 PDF(10748 KB)
PDF(10748 KB)


 PDF(10748 KB)
PDF(10748 KB)
 PDF(10748 KB)
PDF(10748 KB)
赭曲霉毒素A的电化学适体传感检测
 ({{custom_author.role_cn}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}
({{custom_author.role_cn}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}Electrochemical Aptasensor for Detection of Ochratoxin A
 ({{custom_author.role_en}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}
({{custom_author.role_en}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}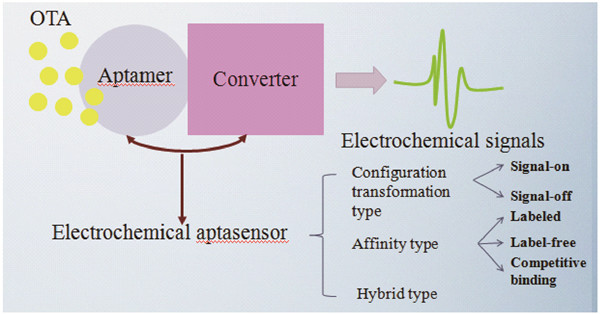
| {{custom_ref.label}} |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |