1 学者概述
Ludo Waltman(1982-),1982年出生于荷兰Dordrecht(多德雷赫特市)。2005年在荷兰Erasmus University Rotterdam获得硕士学位,硕士论文题目为A Theoretical Analysis of Probabilistic Fuzzy Systems(《概率模糊系统的理论分析》)[1]。同年在该校计量经济研究所攻读博士学位,并于2011年获得博士学位。其博士论文的题目为Computational and Game-Theoretic Approaches for Modeling Bounded Rationality(《有限理性建模的理论方法:计算与博弈》)[2]。受到其好友Nees Jan van Eck(下面简称Van Eck, N.J)的影响,2人于2005年一起开始了科学知识图谱的研究。2008年10月,Ludo Waltman和Van Eck, N.J在CWTS参加了普赖斯奖获得者Anthony F. J. van Raan的学术讲座“Measuring Science”,并被Anthony F. J. van Raan发现具有很强的潜力[3]。在同意两位年轻学者继续在Erasmus University Rotterdam读博的情况下,2009年Ludo Waltman和Van Eck, N.J成为莱顿大学科学技术研究中心(CWTS)的兼职研究人员,科学计量也成为他的主要研究方向。2011年,在Anthony F. J. van Raan的努力下,两位青年学者共同加入了CWTS团队(同时引入两位同一方向的学者,对CWTS是艰难的决定),并继续从事科学知识图谱和学术评价的研究。
两位年轻学者毕业之后进一步在科学知识图谱领域做了大量的基础工作,在领域内产生了广泛的影响。鉴于Ludo Waltman在科学计量学领域的影响力,2014年9月,Ludo Waltman被爱思唯尔出版集团任命为Journal of Informetrics期刊的主编,后来因为开放引文(Open Citation)与爱思唯尔出版集团产生分歧,于2019年辞去主编一职,并在国际科学计量学和信息计量学学会(International Society for Scientometrics and Informetrics,简称ISSI)的支持下,于2019年1月成立了ISSI的新会刊Quantitative Science Studies。2018年7月16日,36岁的Ludo Waltman被莱顿大学任命为“科学、技术与创新”方向的教授,并带领团队从事“量化科学研究”(Quantitative Science Studies)。2018年9月,Ludo Waltman被任命为CWTS副主任(Deputy Director),并从2019年1月开始负责该中心的科学研究事业。同年10月,担任Research on Research Institute的副主任(Associate Director)。2021年,由于其在科学计量学研究上的卓越贡献,Scientometrics期刊授予其科学计量学领域的最高奖——普赖斯奖(Derek de Solla Price Medal)。Ludo Waltman也成为自1989年该奖项设立以来最年轻的获奖者。此外,Ludo Waltman在科学计量学具有高的学术影响力,2018-2021年连续四年入选科睿唯安社会科学领域的高被引学者。
2 数据采集与方法
2.1 数据采集
2022年3月3日,在Web of Science中以Ludo Waltman的Research ID:B-5561-2008 进行数据检索,共得到Ludo Waltman发表的99篇论文。对99篇论文的初步统计分析结果显示(如表1):论文的时间跨度为2005-2021年,论文主要来自SSCI和SCI-E数据库,以研究论文和会议论文为主。论文主要发表在信息科学与图书馆学、计算机科学与跨学科应用以及计算机科学与信息系统等领域。在所有论文中,第一作者论文为47篇,占比47.47%。论文的总被引次数达到了11 181次,去除自引的被引频次总计10 954次,H指数达到了40。Ludo Waltman的发文期刊主要是科学计量相关的三大期刊,依次为Journal of Informetrics(28篇,28.28%)、JASIST(12篇,12.12%)以及Scientometrics(8篇,8.08%)。此外,还有5篇论文发表在国际顶级期刊Nature和Science上。
表1 Ludo Waltman论文的基本情况
| 编号 | 指标名称 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 作者 | Ludo Waltman |
| Research ID | B-5561-2008 | |
| 2 | 时间跨度 | 2005-2021 |
| 3 | 论文数 | 99篇 |
| 第一作者论文数/占比 | 47篇/47.47% | |
| 独著论文数/占比 | 7篇/7.07%(2篇论文,5篇编辑材料) | |
| 4 | 收录分布 | SSCI(64篇);SCIE(50篇);CPCI-S(22篇);CPCI-SSH(17篇);ESCI(4篇) |
| 5 | 文献类型 | 研究论文(59篇,59.60%);会议论文(25篇,25.25%);编辑材料(11篇,11.11%); 书信(3篇,3.03%);综述论文(2篇,2.02%) |
| 6 | 主要领域 | 信息科学与图书馆学(66篇,66.67%);计算机科学与跨学科应用(54篇,54.55%); 计算机科学与信息系统(18篇,18.18%);多学科(11篇,11.11%) |
| 7 | 主要期刊 | Journal of Informetrics(28篇,28.28%);JASIST(12篇,12.12%);Scientometrics(8篇,8.08%);Nature(4篇),其中2篇书信,2篇编辑材料;Science(1篇) |
| 8 | 总被引次数/去除自引 | 11181次/ 10954次 |
| 9 | 篇均被引 | 112.94次(去除自引) |
| 10 | WoS施引文献数 | 7712篇 |
| 11 | H指数 | 40(占比40/99=40.4%) |
2.2 数据分析
本文对采集的Ludo Waltman论文数据使用科学计量分析方法和知识图谱方法进行分析。在研究中,采用Web of Science的引文扩展功能,对引用Ludo Waltman研究的施引文献进行分析,以了解其研究论文在引文层面的影响与传播。在科学计量维度上,对论文的时间产出趋势、引证趋势、地理发文量和引文量、高被引论文等进行了分析。从科学知识图谱的角度上,采用可视化的技术分析了Ludo Waltman的合作特征、基于关键词共现网络研究内容特征和施引文献内容特征等。在数据的分析和可视化中,使用自主开发的Bibliographic Analysis Tool 1.0软件和CWTS开发的VOSviewer软件[4]进行数据的预处理、数据统计与可视化分析。
3 学术画像分析结果
3.1 学术产出与影响
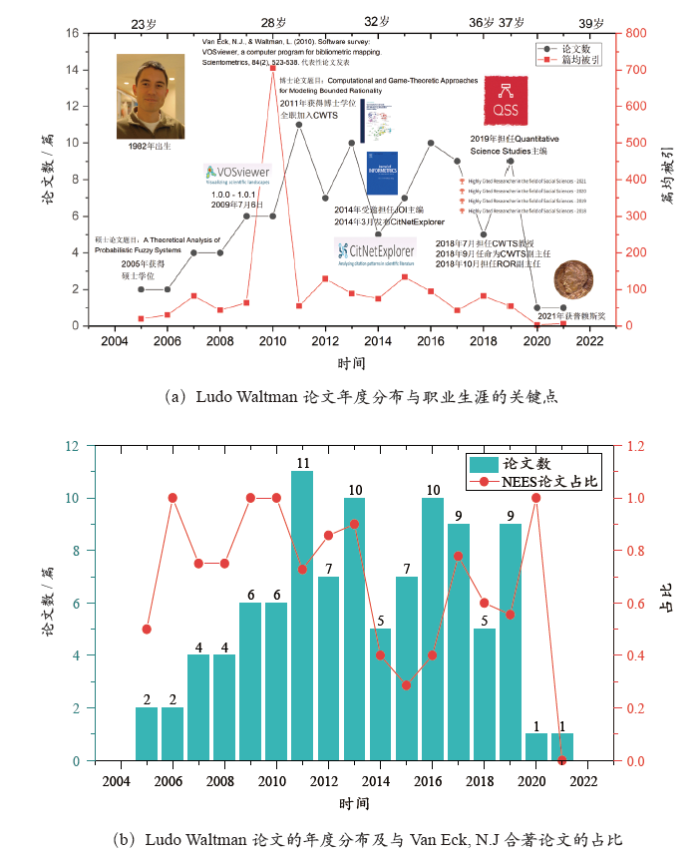
Ludo Waltman的论文年度产出如图1所示,在图1(a)的发文曲线图中标记了其学术生涯中的关键事件。分析结果显示,Ludo Waltman的发文呈现先增长后减少的趋势,见图1(b)。在硕士和博士阶段(2005-2011),其论文数呈显著增长趋势。在博士毕业之后,发文数量有一定下降,但仍然保持较高的产出。从2011年博士毕业到2018年获得教授职位,Ludo Waltman共发表了64篇学术论文,占到所有论文的64.6%。2019年虽然保持了高产,但在刚刚过去的两年里仅仅发表了2篇论文。这或反映了其在获得教授职位后,主要的精力或者重点有所调整。从其社交媒体上了解到,目前Ludo Waltman热衷于开放科学运动(Open Citation/Open Science/Open Reviews)和学术评价方面的工作。
图1
在2005-2021年这段学术生涯中,Van Eck, N.J是其最为密切的伙伴。两人从硕士、博士到CWTS一直保持合作,而这段时间恰是青年人学术和创造力最活跃时期。两人合作发表了大量原创性论文,特别是在科学知识图谱方向上,在一定程度上促进了科学计量学的发展。从二人合著论文的年度比例趋势来看,如图1(b),2005-2013年,合作论文占比虽然有一定波动,但变化并不显著。2014-2016年,Van Eck, N.J论文的比例降到了低谷,2017年以后又呈现了一定的增长趋势。
进一步对2005-2021年WoS核心库中引用Ludo Waltman的施引论文时间趋势进行分析,如图2。从2006-2021年,Ludo Waltman的论文他引共计7 468次。在时间趋势上,整体呈显著的指数增长趋势。在过去三年,每年的被引量都超过1 000次。其中,2021年的被引频次高达2 277次,平均每天被引6.2次。急剧增加的引证次数表征了Ludo Waltman的影响力不断增加。
图2
3.2 合著网络与影响
Ludo Waltman与16个国家或地区的学者建立了合作关系,按照合作论文数量的多少排名依次为美国(11篇)、瑞士(6篇)、斯洛文尼亚(3篇)、西班牙(3篇)、比利时 (2篇)、意大利 (2篇)、瑞典 (2篇)、澳大利亚(1篇)、加拿大 (1篇)、中国(1篇)、匈牙利(1篇)、南非(1篇)、韩国 (1篇)以及英国(1篇)。图3显示,2005-2022年,Ludo Waltman所发表的论文被120个不同的国家或地区引用,表明了Ludo Waltman的影响力在地理分布上的广泛性。其中,代表性的施引国家或地区有美国(1 451次)、中国(1 311次)、西班牙(894次)、英国(729次)、德国(598次)、荷兰(571次)、意大利(537次)、澳大利亚(425次)、巴西(395次)、加拿大(369次)、印度(340次)等。
图3
全球与Ludo Waltman合作的机构共有42个,合作论文数超过2篇的机构有荷兰鹿特丹伊拉斯姆斯大学(24篇)、美国科技战略公司(7篇)、瑞士洛桑联邦理工学院(5篇)、美国印第安纳大学(4篇)、荷兰代尔夫特理工大学(3篇)以及斯洛文尼亚卢布尔雅那大学(3篇)。在全球范围内,有5 709个机构引用了Ludo Waltman的研究论文。除莱顿大学外,代表性的施引机构有阿姆斯特丹大学(140次)、德国马普所(107次)、格拉纳达大学(106次)、中国科学院(92次)、鲁汶大学 (92次)、武汉大学 (92次)、巴仑西亚理工大学(88次)、阿尔梅里亚大学 (87次)、安特卫普大学(82次)以及智利大学(79次)等。
2005-2021年,Ludo Waltman的论文合著率达到了92.93%。其中,2人合作的论文数占比达到了42.42%,3位和4位合著作者的论文数量都为19篇,各自占比19.19%。全部74位合著作者与Ludo Waltman建立的合作网络如图4。从合作网络不难得出,Ludo Waltman目前已经在科学计量学领域与相关学者建立了广泛的合作关系。在这些合作关系中,与Van Eck, N.J的合作最为密切,二者的合著论文数达到了68篇,占Ludo Waltman论文总数的68.69%,其中以Van Eck, N.J为第一作者的论文为20篇,占比达20.2%。在其他合作者中,Van Raan Anthony F. J、Visser Martijn S以及Boyack Kevin W也与Ludo Waltman建立了较为密切的合作关系。
图4
在合作时间维度上,2005年,Ludo Waltman共发表了2篇论文,其中一篇是与其两位硕士生导师Kaymak Uzay和Jan van den Berg共同发表的论文《概率模糊分类器中的最大似然参数估计》[5],另一篇是与Van Eck, N.J以及Jan van den Berg共同发表的论文《一种新的概念关联可视化算法》,该论文也是Ludo Waltman在科学计量领域的第一篇论文[6]。表2列出了与Ludo Waltman合作发文排名前10的学者及其合著的平均年份。结果显示,近期,Ludo Waltman与Boyack Kevin W、Traag Vincent以及Colavizza Giovanni合作密切。
表2 Ludo Waltman的主要合作者
| 编号 | 作者 | 论文数/篇 | 总被引频次 | 平均发文年份 | 篇均被引频次 | 合作占比/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Waltman Ludo | 99 | 11181 | 2013.34 | 112.94 | 100.00 |
| 2 | Van Eck Nees Jan | 68 | 8885 | 2012.69 | 130.66 | 68.69 |
| 3 | Van Raan Anthony F. J | 8 | 944 | 2011.75 | 118.00 | 8.08 |
| 4 | Visser Martijn S | 8 | 880 | 2012.88 | 110.00 | 8.08 |
| 5 | Boyack Kevin W | 7 | 106 | 2017.57 | 15.14 | 7.07 |
| 6 | Kaymak Uzay | 7 | 138 | 2008.00 | 19.71 | 7.07 |
| 7 | Traag Vincent | 7 | 455 | 2018.86 | 65.00 | 7.07 |
