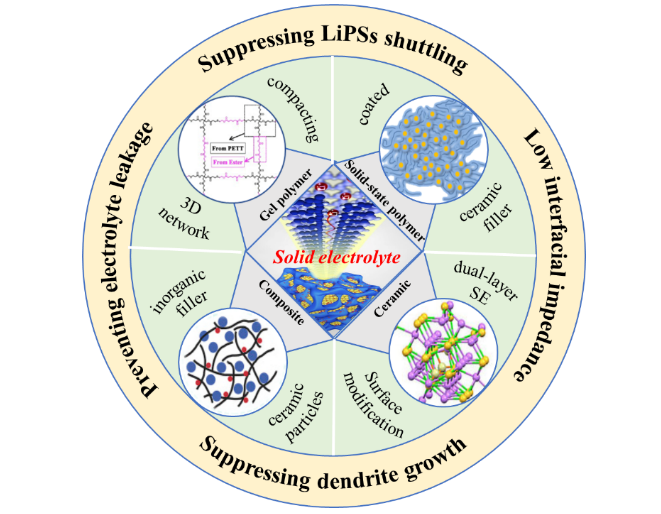
1 引言
2 固态电解质
2.1 凝胶聚合物电解质
2.2 固态聚合物电解质
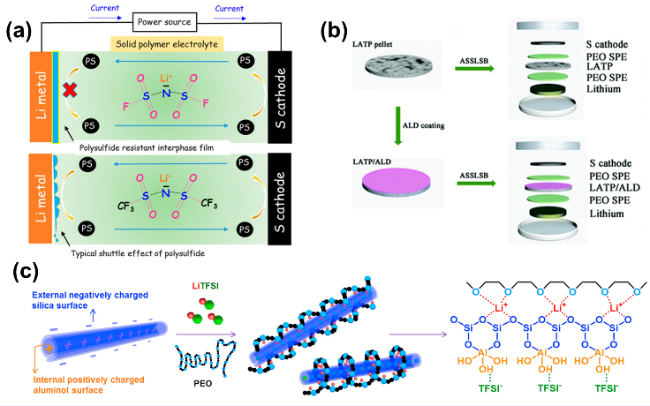
图3 (a)LiFSI有助于形成稳定的界面层[28],(b)Al2O3包覆LATP固态聚合物电解质的制备和全固态锂硫电池结构图[30],(c)HNT添加剂提高离子电导率机理图[35]Fig.3 (a) LiFSI helps the forming of stable interface layer[28]. Copyright 2017, American Chemical Society.(b) Schematic diagram showing the preparation of an ALD coated LATP SSE and the configuration of ASSLSBs[30]. Copyright 2018, Royal Society of Chemistry.(c) Schematic mechanism of HNT addition for enhanced ionic conductivity[35]. Copyright 2017, Elsevier. |
2.3 陶瓷电解质
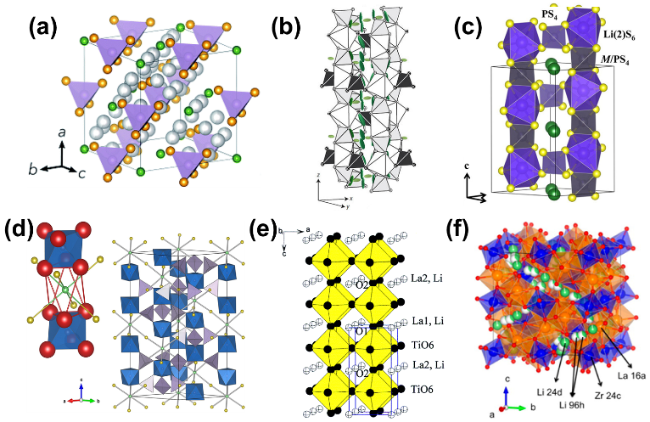
图4 陶瓷电解质晶体结构示意图,(a) Li6PS5Cl[46],(b) Li9.54Si1.74P1.44S11.7C ,(c) Li10GeP2 ,(d) NaSICON[63],(e) Li3 x La2/3- x Ti ,(f) Li7La3Zr2Fig.4 Crystal structure of (a) Li6PS5Cl[46]. Copyright 2019, Royal Society of Chemistry. (b) Li9.54Si1.74P1.44S11.7C . Copyright 2018, Wiley. (c) Li10GeP2 . Copyright 2016, American Chemical Society. (d) NaSICON[63]. Copyright 2014, American Chemical Society. (e) Li3 x La2/3- x Ti . Copyright 2003, American Chemical Society. (f) Li7La3Zr2 . Copyright 2013, American Chemical Society. |
2.4 复合固态电解质
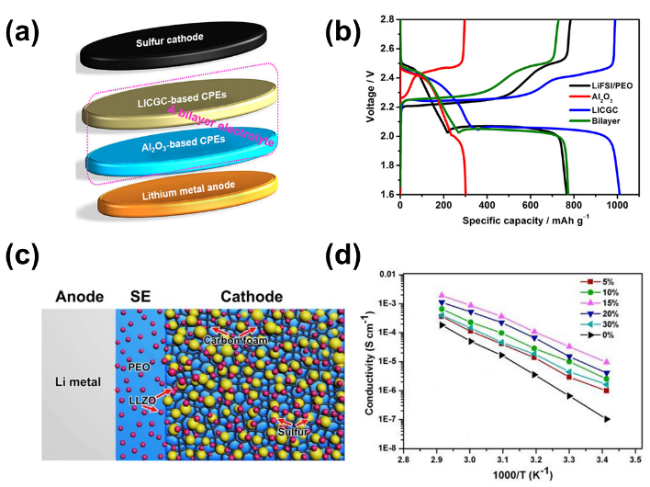
图5 (a)夹层结构电解质的电池示意图;(b)锂硫电池基于不同电解质的充放电曲线图[76](c)混合电解质锂硫电池结构示意图;(d)不同浓度LLZO纳米复合材料对离子电导率的影响[1]Fig.5 (a) Sketch of the cell with a bilayer electrolyte configuration;(b) Discharge/charge profiles of the Li-S battery with different electrolytes[76].(c) Schematic illustration of an all solid-state Li-S battery based on hybrid electrolytes;(d) Arrhenium plots of the conductivity of nanocomposite LLZO-PEO-LiClO4 with different LLZO concentrations[1]. Copyright 2017, American Chemical Society. |
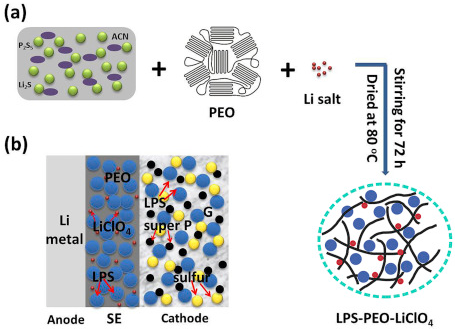
图6 (a) LPS-PEO-LiClO4复合固态电解质的工艺流程图;(b)LPS-PEO-LiClO4固态锂硫电池结构示意图[77]Fig.6 (a) Schematic of fabrication process of LPS-PEO-LiClO4 hybrid solid electrolyte,(b) Schematic illustration of an all solid-state Li-S battery structure based on LPS-PEO-LiClO4 hybrid solid electrolyte[77]. Copyright 2018, American Chemical Society. |
表1 不同固态电解质对锂硫电池电化学性能的影响Table 1 The electrochemical performances of Li-S batteries with various solid-state electrolytes |
| Classification | Molecular formula | Ionic conductivity (S·cm-1) | Electrochemical property | ref | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Current density | Initial capacity (mAh·g-1) | Cycle performance (mAh·g-1) | |||||
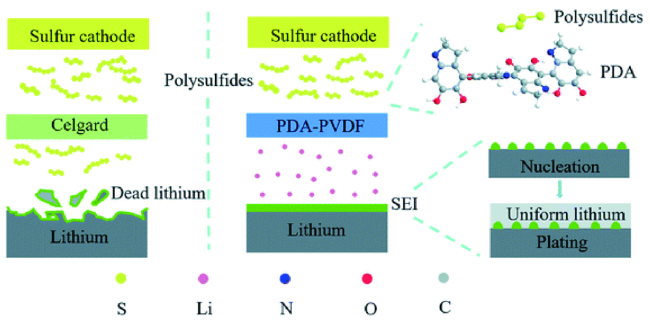
| Gel | PDA-PVDF | — | 0.1 C | 1215.4 | 200th, 868.8 | 19 | |
| PVDF/PEO/ZrO2 | 5.25×10-4(25 ℃) | 0.2 C | 1429 | 200th, 936.1 | 18 | ||
| PVDF-HFP | 6.61×10-4(20 ℃) | 0.5 C | 601 | 100th, 503 | 82 | ||
| PETEA | 1.13×10-2(25 ℃) | 0.1 C | 1219.8 | 100th, 744.1 | 83 | ||
| PVDF/PMMA/PVDF | 1.95×10-3(25 ℃) | 200 mA·g-1 | 1711.8 | 50th, 1145.3 | 84 | ||
| PEO | 1.76×10-3(25 ℃) | 0.1 C | 1182 | 100th, 648 | 85 | ||
| Solid-state polymer | PEO/Al2O3-LATP/PEO | 4.8×10-4(60 ℃) | 0.1 C | 1035 | 100th, 823 | 30 | |
| PEO/Li10SnP2S12 | 1.69×10-4(50 ℃) | 0.2 C | 330 | 50th, 800 | 34 | ||
| PEO/LiFSI | 9.0×10-5(70 ℃) | 0.05C | 900 | 50th, 750 | 28 | ||
| PEO/LiTFSI/MMT | 3.22×10-4(60 ℃) | 0.1 C | 998 | 100th, 634 | 29 | ||
| PEO-LiTFSI-HNT | 1.1×10-4(25 ℃) | 4 C | 809 | 400th, 386 | 35 | ||
| Ceramic | Li6PS5Cl | 3.15×10-3(25 ℃) | 0.176 mA·cm-2 | 1850 | 50th, 1393 | 45 | |
| Li9.54Si1.74P1.44S11.7Cl0.3 | 1.6×10-2(25 ℃) | 80 mA·g-1 | 969 | 60th, 827 | 61 | ||
| Li7P2.9S10.85Mo0.01 | 4.8×10-3(25 ℃) | 0.05 C | 1020 | 30th, 400 | 86 | ||
| LLZTO-MgO | 5×10-4(25 ℃) | 0.2 C | 1130 | 200th, 685 | 87 | ||
| Li7P2.9Mn0.1S10.7I0.3 | 5.6×10-3(25 ℃) | 0.05 C | 791.6 | 60th, 800 | 11 | ||
| Composite | LPS-PEO-LiClO4 | 2.1×10-3(25 ℃) | 0.05 C | 826 | 60th, 394 | 77 | |
| LLZO-PEO-LiClO4 | 1.9×10-3(70 ℃) | 0.05 mA·cm-2 | >900 | 90th, 810 | 1 | ||
| LICGC-CPE | 6×10-4(90 ℃) | 0.05 C | 1111 | 50th, 518 | 76 | ||
| FDE-LAGP | 3.2×10-4(25 ℃) | 1 C | 915 | 1200th, 668 | 13 | ||
3 结论及展望
表2 用于锂硫电池的不同类型固态电解质参数及优缺点比较列表Table 2 Comparison of advantages and disadvantages of various SSEs electrolytes for lithium-sulfur batteries |
| Classification | Materials | Transference number(n) | Conductivity (S·cm-1) | Voltage stability | Activation energy (KJ·mol-1) | Advantage | Disadvantage | ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gel | PVdF-2%SiO2 | 0.31 | 10-4~10-2 | 3~5.1 V | 2.193 | High ionic conductivity | Severe Li dendrite growth | 88 |
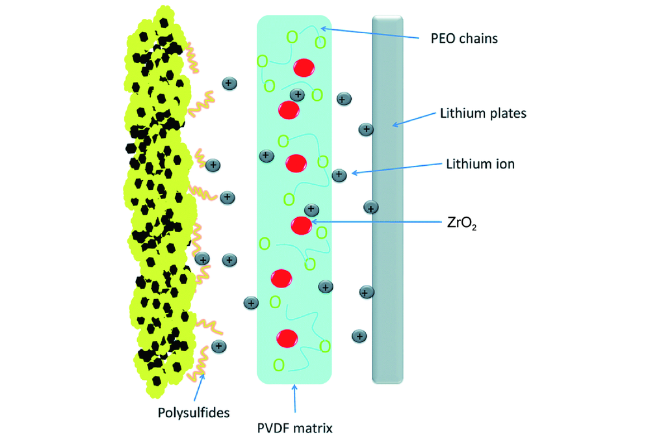
| PVDF/PEO/ZrO2 | 0.71 | / | 1.7~6 V | / | Low interfacial impedance | Severe LiPSs shuttling | 18 | |
| PEO-TEGDME/DIOX | 0.78 | / | 1~4 V | / | / | Poor mechanical strength | 23 | |
| Solid-state Polymer | PEO/Li10SnP2S12 | 0.38 | 10-5~10-4 | — | / | Safety | Low ionic conductivity | 34 |
| PEO-PTEC-LiTFSI | 0.39 | / | 1~5 V | / | No electrolyte leakage | Low voltage, Compatibility | 89 | |
| PEO/LiTFSI/MMT | 0.45 | / | 1~4 V | 42 | Low cost | / | 29 | |
| (PEO-PMMA)-LiClO4 | >0.98 | / | 0~5 V | / | Excellent processability | / | 90 | |
| Ceramic | Li4.08Zn0.04Si0.96O4 | 0.92 | 10-4~10-2 | 1~5.8 V | / | High ionic conductivity | High interfacial Impedance | 91 |
| Li9.54Si1.74P1.44S11.7Cl0.3 | / | / | 0.2~5 V | 24.6 | Preventing LiPSs shuttling | / | 61 | |
| Li7P2.9S10.85Mo0.01 | / | / | 0.5~5 V | 22.7 | / | High cost | 86 | |
| Li7P2.9Mn0.1S10.7I0.3 | / | / | 0.2~5 V | 20.8 | Wide electrochem. window | Sensitive to moisture11 | ||
| Li11AlP2S12 | ~1 | / | 0.5~5 V | 25.4 | / | / | 55 | |
| Composite | FDE-LAGP | 0.83 | 10-4~10-3 | / | / | l Preventing LiPSs shuttling | Limited capacity | 13 |
| PEO-20%LAGP | 0.378 | / | 2.5~6 V | / | / | / | 75 | |
| LPS-PEO-LiClO4 | / | / | 0.2~5 V | 24.43 | Suppressing Li dendrite | / | 77 | |
| P(VdF-HFP)/LLZO | 0.82 | / | 0~5 V | / | / | / | 92 |