 PDF(1047 KB)
PDF(1047 KB)


 PDF(1047 KB)
PDF(1047 KB)
 PDF(1047 KB)
PDF(1047 KB)
金纳米粒子和聚合物复合体系分子设计与组装过程的计算机模拟
 ({{custom_author.role_cn}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}
({{custom_author.role_cn}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}Computer Simulation Study on the Molecular Design and the Self-Assembly Process of Au-Nanoparticle and Polymer Composite System
 ({{custom_author.role_en}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}
({{custom_author.role_en}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}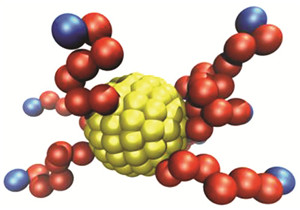
| {{custom_ref.label}} |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |