 PDF(2036 KB)
PDF(2036 KB)


 PDF(2036 KB)
PDF(2036 KB)
 PDF(2036 KB)
PDF(2036 KB)
基于微流控芯片的CD4+T淋巴细胞计数检测
 ({{custom_author.role_cn}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}
({{custom_author.role_cn}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}CD4 +T Lymphocyte Counting Technologies Based on Microfluidic Chip
 ({{custom_author.role_en}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}
({{custom_author.role_en}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}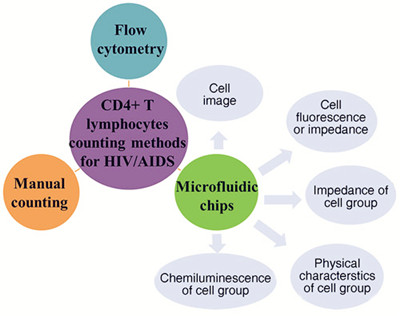
| {{custom_ref.label}} |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |