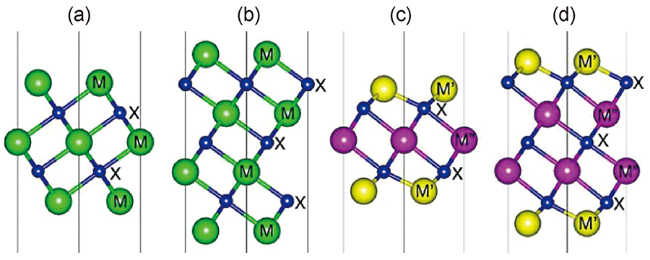
1 引言
2 MXenes的合成
表1 部分基于HF溶液刻蚀的MXenes 的制备反应条件Table 1 The preparation reaction conditions of HF etched MXenes were partly based on HF etched MXenes |
| Precursor type | Composition | Etching method | MXene | ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M2AX 211 | Ti2AlC | 10% conc.-10 h-RT | Ti2CTx | 49 |
| V2AlC | 50% conc.-90 h-RT | V2CTx | 53 | |
| Nb2AlC | 50% conc.-90 h-RT | Nb2CTx | 53 | |
| M3AX2 312 | Ti3AlC2 | 50% conc.-2 h-RT | Ti3C2Tx | 48 |
| Ti3SiC2 | HF 30% conc. + H2O2 35% conc.-45 h-40 ℃ | Ti3C2Tx | 62 | |
| Ti3AlCN | 30% conc.-18 h-RT | Ti3CNTx | 49 | |
| M4AX3 413 | V4AlC3 | 40% conc.-165 h-RT | V4C3Tx | 54 |
| Nb4AlC3 | 49% conc.-140 h-RT | Nb4C3Tx | 55 | |
| Ta4AlC3 | 50% conc.-72 h-RT | Ta4C3Tx | 49 |
3 MXenes的结构与性质
3.1 MXenes的结构
3.2 用于气体传感的MXenes电子特性
4 MXenes的气体传感应用
4. 1 MXenes表面吸附计算
图3 (a)不同气体在Ti2CO2 MXene上的吸附位点[81];(b)电荷密度分布图[81];(c)利用吸附的NH3和CO2气体分子预测的Ti2CO2的I-V特性[81];(d) 利用吸附的SO2气体分子预测的Sc2CO2的I-V特性[83]Fig.3 (a) Adsorption sites of different gases on Ti2CO2 MXene[81];(b) charge adsorbed density distribution[81];(c) predicted I-V characteristics of Ti2CO2 with NH3 and CO2 molecules[81];(d) predicted I-V characteristics of Sc2CO2 with SO2 molecules[83] |
4. 2 MXenes的气体传感性能
图4 (a)由Ti3C2Tx滴铸在叉型电极上制成的气体传感器[88];(b)传感器暴露于100 ppm丙酮、乙醇、氨和丙醛时的最大信噪比值[89];(c)室温(25 ℃)下,100 ppm的丙酮、乙醇、氨、丙醛、NO2、SO2和10 000 ppm CO2时的响应值[89];(d)暴露于ppb浓度范围(50~1000 ppb)的丙酮、乙醇和氨气时,响应值随时间的变化图[89]Fig.4 (a) A gas sensor made from Ti3C2Tx drop-cast on an interdigitated circuit[88];(b) Maximal SNR values of sensors upon exposure to 100 ppm of acetone, ethanol, ammonia, and propanal[89];(c) Maximal resistance change upon exposure to 100 ppm of acetone, ethanol, ammonia, propanal, NO2, SO2, and 10 000 ppm of CO2 at room temperature(25 ℃)[89];(d) Resistance variation versus time upon exposure to highly diluted acetone(top), ethanol(middle), and ammonia(bottom) in ppb concentration range(50~1000 ppb)[89] |
表3 MXene基气体传感器的气体传感性能Table 3 Gas sensing performance of MXene-based gas sensor |
| Material | Gas species | LOD | Response ((Rg-Ra/Ra)% | Temperature | ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ti3C2Tx MXene | ammonia | 100 ppb | 0.1% | RT | 89 |
| ethanol | 100 ppb | 0.25% | |||
| acetone | 50 ppb | 0.15% | |||
| 3D Ti3C2Tx MXene | acetone | 50 ppb | 0.08% | RT | 97 |
| V2CTx MXene | hydrogen | 2 ppm | 0.04% | RT | 90 |
| TiO2/Ti3C2Tx | ammonia | 0.5 ppm | 1% | 25 ℃ | 93 |
| Single-Layer Ti3C2Tx MXene(NaF +HCl etched) | ammonia | 10 ppm | 0.8% | 25 ℃ | 99 |
| W18O49/Ti3C2Tx | acetone | 170 ppb | 1.6(Ra/Rg) | 300 ℃ | 92 |
| Alkalized organ-like Ti3C2Tx MXene | ammonia | 10 ppm | — | RT | 100 |
| V4C3Tx MXene | acetone | 1 ppm | — | 25 ℃ | 91 |
| Ti3C2Tx/WSe2 hybrids (n-type sensing behavior) | ethanol | 1 ppm | — | RT | 94 |
| Fe2(MoO4)3/MXene composite | n-butanol | 5 ppm | — | 120 ℃ | 101 |
aRT stands for room temperature. |
图5 (a) Ti3C2Tx和Ti3C2Tx/WSe2气体传感器对1~40 ppm乙醇的实时传感响应[94];(b) Ti3C2Tx/WSe2异质结构的传感响应机理[94];(c)部分氧化的MXenes薄膜的多传感器阵列芯片[95];(d)部分氧化的MXenes传感器的线性判别分析图[95]Fig.5 (a) Real-time sensing response of Ti3C2Tx and Ti3C2Tx/WSe2 gas sensors upon ethanol exposure with concentrations ranging from 1 to 40 ppm[94];(b) Enhanced sensing mechanism of Ti3C2Tx/WSe2 heterostructure[94];(c) A multielectrode chip with a film of partially oxidized MXenes flakes prepared by drop-casting[95];(d) LDA diagram of partially oxidized MXenes sensor[95] |
图6 (a) MXene/GO纤维纺丝工艺示意图;(b)室温下MXene/rGO在纤维循环弯曲过程中对100 ppm NH3测试的电阻变化;(c)将MXene/rGO气体传感器编织在实验室外套中,并连接到万用表上;(d) 在实验室外套上的MXene/rGO传感器对100 ppm NH3实时响应图[98]Fig.6 (a) Schematic illustration of the spinning process for MXene/GO hybrid fiber;(b) The resistance change of MXene/rGO hybrid fiber exposed to 100 ppm of NH3 at room temperature during fiber cyclic bending;(c) MXene/rGO hybrid fibers were woven in a lab coat and connected to a multimeter;(d) Gas response of 100 ppm of NH3 molecules in MXene/rGO hybrid fibers woven into a lab coat[98] |
4.3 MXenes的气敏机理
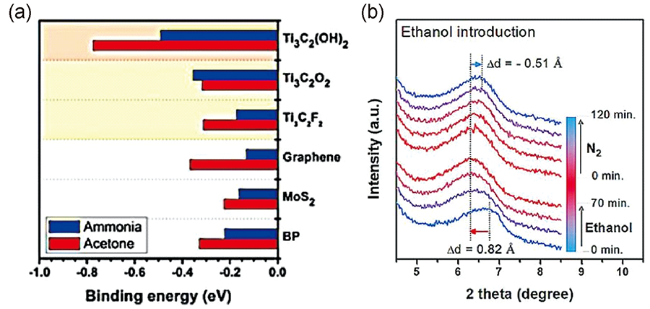
图7 (a)丙酮与氨在Ti3C2(OH)2、Ti3C2O2、Ti3C2F2、石墨烯、MoS2、BP上的最低结合能[89];(b) Ti3C2Tx经过0.1%的乙醇吹扫70 min及N2吹扫120 min吸附的乙醇被脱附带走后(002)的峰位移[106]Fig.7 (a) Minimum binding energies of acetone and ammonia on Ti3C2(OH)2, Ti3C2O2, Ti3C2F2, graphene, MoS2, and BP[89];(b) The(002) peak shift of Ti3C2Tx film during introduction of ethanol(0.1%) for 70 min, followed by N2 purging for 120 min to purge out target gases[106] |