 PDF(16743 KB)
PDF(16743 KB)


 PDF(16743 KB)
PDF(16743 KB)
 PDF(16743 KB)
PDF(16743 KB)
激活型有机光声造影剂的应用
 ({{custom_author.role_cn}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}
({{custom_author.role_cn}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}Applications of Activatable Organic Photoacoustic Contrast Agents
 ({{custom_author.role_en}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}
({{custom_author.role_en}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}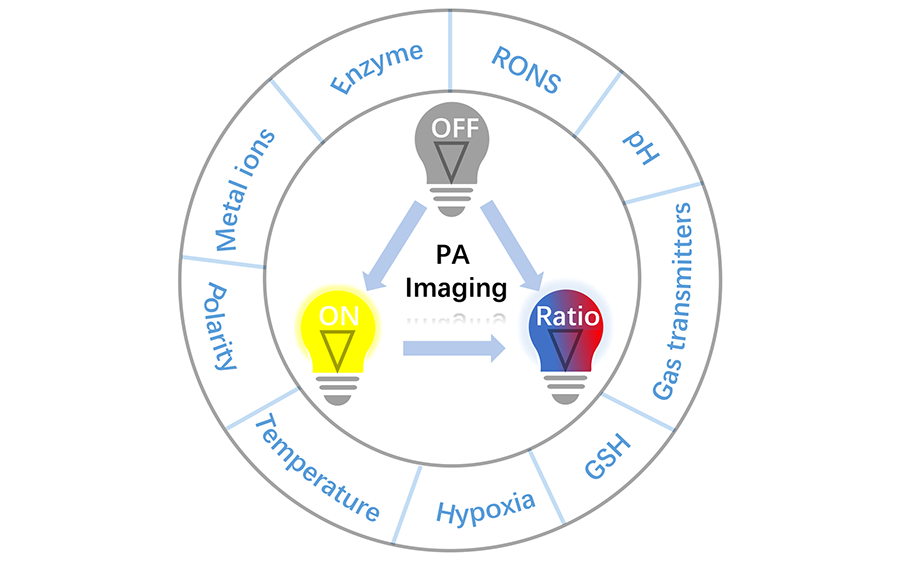
| {{custom_ref.label}} |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |