 PDF(2866 KB)
PDF(2866 KB)


 PDF(2866 KB)
PDF(2866 KB)
 PDF(2866 KB)
PDF(2866 KB)
发光液晶高分子:分子构筑、结构与性能及其应用
 ({{custom_author.role_cn}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}
({{custom_author.role_cn}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}Luminescent Liquid Crystalline Polymers: Molecular Fabrication, Structure-Properties and Their Applications
 ({{custom_author.role_en}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}
({{custom_author.role_en}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}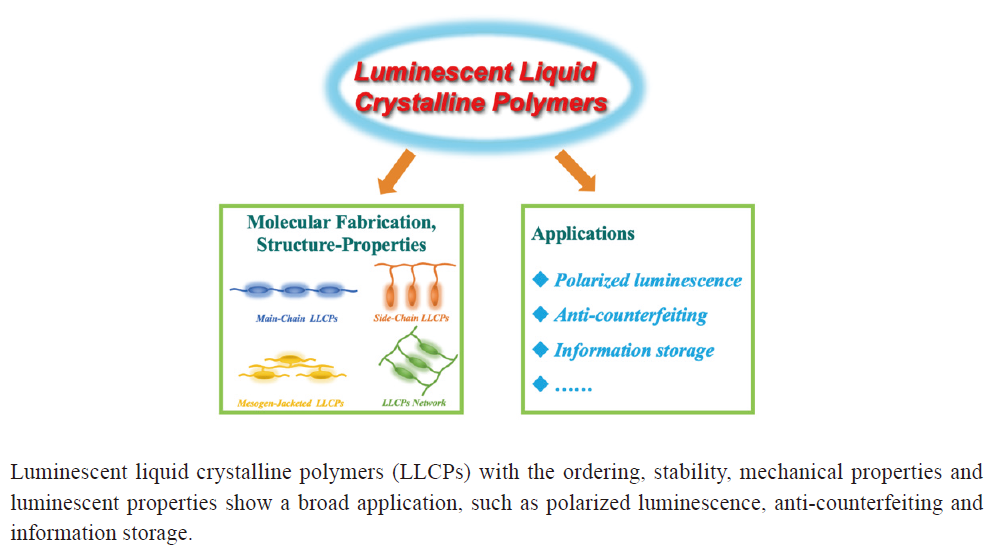
| {{custom_ref.label}} |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |