 PDF(6472 KB)
PDF(6472 KB)


 PDF(6472 KB)
PDF(6472 KB)
 PDF(6472 KB)
PDF(6472 KB)
基于肽组装凝胶的超分子模拟酶
 ({{custom_author.role_cn}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}
({{custom_author.role_cn}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}Supramolecular Artificial Enzyme Based on Assembling Peptide Gel
 ({{custom_author.role_en}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}
({{custom_author.role_en}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}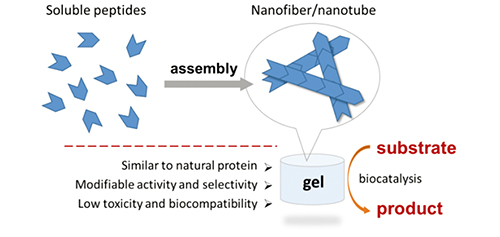
| {{custom_ref.label}} |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |