 PDF(13374 KB)
PDF(13374 KB)


 PDF(13374 KB)
PDF(13374 KB)
 PDF(13374 KB)
PDF(13374 KB)
超亲水超疏油油水分离膜的制备及其性能
 ({{custom_author.role_cn}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}
({{custom_author.role_cn}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}Preparation and Performance of Superhydrophilic and Superoleophobic Membrane for Oil/Water Separation
 ({{custom_author.role_en}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}
({{custom_author.role_en}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}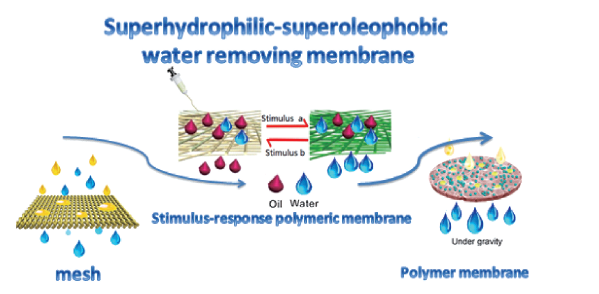
| {{custom_ref.label}} |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |