |
| Ti3AlC2 | Ti3C2Tx | HCl-NaBF4 | 12 M HCl-5.3 mol NaBF4 | 180 | 16 | NA | 32 | |
| Ti3AlC2 | Ti3C2Tx | NaHF2, KHF2, NH4HF2 | 1 M | 60 | 8 | NA | 49,50 | |
| Ti4AlN3 | Ti4N3Tx | KF-LiF-NaF | 59 wt% KF + 29 wt% LiF + 12 wt% NaF | 550 | 0.5 | NA | 51 | |
| Ti3AlC2 | Ti3C2Tx | NaOH | 27.5 M | 270 | 12 | 92% | 52 | |
| Ti3AlC2 | Ti3C2Tx | NH4Cl-TMA·OH | 1 M NH4Cl + 0.2 M TMA·OH | RT | NA | > 90% | 53 | |
| Precursor | MXenes | Etchant | Concentration | T ( ℃) | Time (h) | Yield | ref | |
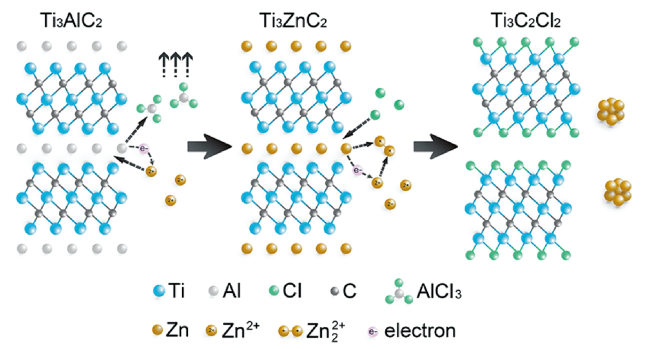
| Ti3AlC2,Ti2AlC, Ti2AlN, V2AlC | Ti3C2Cl2, Ti2CCl2, Ti2NCl2, V2CCl2 | ZnCl2 | MAX:ZnCl2 = 1:6 (molar ratio) | 550 | 5 | NA | 54 | |
| Ti3SiC2 | Ti3C2Cl2 | CuCl2 | MAX:CuCl2 = 1:3 (molar ratio) | 750 | 24 | NA | 55 | |
| Ti2AlC | Ti2CCl2 | CdCl2 | MAX:CdCl2 = 1:3 (molar ratio) | 650 | - | NA | ||
| Ta2AlC, Nb2AlC | Ta2CCl2, Nb2CCl2 | AgCl | MAX:AgCl = 1:5 (molar ratio) | 700 | - | NA | ||
| Ti3AlC2, Ti3ZnC2 | Ti3C2Cl2 | FeCl2, CoCl2, NiCl2, CuCl2, | MAX :Salt = 1:3 (molar ratio) | 700 | - | NA | ||
| Ti3AlC2 | Ti3C2I, Ti3C2Br2 | CuI, CuBr2 | MAX:Salt = 1:6, 1:4 (molar ratio) | 700 | - | NA | ||
(NA:对应的文献报道未给出MXenes的产率) |
2.1 含氟刻蚀剂制备MXenes
图2 (a) Ti3AlC2 MAX相被HF刻蚀前后(i, ii)以及剥离后Ti3C2Tx MXene纳米片(iii)的XRD图谱[23];(b)Ti3AlC2刻蚀前的SEM照片[30];(c)HF刻蚀Ti3AlC2后的SEM照片[30];(d)以HCl-LiF为蚀刻剂合成Ti3C2Tx MXene的两种不同的刻蚀路径[45];(e) Ti3AlC2和氟氢化物的反应机理图[49];(f)熔融氟盐刻蚀Ti4AlN3制备Ti4N3Tx的合成机理图[51]Fig.2 (a) XRD pattern for Ti3AlC2 MAX before (i) and after (ii) HF treatment, and the exfoliated Ti3C2Tx MXene nanosheets (iii)[23]; (b) SEM micrograph of Ti3AlC2 MAX before HF treatment[30]; (c) SEM micrograph of Ti3AlC2 MAX after HF treatment[30]; (d) Synthesis of Ti3C2Tx via two different routes using HCl-LiF as the etching solution[45]; (e) Schematic illustration of reaction between Ti3AlC2 and bifluorides[49]; (f) Schematic illustration of the synthesis of Ti4N3Tx by etching Ti4AlN3 in molten salts[51] |
2.2 无氟刻蚀剂制备MXenes
图3 (a)水热辅助碱刻蚀法制备无氟MXenes;(b)不同水热温度和NaOH浓度下合成产物Ti3C2Tx MXene的示意图(红圈:MXene;黑色方块:MAX;蓝色三角形:钛酸钠(NTOs))[52]Fig.3 (a) Hydrothermal method in alkali for fluorine-free MXenes; (b) Formation of Ti3C2Tx MXene under various hydrothermal temperatures and NaOH concentrations (Red circles: MXene; black squares: MAX; blue triangles: sodium titanate (NTOs))[52] |
表2 不同刻蚀方法制备MXenes的优缺点对比Table 2 Advantages and disadvantages comparison of MXenes prepared by different etching methods |
| Etching method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| HF etching | A simple and universal method | High danger and toxicity |
| Fluoride salts and acids in-situ formed HF | A simple and universal method | High danger and toxicity |
| Bifluoride etching | Simple and controllable process | Danger and toxicity, and only for the synthesis of Ti3C2Tx MXene |
| Molten fluoride salts etching | Simple process | Only for the synthesis of Ti4N3Tx MXene, and easy to corrode equipment at high temperature |
| Alkali etching | Fluoride-free | Complex operation conditions and only for the synthesis of Ti3C2Tx MXene |
| Electrochemical etching | Fluoride-free | Complex and uncontrollable operation conditions, and easily over-etching to produce carbide-derived carbon (CDC) |
| Lewis acidic etching | A simple, fluoride-free and universal method | Many MXenes are still in the theoretical calculations |
3 MXenes的结构调控
3.1 MXenes的层间距调控
表3 不同插层剂作用后Ti3C2Tx晶格常数c的对比Table 3 The comparison of lattice parameter (c) of Ti3C2Tx via different intercalations |
| MXenes | Etchant | Intercalation agents | c-Lattice parameter(c-LP) | ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ti3C2Tx | 50 wt% HF | - | 19.50 ± 0.10 Å | 70 |
| Ti3C2Tx | 50 wt% HF | N2H4·H2O (HM) | 25.48 ± 0.02 Å | 70 |
| Ti3C2Tx | 50 wt% HF | Urea | 25.00 ± 0.02 Å | 70 |
| Ti3C2Tx | 50 wt% HF | DMSO | 35.04 ± 0.02 Å | 70 |
| Ti3C2Tx | 50 wt% HF | HM-DMF | 26.8 ± 0.10 Å | 70 |
| Ti3C2Tx | 1 M NH4Cl-0.2 M TMA·OH | TMAOH | 22.60 Å | 53 |
| Ti3C2Tx | 50 wt% HF | - | 20.30 Å | 76 |
| Ti3C2Tx | 50 wt% HF | LiOAc | 24.50 Å | 76 |
| Ti3C2Tx | 50 wt% HF | NaOH | 25.10 Å | 76 |
| Ti3C2Tx | 50 wt% HF | KOH | 25.40 Å | 76 |
| Ti3C2Tx | 50 wt% HF | Na2SO4 | 21.0 Å | 76 |
| Ti3C2Tx | 50 wt% HF | K2SO4 | 21.40 Å | 76 |
| Ti3C2Tx | 50 wt% HF | MgSO4 | 21.30 Å | 76 |
| Ti3C2Tx | 50 wt% HF | ZnSO4 | 21.70 Å | 76 |
| Ti3C2Tx | 50 wt% HF | NH4OH | 25.30 Å | 76 |
| Ti3C2Tx | 40 wt% HF | LiOH | 25.00 Å | 77 |
| Ti3C2Tx | 40 wt% HF | LiOH/SnCl4 | 25.20 Å | 77 |
| Ti3C2Tx | 6 M HCl-5 M LiF | - | 27.0~28.0 Å | 80 |
| Ti3C2Tx | HCl-LiF | - | 22.60 Å | 81 |
| Ti3C2Tx | 1 M NH4HF2 | - | 24.80~24.90Å | 49,50 |
| Ti3C2Tx | 1 M NaHF2 | - | 21.40 Å | 49 |
| Ti3C2Tx | 1 M KHF2 | - | 24.80 Å | 49 |
| Ti3C2Tx | NaOH | - | 24.0 Å | 52 |
| Ti3C2Tx | ZnCl2 | - | 22.24 Å | 54 |
图6 (a) TMA·OH插入Ti3C2Tx层间示意图[74];(b)阳离子插层Ti3C2Tx MXenes示意图[79];(c)阳离子插层和离子交换法改性MXene[78]:(i) V2AlC的蚀刻和阳离子插层示意图,(ii) V2AlC、(iii) V2CTx、(iv)碱化后V2CTx和(v) Ca2+插层后的V2CTx对应的(002)面XRD衍射峰和SEM图像;(d) MXene纳米片(i, ii)、真空干燥的致密MXene (D-MF)膜(iii)、冷冻干燥的三维多孔MXene (3D-PMF)膜(iv)和冷冻干燥的三维多孔MXene/碳纳米管(3D-PMCF)膜(v)的制备流程图,以及(vi)三种膜对应的XRD图谱[86]Fig.6 (a) Schematic illustration of the intercalation of TMA·OH between Ti3C2Tx layers[74]; (b) Schematic illustration of cation-intercalated Ti3C2Tx MXenes[79]; (c) Modified MXene by the cation intercalation and ion-exchange method[78]: (i) schematic illustration of the etching process of V2AlC and the cation intercalation behaviors, the corresponding (002) diffraction peaks of XRD and the SEM images of (ii) V2AlC, (iii) V2CTx, (iv) alkalizated V2CTx, and (v) V2CTx after Ca2+ intercalation; (d) Schematic illustration of the fabrication process of MXene nanosheets (i, ii), vacuum-dried dense MXene (D-MF) film (iii), freeze-dried porous MXene (3D-PMF) film (iv), and freeze-dried 3D porous MXene/CNTs (3D-PMCF) film (v), and (vi) XRD patterns corresponding to the three films[86] |
3.2 MXenes表面基团调控
表4 MXenes的表面基团调控方法Table 4 Summary of surface termination regulation methods for MXenes |
| MXenes | Etching method | Before regulation | Regulation methods | After regulation | ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ti2CTx | HF etching | —F、—OH and —O | Annealing treatment at 1100 ℃ in Ar/H2 atmosphere | Lots of —O groups and few -OH groups | 100 |
| Ti3C2Tx | - | —F、—OH and —O | KOH treatment | Lots of —O groups and few —F and —OH groups | 98 |
| Ti3C2Tx | - | —F、—OH and —O | KOAc treatment | Lots of —O groups and few —F and —OH groups | 98 |
| Ti3C2Tx | HF etching | —F、—OH and —O | NaOH treatment and then calcined at 600 ℃ under vacuum | Lots of —O groups and —OH groups | 104 |
| Ti3C2Tx | HF etching | —F、—OH and —O | NaOH treatment and then calcined at 550 ℃ under vacuum | Lots of —O groups and few —F and —OH groups | 105 |
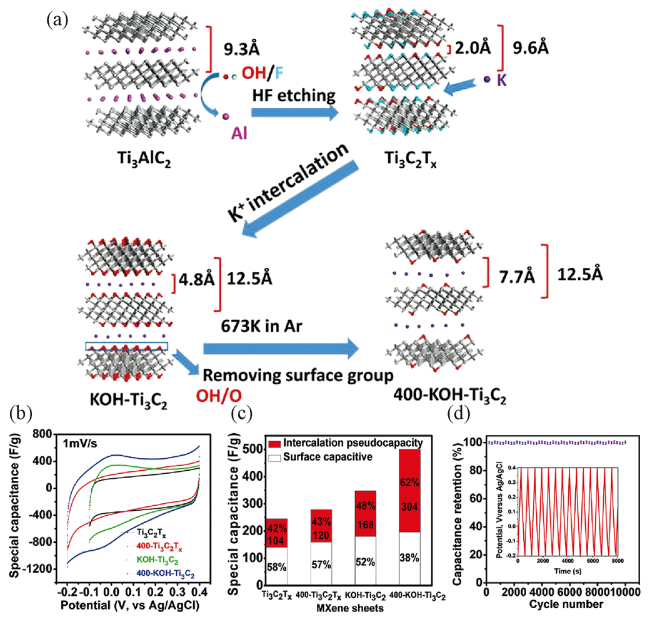
| Ti3C2Tx | HF etching | —F、—OH and —O | KOH treatment and then calcined at 400 ℃ in Ar atmosphere | Lots of —O groups and few —F and —OH groups | 101 |
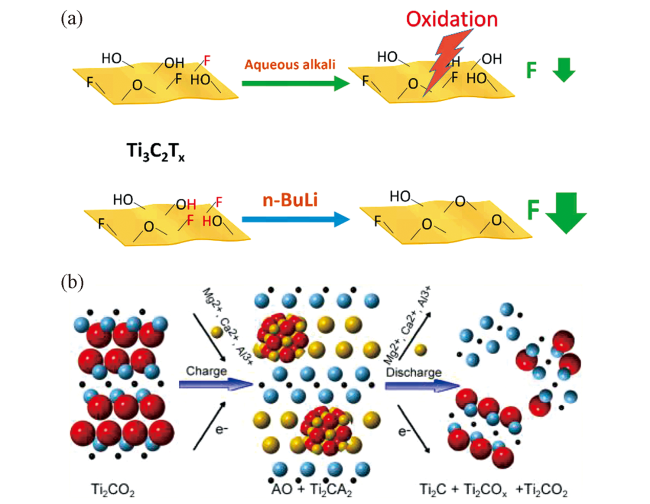
| Ti3C2Tx | HF etching | —F、—OH and —O | n-butyllithium | Lots of —O groups and few —F groups | 46 |
| Ti3C2Tx, Ti2CTx, Nb2CTx | Lewis acidic etching | —Br | Li2Te | —Te | 103 |
| —Cl | Li2O | —O | |||
| —Br | Li2S | —S | |||
| —Cl | NaNH2 | —NH | |||
| —Br | LiH | Bare MXene |
4 MXenes在电化学储能中的应用
4.1 超级电容器
