1 引言
2 活性气态汞采集和分析方法
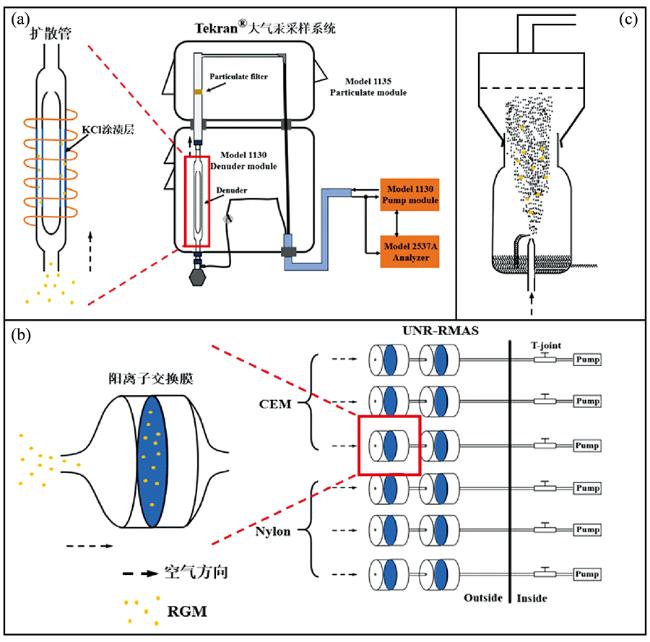
2.1 活性气态汞的采集方法
表1 活性气态汞采集和分析方法的比较Table 1 Comparison of sampling and analysis of reactive gaseous mercury |
| Sampling methods | Material types | Analysis | Speciation | Time | Flow rate (L·min-1) | LOD (pg·) | Application | Comments | ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KCl-coated denuder | KCl | Acid rinse, SnCl2-CVAFS/Thermal desorption, CVAFS | Total RGM | 1~12 h | 10 | 0.5~6.2 | Tekran® 1130 | Automated, easy operation | 20 |
| Multi-membrane filter | CEM | Acid digestion, SnCl2-CVAFS | Total RGM | 2 w | NA | 0.02~ 0.19a | Aerohead plate | Passive, easy operation | 26 |
| 2 w | NA | 5 | Box sampler | Passive, easy operation | 27 | ||||
| 2 w | 1 | 15 | UNR-RMAS | Manual, easy operation | 28 | ||||
| Nylon membrane | Temperature programmed desorption, CVAFS | Total RGM, and possible species (HgBr2, HgCl2, HgSO4, HgO, Hg(NO3)2) | 2 w | 1 | NA | UNR-RMAS | Manual, species identification | 28 | |
| Mist chamber | HCl/NaCl | SnCl2-CVAFS | Total RGM | 1 h | 15~20 | 4 | NA | Manual, complicated operation | 29 |
| Others | MnO2 sorbent | Solvent trapping, injection, GC-MS | Hg(NO3)2 | 1 h | NA | NA | NA | Species identification | 30 |
| Particle-based sorbent trap | Thermal desorption, APCI-MS | HgBr2, HgCl2 | 24 h | ~1 | 4~11 | NA | Species identification | 31 |
LOD-Limit of detection; CEM-cation exchange membrane; CVAFS-Cold vapor atomic fluorescence spectroscopy; Tekran®1130-Tekran®1130 active mercury sampler; GC-MS-Gas chromatography mass spectrometry; APCI-MS-Atmospheric pressure chemical ionization mass spectrometry; UNR-RMAS-University of Nevada, Reno-Reactive Mercury Active Systems NA-Not available; a-The unit is ng·m-2·h-1 |
2.1.1 镀KCl扩散管法
2.1.2 多级滤膜法
2.1.3 回流喷雾箱法
2.1.4 三种采样方法的观测结果比较
2.1.5 活性气态汞采样方法的影响因素
表2 不同采样方法活性气态汞观测结果的比较Table 2 Comparison of reactive gaseous mercury monitoring results by different sampling methods |
| Year | Sampling methods | RGM (pg·m-3) | Flow rate (L·min-1) (Sampling time) | Blank | MDL | ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1998 | Mist chamber with 0.1 M HCl | 16 | 12(23 h) | NA | NA | 9 |
| Tubular KCl-coated denuders | 22±3 | 1(23 h) | NA | NA | ||
| Annular KCl-coated denuders | 14.1 | 5(23 h) | NA | NA | ||
| 1999 | Multistage filter packs | 54.2 | 3~5(6、24 h) | NA | 7 pg | 44 |
| Refluxing mist chambers | 16.9 | 10(75~120 min) | NA | 5 pg | ||
| KCl-coated denuders | 44.4 | 10(100~120 min) | NA | 15 pg | ||
| 2011 | KCl-coated denuders | 13.6 | 4(1 h) | <5 pg·m-3 | <5 pg·m-3 | 34 |
| Cation exchange membranes | 38.3 | 1(2 w) | 310±230 pg | NA | ||
| Nylon membranes | 25.6 | 1(2 w) | 20±40 pg | NA | ||
| 2014 | Tekran®1130 | 22.3±4.7 | 7(1 h) | NA | NA | 28 |
| UNR-RMAS(cation exchange membrane) | 82.5±30.0 | 1(1~2 w) | 0.2±0.3 ng(n=96) | 0.3 ng | ||
| UNR-RMAS(nylon membrane) | 14.2±10.3 | 1(1~2 w) | 0.006±0.02 ng (n=80) | 0.006 ng | ||
| 2019 | Tekran®1130 | 3 | 5.5(2 h) | NA | NA | 35 |
| UNR-DCS(cation exchange membrane) | 20 | 2(1 w) | NA | 40 pg | ||
| UNR-RMAS(cation exchange membrane) | 49 | 1(1 w) | NA | 40 pg | ||
| UNR-RMAS(nylon membrane) | 8 | 1(1 w) | NA | 40 pg | ||
| 2014 | Tekran®1130 | 2.0±3.6 | 10(1 h) | NA | 1.5 pg·m-3 | 37 |
| UNR-RMAS(cation exchange membrane) | 24±15 | 1(2 w) | 0.37±0.26 ng (n=77) | 2~68 pg·m-3 | ||
| UNR-RMAS(nylon membrane) | 0.6±0.5 | 1(2 w) | 0.03±0.03 ng (n=69) | 0.01~14.6 pg·m-3 | ||
| 2017 | KCl-coated denuder | 9.92±17.44 | ~1(3 h) | 27.6±2.9 pg(n=11) | 3 pg | 40 |
| KCl-coated glass fiber filter | 87.25±101.29 | ~1(3 h) | 57.3±5.2 pg(n=11) | 3 pg | ||
| KCl-coated quartz sand tube | 203.75±139.09 | ~1(3 h) | 29.8±4.5 pg(n=11) | 3 pg | ||
| Cation exchange membrane | 264.78±130.19 | ~1(3 h) | 79.8±9.5 pg(n=8) | 3 pg |
UNR-DCS-University of Nevada, Reno-Dual Channel Systems; MDL-Method detect limit NA-Not available |
2.2 活性气态汞的分析方法
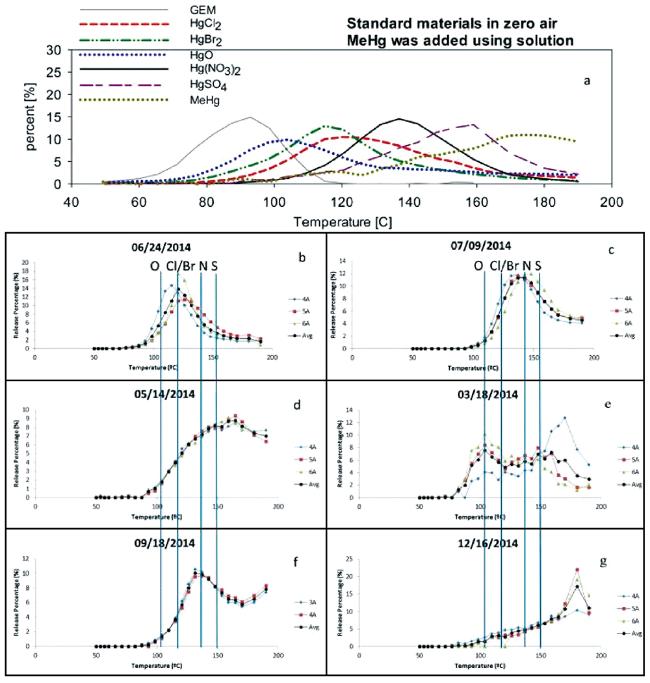
图2 不同汞化合物(a)和野外样品(b~g)的程序升温热解析图谱。通过比对野外样品和汞标准品的程序升温热解析图谱,推断野外样品中汞的形态。(b)HgCl2、HgBr2;(c)Hg-S和Hg-N类化合物;(d)汞的混合物;(e)HgO、Hg-N和Hg-S类化合物;(f)Hg-N类以及峰出现高拖尾的未知化合物;(g)峰值逐渐升高的未知化合物[28] Fig. 2 Temperature programmed desorption profiles of different Hg compounds (a) and field samples(b~g). By comparing temperature programmed desorption profiles of field sample to those of mercury standard, the Hg species in field samples could be inferred;(b) shows HgCl2/HgBr2;(c) shows Hg-sulfur, and nitrogen compounds;(d) shows a mixture of compounds;(e) shows HgO, Hg-nitrogen, and sulfur compounds;(f) shows Hg-nitrogen compounds with an unknown compound producing a high residual tail, and(g) shows a gradual increase with an unknown peak[28]. Copyright 2016, American Chemical Society |
3 大气中活性气态汞的赋存与转化
3.1 大气中活性气态汞的生成机制
表3 国内外不同地点的活性气态汞浓度对比Table 3 Comparison of reactive gaseous mercury from worldwide locations |
| Continent | Site | Region | Type | Period | RGM(pg·m-3) | ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Northern Hemisphere | ||||||
| Asia | Beijing | North China | Urban | 2015~2016 | 18.47±22.27 | 74 |
| Miyun | North China | Remote | 12/2008~11/2009 | 10.1±18.8 | 75 | |
| Ningbo | Yangtze River Delta | Urban | 7/2013~1/2014 | 197±246 | 76 | |
| Guiyang | Southwest China | Urban | 8~12/2009 | 35.7±43.9 | 77 | |
| Xiamen | Southeast China | Coastal | 3/2012~2/2013 | 61.05±69.41 | 78 | |
| Chongming | East China | Coastal | 2009~2012 | 8.0±8.8 | 79 | |
| Taoyuan | Taiwan, China | Remote | 10/2017~9/2018 | 12.1±34.3 | 80 | |
| Bohai Sea/Yellow Sea | Northeast China | Sea | Spring/2014 | 2.5±1.7 | 81 | |
| Fall/2014 | 4.3±2.5 | |||||
| South China Sea | South China | Sea | 9/2015 | 6.1±5.8 | 82 | |
| Mt. Changbai | Northeast China | Mountain | 7/2013~7/2014 | 5.4±6.4 | 83 | |
| Mt. Waliguan | Northwest China | Mountain | 9/2007~9/2008 | 7.4±4.8 | 84 | |
| North America | Nevada | Reno | Urban | 2/2007~1/2009 | 18±22 | 85 |
| Michigan | Detroit | Urban | 2004 | 15.5±54.9 | 86 | |
| Dexter | Rural | 2004 | 3.8±6.6 | |||
| Canada | Toronto | Remote | 12/2003~11/2004 | 14.2±13.2 | 87 | |
| Mexico | Mexico City | Urban | 3/2006 | 62±64 | 88 | |
| Oregon, U.S.A. | Mt. Bachelor | Mountain | 5~8/2005 | 43 | 89 | |
| Colorado, U.S.A. | Mt. Rocky | Mountain | 4~7/2008 | 20 | 90 | |
| Alaska, U.S.A. | Beaufort Sea | Sea ice | 3~4/2009 | 30.1 | 91 | |
| Europe | Mediterranean Sea | - | Coastal/Sea | Summer/2015 | 11.8±15.0 | 92 |
| Southern Hemisphere | ||||||
| Amsterdam Island | - | Ocean | 1/2012~12/2013 | 0.34 | 93 | |
| Africa | South Africa | - | Ocean | 10/2006 | 3.4±4 | 94 |
3.2 大气中活性气态汞的赋存
3.3 大气中活性气态汞的清除
表4 活性气态汞的不同清除方式及其影响因素Table 4 Different depletion ways of reactive gaseous mercury and the influencing factors |
| Depletion ways | RGM behaviors | Influencing factors |
|---|---|---|
| Deposit to land surface | Dry deposition | RGM species Environmental conditions Land surface types |
| Gas-liquid partition | Wet deposition | RGM species Temperature Precipitation types |
| Gas-particle partition | Transform to PBM | RGM species Temperature Aerosol compositions |
| Photochemical reduction | Transform to GEM | RGM species Solar radiation |