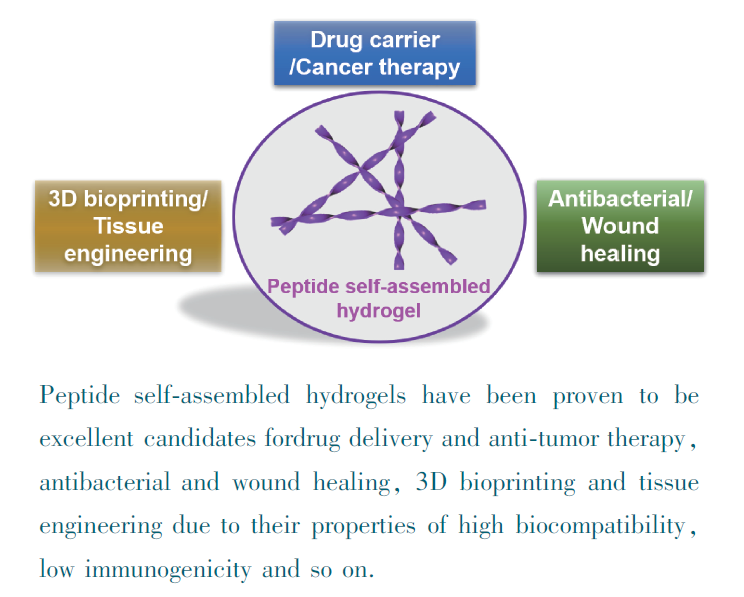
1 引言
2 肽组装水凝胶的制备方法
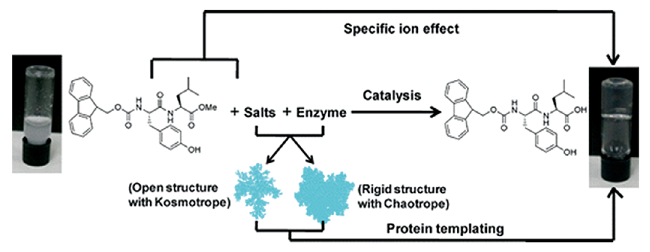
2.1 酶催化的肽自组装水凝胶
2.2 化学/物理交联水凝胶
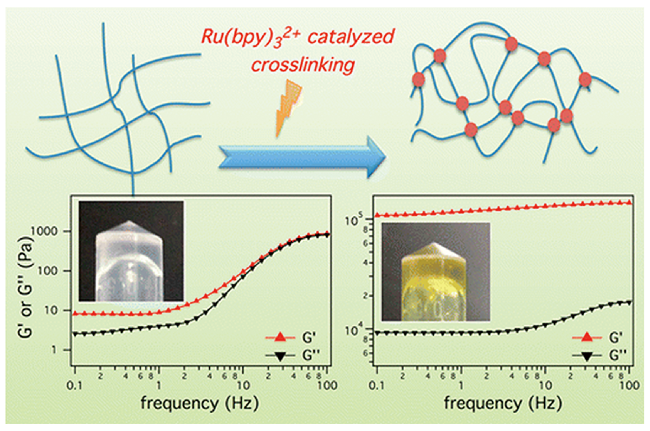
2.3 光催化交联的水凝胶
表1 肽自组装水凝胶制备方法汇总表Table 1 Summary table of preparation methods for self-assembled peptide hydrogels |
| Peptide molecular species | Crosslinking methods | ref |
|---|---|---|
| Fmoc-Phe /(Phe)2 | Thermolysin | 45 |
| Fmoc-YL-OMe | Subtilisin | 49 |
| Ac-YYYpY-OMe | Tyrosinase | 44 |
| CRB-GDFDFpDY | Alkaline phosphatase | 50 |
| Fmoc- (Phe)3 | Genipin | 52 |
| LIVAGKC | Cysteine disulfide bond | 53 |
| Nap-YYF | PEGMA | 54 |
| Fmoc-FF/PLL-SH | Disulfide bond | 56 |
| Short peptide hyaluronic acid complex | UV | 57 |
| YYAYY | White light | 60 |
| Fmoc-FFEEK(D)GGY | Visible light | 61,62 |
3 肽自组装水凝胶的生物学应用
3.1 药物递送和抗肿瘤治疗
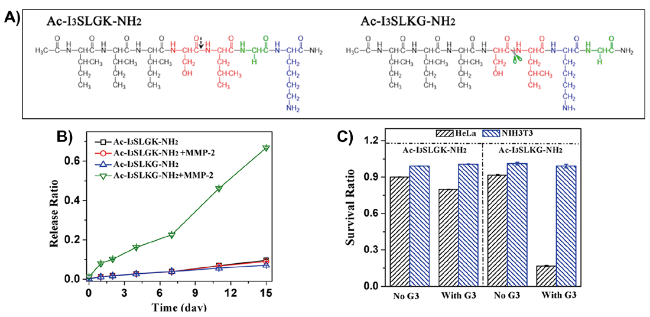
图4 A) 肽分子结构式;B) G3 (G(IIKK)3-NH2) 在含与不含MMP-2的Ac-I3SLGK-NH2凝胶中的释放情况;C) NIH 3T3 和 HeLa 细胞在负载和未负载 G3 的两种肽凝胶上孵育 24 h 后的存活率[65]Fig.4 A) Molecular structures of the designed peptides; B) G3 (G(IIKK)3-NH2) release from the G3-loaded Ac-I3SLGK-NH2+MMP2 and Ac-I3SLGK-NH2 gels in the presence and absence of MMP-2; C) Viability of NIH 3T3 and HeLa cells on the two peptide gels with and without G3 loading. After incubation for 24 h, the cell viability was determined by MTT assays[65] |
图5 A) 静电相互作用驱动的Fmoc-FF/PLL-SH共组装形成水凝胶的示意图; B) 在有或没有 Fmoc-FF/PLL-SH 水凝胶处理的情况下的肿瘤组织生长情况,其中插图为水凝胶植入12 天后切除的 B16 肿瘤组织的照片; C) 不同处理后 CD4+T/CD8+T 的比值[56]Fig.5 A) Schematic diagram of the formation of Fmoc-FF/PLL-SH hydrogels based on electrostatic interaction-triggered co-assembly; B) Suppression of tumor growth with or without Fmoc-FF/PLL-SH hydrogel treatment. Images of the excised B16 tumor tissues at 12 days post implantation (inset); C) The ratio of CD4+T/CD8+T after different treatment[56] |
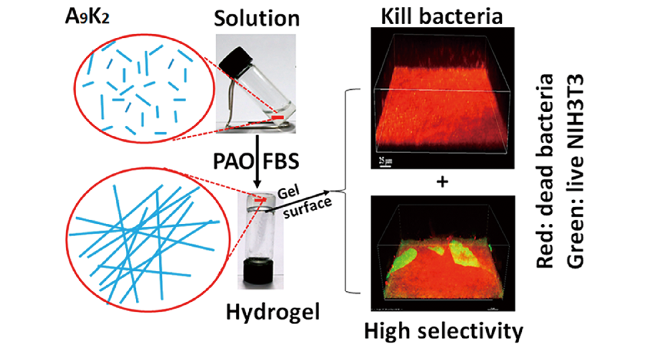
3.2 抗菌和伤口愈合
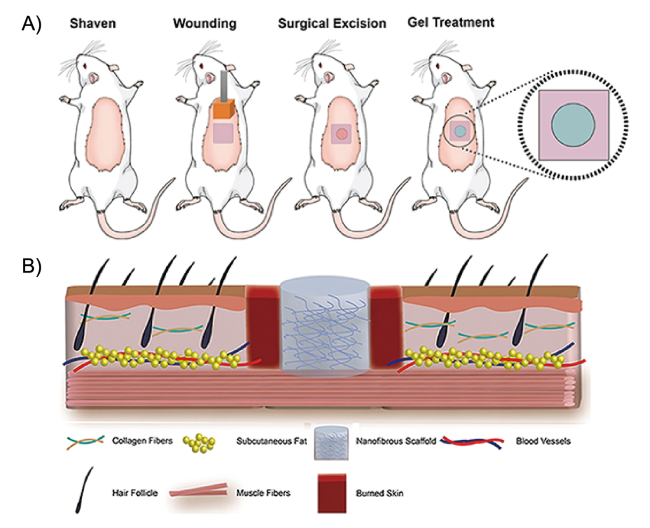
图7 全层烧伤模型示意图:A) 将预热的铝板涂在麻醉小鼠剃光的背上;然后去除受伤的皮肤并涂抹水凝胶; B) 水凝胶植入伤口部位的示意图[92]Fig.7 Schematic representation of the full-thickness burn wound model: A) A pre-heated aluminum plaque was applied to the shaved dorsum of the anesthetized mouse; followed by the removal of the injured skin and the application of the hydrogel. B) A schematic of the hydrogel-implanted wound site[92] |
3.3 3D打印与组织工程
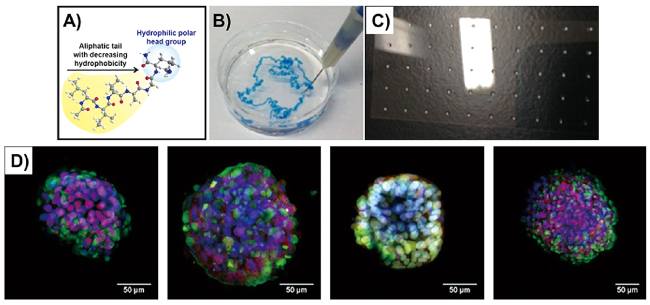
图8 A) 脂肪族超短肽的分子结构; B)肽自组装水凝胶可连续注射性能表征; C)通过连续沉积肽溶液和含有细胞和/或小分子的 PBS 缓冲液打印的液滴阵列;D)在水凝胶中培养人胚胎干细胞H1[96]Fig.8 A) Molecular structure of aliphatic ultrashort peptides; B) characterization of continuous injectable properties of peptide assembled hydrogel by extruding hydrogel into a concentrated salt bath; C) printed droplet arrays via sequential deposition of peptide and PBS containing cells and/or small molecules; D) Human H1 embryonic stem cells encapsulated in the hydrogels[96] |