图8 (a) K+插层和表面基团改性Ti3C2Tx MXene原理图;(b) 1 M H2SO4中,不同MXene基电极在1 mV·s-1扫描速率下的循环伏安曲线;(c) 1 mV·s-1的扫描速率时,不同MXene基材料的插层赝电容和表面电容的贡献量;(d) 400-KOH-Ti3C2电极在1M H2SO4中的容量保持率测试,插图对应1 A·g-1电流密度下的恒流充放电图[101]Fig.8 (a) Schematic of K+ intercalation with surface terminations to modify Ti3C2Tx; (b) cycle voltammetry profiles at 1 mV·s-1 for different MXene-based electrodes in 1 M H2SO4; (c) Comparison of capacitance for MXene sheets (at scan rate of 1 mV·s-1 ), the total capacitance is separated into intercalation pseudocapacity and surface capacitive contributions; (d) capacitance retention test of 400-KOH-Ti3C2 electrode in 1 M H2SO4, inset shows galvanostatic cycling data collected 1 A·g-1[101] |
4.2 锂离子电池
图9 (a) PVP-Sn(IV)@Ti3C2纳米复合材料的制备工艺示意图;(b) PVP-Sn(Ⅳ)@Ti3C2电极在216.5 mA·cm-3 (0.1 A· ) 电流密度下的充放电曲线;(c)不同电极在216.5 mA·cm-3 (0.1 A·g-1)电流密度下的循环性能和库仑效率;(d) PVP-Sn(IV)@Ti3C2电极的倍率性能[77]Fig.9 (a) Schematic illustration of the fabrication process of PVP-Sn(Ⅳ)@Ti3C2 nanocomposites; (b) Charge-discharge profiles of the PVP-Sn(Ⅳ)@Ti3C2 electrode at different cycles with a current density of 216.5 mA·c (0.1 A· ); (c) Cycling performance and Coulombic efficiency of different electrodes at a current density of 216.5 mA·c (0.1 A·g-1); (d) Rate performance of the PVP-Sn(Ⅳ)@Ti3C2 electrode[77] |
4.3 其他金属离子电池
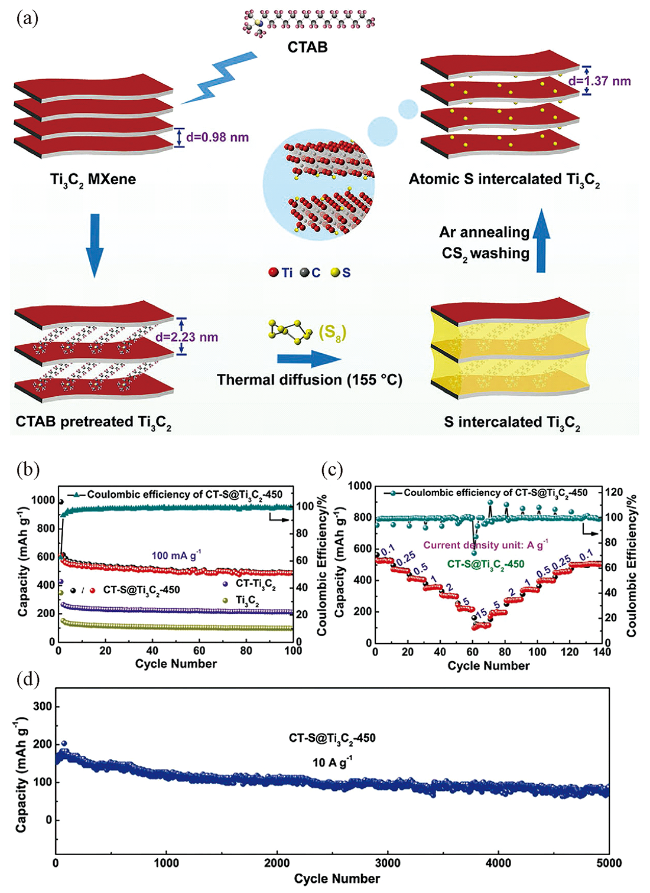
图10 (a) S原子嵌入Ti3C2 MXene的合成示意图;(b) Ti3C2、CTAB处理的Ti3C2 (CT-Ti3C2)和CTAB处理后再经450 ℃热处理S原子插层的Ti3C2 (CT-S@Ti3C2-450)电极在0.1 A·g-1电流密度下的循环性能;(c) CT-S@Ti3C2-450在不同电流密度下的速率性能;(d) CT-S@Ti3C2-450电极在10 A·g-1电流密度下的长循环性能[125]Fig.10 (a) Schematic illustration of the synthesis of S atoms intercalated Ti3C2 MXene; (b) The cycling performance of Ti3C2, CTAB-Ti3C2, and CTAB-S@Ti3C2-450 electrodes at a current density of 0.1 A·g-1; (c) Rate performance of CT-S@Ti3C2-450 at different current densities; (d) The long cycling performance of CT-S@Ti3C2-450 at a current density of 10 A·g-1[125] |