 PDF(1764 KB)
PDF(1764 KB)


 PDF(1764 KB)
PDF(1764 KB)
 PDF(1764 KB)
PDF(1764 KB)
纳米晶纤维素手性向列型液晶相结构的形成、调控及应用
 ({{custom_author.role_cn}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}
({{custom_author.role_cn}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}Formation, Tuning and Application of Chiral Nematic Liquid Crystal Phase Based on Nanocrystalline Cellulose
 ({{custom_author.role_en}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}
({{custom_author.role_en}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}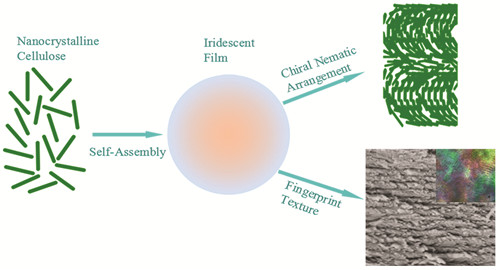
| {{custom_ref.label}} |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |