 PDF(1747 KB)
PDF(1747 KB)


 PDF(1747 KB)
PDF(1747 KB)
 PDF(1747 KB)
PDF(1747 KB)
人参皂苷类化合物样品前处理及分析检测
 ({{custom_author.role_cn}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}
({{custom_author.role_cn}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}Sample Pretreatment, Analysis and Detection of Ginsenosides
 ({{custom_author.role_en}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}
({{custom_author.role_en}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}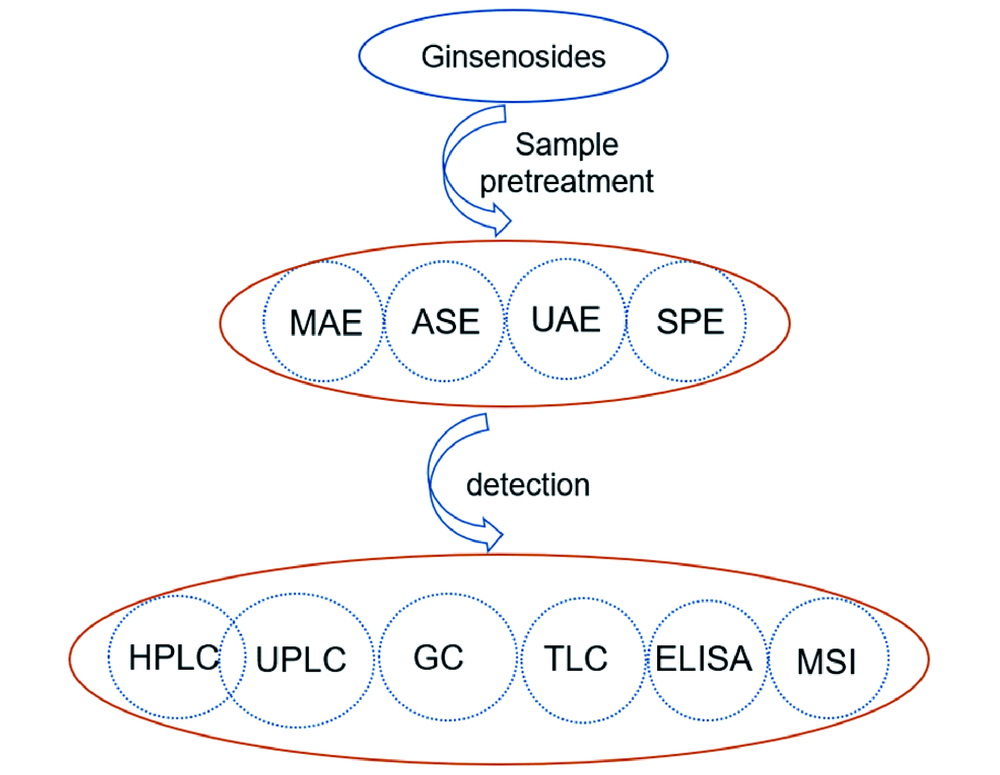
| {{custom_ref.label}} |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |