 PDF(1390 KB)
PDF(1390 KB)


 PDF(1390 KB)
PDF(1390 KB)
 PDF(1390 KB)
PDF(1390 KB)
超分子化学中的多点统计作用:设计与应用
 ({{custom_author.role_cn}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}
({{custom_author.role_cn}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}Multisite Statistical Interactions in Supramolecular Chemistry: Design and Application
 ({{custom_author.role_en}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}
({{custom_author.role_en}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}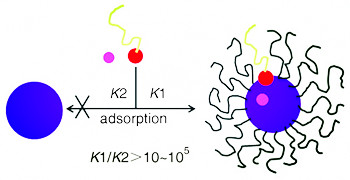
| {{custom_ref.label}} |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |