 PDF(1072 KB)
PDF(1072 KB)


 PDF(1072 KB)
PDF(1072 KB)
 PDF(1072 KB)
PDF(1072 KB)
高级还原技术:一种水处理新技术
 ({{custom_author.role_cn}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}
({{custom_author.role_cn}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}Advanced Reduction Processes: A Novel Technology for Water Treatment
 ({{custom_author.role_en}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}
({{custom_author.role_en}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}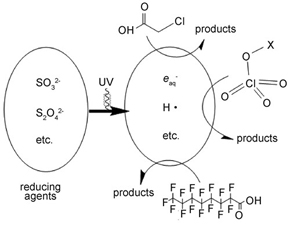
| {{custom_ref.label}} |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |