1 引言
2 手性钙钛矿纳米材料的构筑策略
图1 (a) 不同维数手性钙钛矿结构示意图;(b) 手性胺阳离子参与钙钛矿的结晶;(c) 手性配体表面诱导的钙钛矿纳米晶;(d) 超分子组装体系中诱导的手性钙钛矿纳米晶Fig. 1 (a) Schematic diagram of chiral perovskite structure with different dimensions; (b) Chiral amine cations participate in crystallization of perovskite; (c) Surface chiral ligand-induced perovskite nanocrystals; (d) Chiral perovskite nanocrystals induced in supramolecular assembly system |
3 不同维数手性钙钛矿纳米材料的研究进展
3.1 一维手性钙钛矿纳米线
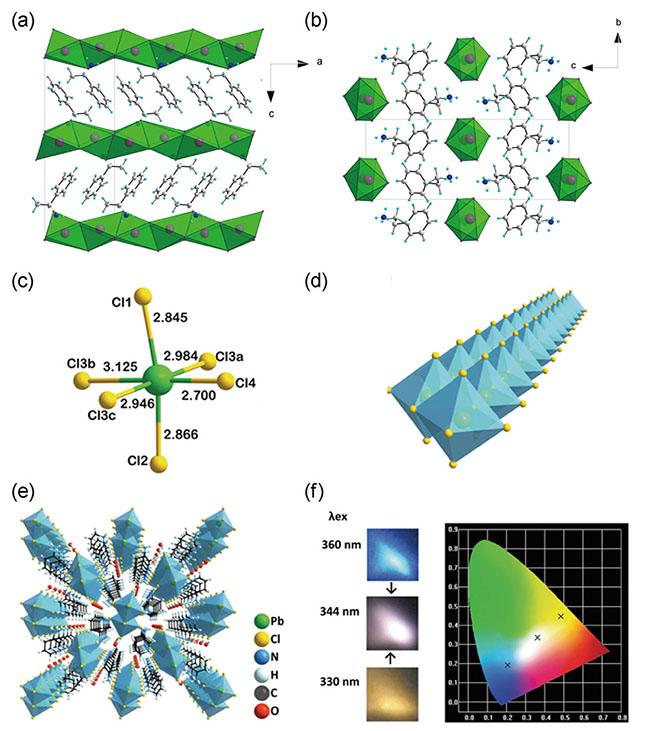
图2 [(S)-苯乙胺][PbBr3]形成的一维手性钙钛矿单晶(a) 沿b轴观察;(b) 沿a轴观察[16];(c) 一维手性钙钛矿C5H14N2PbCl4·H2O中扭曲的八面体PbCl6具有不均一的Pb—Cl键长;(d) 扭曲的八面体PbCl6形成无限双链;(e) C5H14N2PbCl4·H2O的堆叠架构;(f) C5H14N2PbCl4·H2O的光致发光照片和相应的色度坐标,激发波长分别在330 nm、344 nm和360 nm[27] Fig. 2 [(S)-Phenethylammonium][PbBr3] 1D chiral perovskite single crystal (a) viewed along the b axis; (b) viewed along the a axis[16]; (c) Distorted PbCl6 octahedron with inhomogeneous Pb—Cl bond lengths in 1D chiral perovskite C5H14N2PbCl4·H2O; (d) Infinite double-chain formed by distorted PbCl6 octahedra; (e) Packing framework of C5H14N2PbCl4·H2O; (f) Photoluminescence photographs and corresponding chromaticity coordinates of C5H14N2PbCl4·H2O excited at 330 nm, 344 nm, and 360 nm[27] |
3.2 二维手性有机-无机杂化钙钛矿薄膜
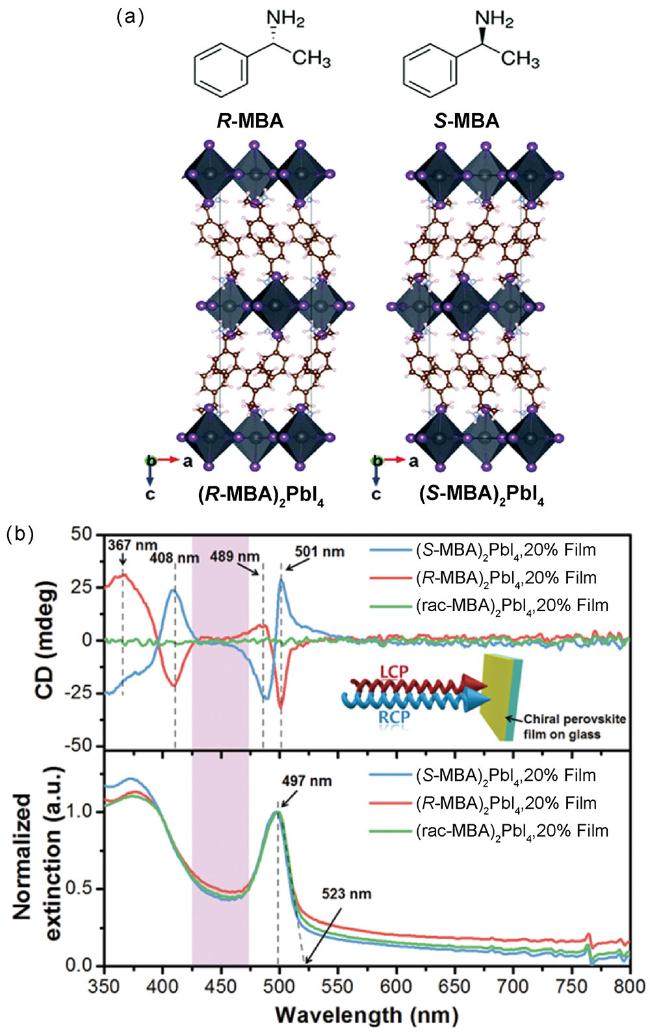
图3 (a) 上图:R-MBA和S-MBA的分子结构,下图:(R-MBA)2PbI4和(S-MBA)2PbI4的晶体结构;(b) (R-MBA)2PbI4、(S-MBA)2PbI4和(rac-MBA)2PbI4薄膜的CD光谱(上)和归一化吸收光谱(下)[30]Fig. 3 (a) Molecular structures of R-MBA and S-MBA (up), crystalline structures of (R-MBA)2PbI4 and (S-MBA)2PbI4 (down); (b) Transmission CD spectra (up), and normalized extinction spectra (down) of (R-MBA)2PbI4, (S-MBA)2PbI4 and (rac-MBA)2PbI4 [30] |
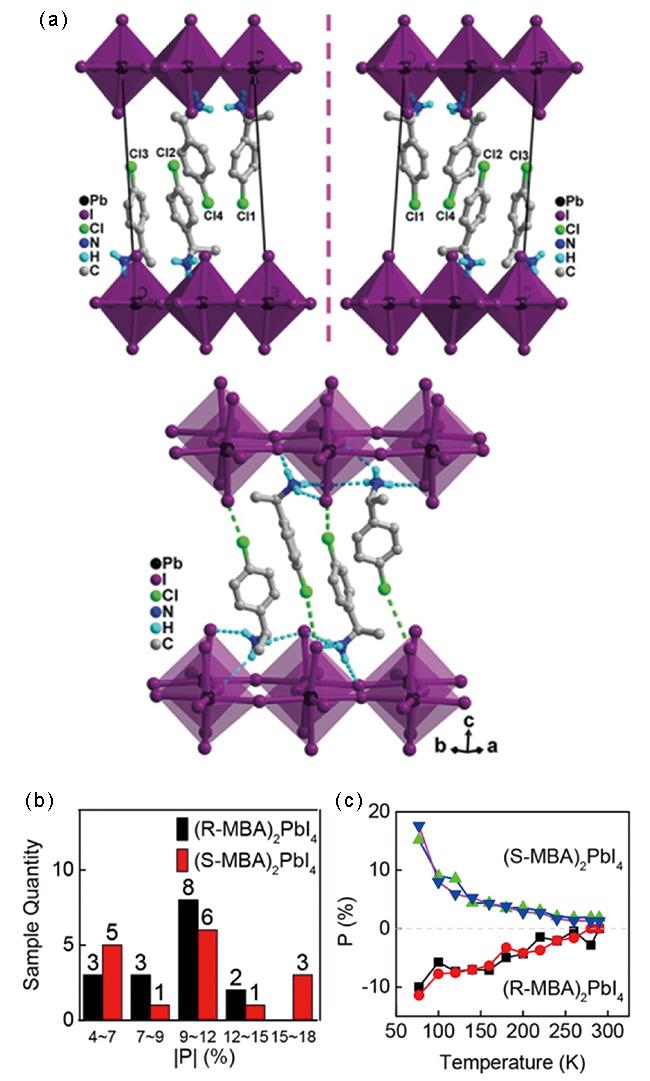
图4 (a) 上图:R-LIPF和S-LIPF晶体结构的堆积视图,显示镜像关系,下图:有机阳离子与无机层之间的氢键作用和卤素-卤素相互作用[33];2D手性钙钛矿(R-/S-MBA)2PbI4中的圆偏振光致发光:(b) 圆偏振发光偏振度 | P | 的统计直方图,激发波长:473 nm,温度:77 K;(c) 偏振度随温度的变化图[34]Fig. 4 (a) Up: Packing views of the crystal structures of R-LIPF and S-LIPF, showing a mirror-image relationship, down: Hydrogen-bonding and halogen-halogen interactions between the organic cations and inorganic layers[33]; Circularly polarized photoluminescence in 2D chiral perovskites (R- and S-MBA)2PbI4: (b) Statistical histogram of the degree of circularly polarized PL |P| for (R- and S-MBA)2PbI4 excited by a 473 nm laser at 77 K; (c) Degree of circularly polarized PL (P) as a function of temperature of two microplates for each type of chiral 2D perovskites[34] |
3.3 准二维手性有机-无机杂化钙钛矿
图5 (a) 具有不同无机层(<n>)的RDCP的结构示意图。 手性强度随<n>层的增加而降低;(b) rac-RDCP、R-RDCP和S-RDCP在磁场下从-7 T到7 T的光致发光偏振度[42]Fig. 5 (a) Schematic illustration of the structures of RDCPs with different inorganic layers (<n>). Chirality decreases with increasing <n> layers; (b) Degree of photoluminescence polarization for rac-RDCP, R-RDCP, and S-RDCP with magnetic field varied from -7 T to 7 T[42] |
3.4 三维手性钙钛矿纳米晶
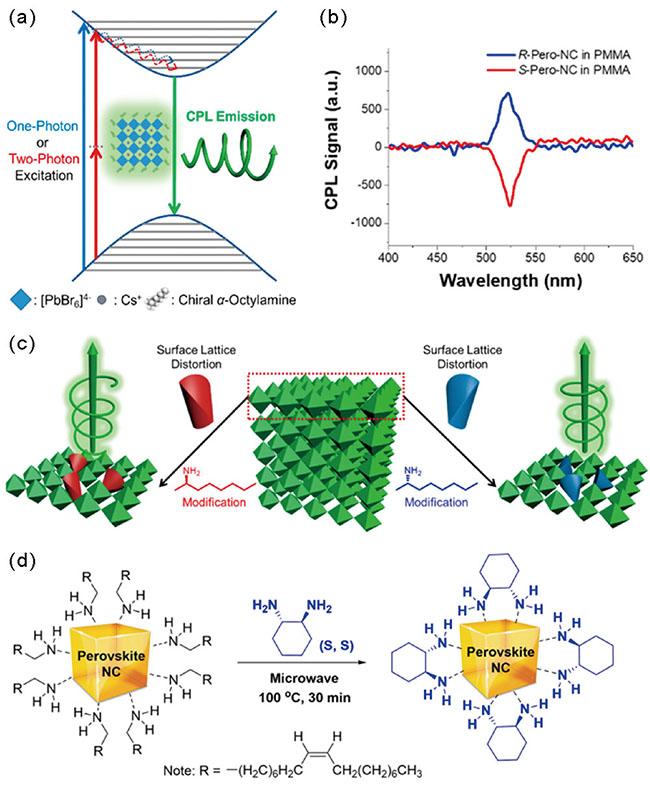
图6 (a) 钙钛矿纳米晶单光子或双光子圆偏振发光;(b) PMMA膜中手性钙钛矿纳米晶的双光子上转换圆偏振发光(TP-UCPL)光谱;(c) 手性CsPbBr3钙钛矿中手性来源的机理解释[47];(d) 使用DACH对映体在油胺封端的钙钛矿纳米晶上进行配体交换:正己烷中油胺封端的钙钛矿纳米晶(左)和正己烷中S-DACH封端的钙钛矿纳米晶(右)[24]Fig. 6 (a) Single-photon or two-photon circularly polarized emission of perovskite nanocrystals; (b)Two-photon upconverted circularly polarized luminescence (TP-UCPL) spectra of chiral perovskite nanocrystals in PMMA film; (c) Schematic illustration of the origin of chirality in chiral CsPbBr3 perovskite[47]; (d) Ligand exchange on an OA-capped perovskite NC using pure enantiomers of DACH: OA-capped perovskite NC in n-hexane (left) and S-DACH-capped perovskite NC in n-hexane obtained by ligand exchange (right)[24] |