| 8 | Van Leeuwen Thed N | 7 | 866 | 2011.86 | 123.71 | 7.07 |
| 9 | Colavizza Giovanni | 6 | 96 | 2017.67 | 16.00 | 6.06 |
| 10 | Wouters Paul | 6 | 1024 | 2014.67 | 170.67 | 6.06 |
在论文影响力维度上,Ludo Waltman与Van Eck, N.J合著论文的被引频次累计达到了8 885次,占Ludo Waltman总被引频次的79.47%。其中,Van Eck, N.J作为第一作者的论文Software Survey: VOSviewer, a Computer Program for Bibliometric Mapping在Ludo Waltman论文中位列被引频次第一位,累计被引达到了3 114次,占比26.37%。这进一步表明了Van Eck, N.J在Ludo Waltman学术影响力中的重要贡献。在论文的篇均被引维度上,Ludo Waltman与Wouters Paul合著的6篇论文(包括两篇Nature论文)篇均被引达到了170.67次。其中,2015年发表在Nature的The Leiden Manifesto for Research Metrics(《莱顿宣言》)一文被引达到了710次,是引文量的主要贡献者。
3.3 研究主题与传播主题
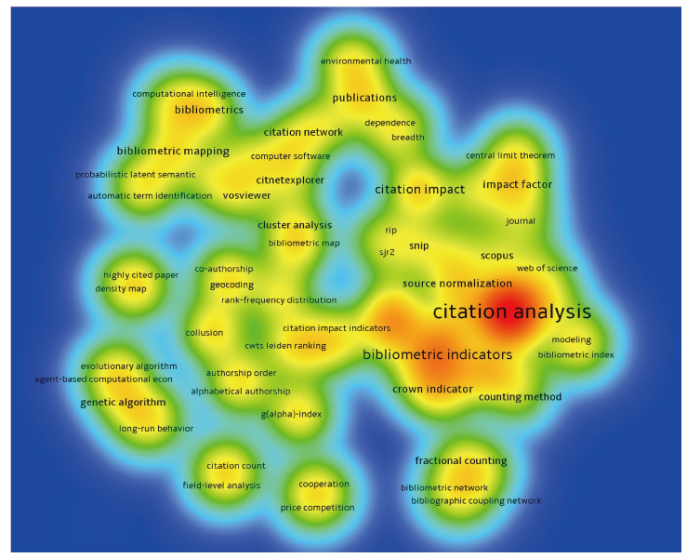
对Ludo Waltman的99篇论文的关键词进行消歧处理,最后得到的关键词列表共包含129个关键词。对关键词共现进行分析,得到关键词密度图(图5)。关键词词频结果显示,仅仅出现了1次的关键词数量达到了105个,占比达81.40%。词频为2的关键词数量13个,占比10.08%。排名前10的关键词的词频都超过了2次,包含citation analysis(引文分析,14次)、bibliometric indicators(文献计量指标,6次)、field normalization(领域标准化,6次)、citation impact(引文影响力,4次)以及normalization(标准化,4次)、bibliometric mapping(文献计量图谱,3次)、bibliometrics(文献计量,3次)、crown indicator(皇冠指数,3次)、impact factor(影响因子,3次)、publications(出版物,3次)以及source normalization(来源标准化,3次)。从关键词集聚特征也不难得出,Ludo Waltman的研究围绕引文分析(citation analysis)开展了大量科技评价的研究工作,涉及的研究关键词有文献计量指标、领域标准化、皇冠指数以及影响因子等。此外,以bibliometric mapping和publications为核心,分别形成了科学知识图谱研究和出版物网络分析的群落。在科学知识图谱的关键词网络中,涉及的相关关键词有VOSviewer, CitNetExplorer以及science mapping等。在论文主题影响力维度上,论文中科学知识图谱研究的关键词具有显著的引文影响力。
图5
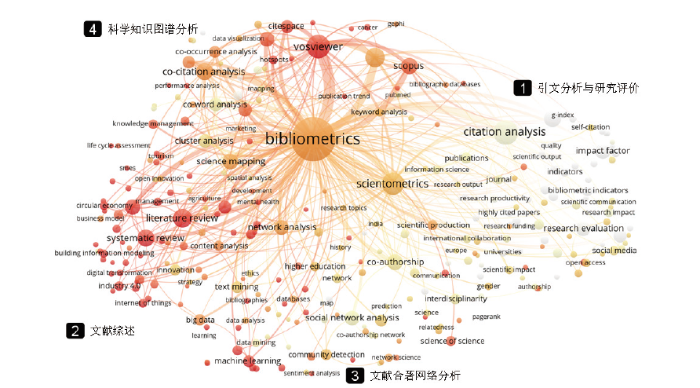
对引用了Ludo Waltman的7 000余篇论文的关键词进行分析,提取了出现频次不小于10次的295个关键词,结果如图6。从分析的结果来看,施引文献的主题可以分为4个方面,分别为引文分析与研究评价、文献综述、文献合著网络分析以及科学知识图谱分析。从引用的趋势来看,目前引用Ludo Waltman论文最为活跃的主题分布在“科学知识图谱和文献综述”中。这反映了Ludo Waltman 和Van Eck, N.J开发的VOSviewer已经成为文献图谱中重要的分析工具,且被大量应用在文献综述的研究中。
图6
3.4 引文分析
3.4.1 Ludo Waltman高被引论文分析
图7展示了Ludo Waltman的99篇论文的被引分布。从分析结果来看,引证次数呈现了极大的不平衡,少数论文贡献了其大多数的引证量。正如前文提到的,排名第一的论文所贡献的引文量达到了26.37%。前20%的论文所贡献的引文量达到了76.38%,h-核论文(40篇论文)所贡献的引文量达到了89.40%。表3列出了Ludo Waltman被引频次TOP10论文。从分析结果来看,以Ludo Waltman为第一作者的4篇论文中,除一篇为综述论文外,其他都是研究论文,都是对创新方法的研究。在所有论文中,涉及网络聚类的有4篇。此外还包含一篇发表在Nature上的社论和一篇发表在Science上的综述性长文。
图7
进一步对Ludo Waltman的40篇h-核论文进行文献的耦合分析,如图8。40篇论文通过耦合聚类分析形成了3个方向,分别为#1 科技评价及应用、#2 科学知识图谱和#3 网络聚类分析。在科技评价的研究中,Ludo Waltman的研究内容涉及引文影响力分析与数据标准化[7⇓-9]、Leiden大学排名[10]、h指数[11]以及皇冠指数[12,13]的研究和完善等。在网络聚类分析中,Ludo Waltman等开发或者改进了网络的聚类分析方法,并很好地应用在了对引文网络的聚类中。例如,设计了新的聚类算法,包括Leiden聚类算法[14]和smart local moving算法[15]。并在新的聚类算法的基础上,开发了CitNetExplorer[16]并优化和补充了VOSviewer[17]中基于引证的文献聚类功能。科学知识图谱的研究是Ludo Waltman与Van Eck, N.J涉足最早的领域,该聚类中的文献也组成了当前VOSviewer的基础。在该聚类中,最具影响力的论文为2010年由Van Eck, N.J和Ludo Waltman共同在Scientometrics发表的系统介绍VOSviewer功能的论文[18]。该论文介绍了VOSviewer的核心算法、核心功能以及优势,成为后来进行科学知识图谱研究或使用VOSviewer绘制科学知识图谱的基础论文。此外,Van Eck, N.J和Ludo Waltman对若干知识图谱绘制的基础问题进行了研究和分析,包括知识单元的相似可视化算法(VOS)[19]、图谱映射和聚类的一体化[20]、矩阵的标准化方法[21]、知识单元的映射方法[22]、文献图谱中的计数[23]等。
表3 Ludo Waltman被引频次排名前10的论文
| 序号 | 标题 | 来源刊物 | 发文时间 | 单篇被引频次 | 累计被引频次 | 累计占比/% | 第一作者 | 论文亮点 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping《软件调查:VOS viewer一个用户文献图谱的软件》 | Scientometrics 《科学计量学》 | 2010 | 3114 | 3114 | 26.37 | van Eck NJ | 设计开发的新兴VOSviewer软件的全面介绍 |
| 2 | The Leiden Manifesto for research metrics《莱顿研究计量宣言》 | Nature 《自然》 | 2015 | 710 | 3824 | 32.38 | Hicks D | 莱顿宣言提出了基于计量评价的若干注意事项。 |
| 3 | A unified approach to mapping and clustering of bibliometric networks《文献计量网络图谱映射与聚类的一体化》 | Journal of Informetrics 《信息计量学》 | 2010 | 625 | 4449 | 37.67 | Waltman L | 完善了文献网络的映射和聚类算法。 |
| 4 | A review of the literature on citation impact indicators《引文影响指标的文献综述》 | Journal of Informetrics 《信息计量学》 | 2016 | 440 | 4889 | 41.39 | Waltman L | 全面综述了基于引文的评价指标 |
| 5 | From Louvain to Leiden: guaranteeing well-connected communities《从鲁汶到莱顿:保证连接良好的社群》 | Scientific Reports 《科学报告》 | 2019 | 427 | 5316 | 45.01 | Traag VA | 提出了新的聚类算法——莱顿算法 |
| 6 | A smart local moving algorithm for large-scale modularity-based community detection《基于大规模模块化的社区检测的智能局部移动算法》 | European Physical Journal B 《欧洲物理学报B》 | 2013 | 362 | 5678 | 48.07 | Waltman L | 提出了新的聚类算法smart local moving |
| 7 | Citation-based clustering of publications using CitNetExplorer and VOSviewer《使用CitNetExplorer和VOSviewer对出版物进行基于引文的聚类》 | Scientometrics 《科学计量学》 | 2017 | 336 | 6014 | 50.92 | van Eck NJ | 在软件VOSviewer和CitNetExplorer 中实现了引文网络分析 |
| 8 | Science of science《科学学》 | Science 《科学》 | 2018 | 332 | 6346 | 53.73 | Fortunato S | 在Science上发表的科学学的综述性论文,凸显了量化科学分析在科学学研究中的重要价值。 |
| 9 | How to Normalize Cooccurrence Data? An Analysis of Some Well-Known Similarity Measures《如何对共现数据进行标准化:对一些知名相似性测度的分析》 | JASIST 《信息科学技术学会会刊》 | 2009 | 324 | 6670 | 56.47 | van Eck NJ | 对科学计量共现矩阵的标准化问题进行了系统的研究,并提出了VOS标准化方法。 |
| 10 | A new methodology for constructing a publication-level classification system of science《构建出版物级科学分类系统的新方法》 | JASIST 《信息科学技术学会会刊》 | 2012 | 297 | 6967 | 58.99 | Waltman L | 研究了在论文层面科学领域分类。 |
图8
3.4.2 Ludo Waltman高被引参考文献分析
图9
表4 Ludo Waltman所引用了的主要参考文献
| 序号 | 第一作者 | 期刊 | 发文时间 | 论文标题 | 被引频次 | 所属聚类 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Waltman L | JASIST | 2012 | A new methodology for constructing a publication-level classification system of science《构建出版物级科学分类系统的新方法》 | 19 | 3 | [24] |
| 2 | Van Eck NJ | Scientometrics | 2010 | Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping《软件调查:VOS viewer一个用户文献图谱的软件》 | 18 | 3 | [18] |
| 3 | Waltman L | Journal of Informetrics | 2011 | Towards a new crown indicator: Some theoretical considerations《关于新冠指数的一些理论思考》 | 18 | 1 | [12] |
| 4 | Hirsch JE | PNAS | 2005 | An index to quantify an individual’s scientific research output《量化个人科研产出的指数》 | 16 | 1 | [25] |
| 5 | Van Eck NJ | PLoS One | 2013 | Citation Analysis May Severely Underestimate the Impact of Clinical Research as Compared to Basic Research《与基础研究相比,引文分析可能严重低估了临床研究的影响》 | 11 | 1 | [26] |
| 6 | Zitt M | JASIST | 2008 | Modifying the journal impact factor by fractional citation weighting: The audience factor《通过分数引用权重修改期刊影响因子:受众因子》 | 11 | 1 | [27] |
| 7 | Lundberg J | Journal of Informetrics | 2007 | Lifting the crown—citation z-score《提高皇冠引用z分数》 | 10 | 1 | [28] |
| 8 | Peters HPF | Res Policy | 1993 | Co-word-based science maps of chemical engineering. Part I: Representations by direct multidimensional scaling《基于共词的化学工程图谱. 第一部分:通过直接的多维尺度进行表述》 | 10 | 2 | [29] |
| 9 | Waltman L | Journal of Informetrics | 2010 | A unified approach to mapping and clustering of bibliometric networks《文献计量网络图谱映射与聚类的一体化》 | 10 | 3 | [20] |
4 总结与讨论
4.1 总结
本文对2021年普赖斯奖获得者Ludo Waltman所发表的学术论文进行了科学计量学与知识图谱分析,绘制了该学者的学术画像。作为国际科学计量学领域获得普赖斯奖最年轻的学者,他的全面学术画像对我国青年科学计量学学者有重要的学习价值。现对本研究的结果总结如下。
(1)WoS核心合集收录了2005-2021年的Ludo Waltman的各类学术论文99篇,其中,第一作者论文占比为47.47%,合作论文占比92.93%。论文主要聚焦信息科学与图书馆学以及计算机科学与跨学科应用领域,主要刊载在Journal of Informetrics、JASIST和Scientometrics期刊上。在2005-2021年的职业生涯中,Van Eck, N.J是其最重要的合作伙伴,二人合作发文量达到Ludo Waltman论文总量的68.68%,合作论文的被引次数贡献了Ludo Waltman所有论文引证次数的79.47%。
(2)Ludo Waltman虽然在全球范围内与相关国家或地区以及机构建立了广泛的合作关系,但合作强度比较弱,主要还是以机构内部合作为主。作为年轻学者,Ludo Waltman的论文被WoS核心库引用7 712次,引用来自120个国家或地区的3 000多家机构,2018-2021年,他连续4次荣膺科睿唯安的全球社会科学领域高被引学者。作为科学计量学领域的新星,在获得普赖斯奖后,其未来势必会吸引越来越多的合作者,无论是合作论文数还是影响力都将得到进一步提升。
(3)Ludo Waltman的论文聚焦以引文分析为核心的学术评价研究和知识图谱分析。研究结果显示,其涉及科学知识图谱的研究具有显著影响力。这一领域是Ludo Waltman和Van Eck, N.J两人较早开展的研究领域,不仅持续时间长,且在方法和工具上都有所突破,因而被科学计量领域内外广泛引用。40篇h-核论文表明Ludo Waltman 的高影响力论文主要来自科技评价及应用、网络聚类分析和科学知识图谱。其引用参考文献聚类与其所发表的论文聚类类似,主要集中在科技评价及应用、图谱绘制技术与应用以及图谱绘制原理。从其高被引论文的实际贡献来讲,这些论文是在其强大的数理能力背景下完成的,在科学计量领域具有较高的原创性和影响力。
4.2 讨论
Ludo Waltman因为与Van Eck, N.J的相识而进入科学计量学领域,又因为参加Anthony F. J. van Raan的学术讲座而有机会获得CWTS的研究职位。从分析结果来看,Ludo Waltman能从经济计量学向科学计量学成功转型,主要有以下两大要素:一方面,Ludo Waltman的成就与Van Eck, N.J的贡献密不可分,因为Ludo Waltman在科学计量学领域的知名度是通过科学知识图谱获得的,而这正是Van Eck, N.J在硕士和博士期间的主要工作。笔者曾经在2018年预测,他们作为科学计量学领域新的双子星,共同获得普赖斯奖是指日可待的[4]。另一方面,Ludo Waltman的成功还在于其具有很强的数理能力,这在他所发表的科技评价数理模型和网络聚类算法设计中可见一斑。深厚的数理基础使得Ludo Waltman在科学计量学领域具备了很强的竞争力。这也为科学计量学领域的青年科研人员带来一定的启示。两位年轻学者能在科学计量学领域迅速成长并拥有知名度,与当时科学计量学领域发展迅速且科学知识图谱极具应用前景有关。追踪研究热点能让年轻学者迅速在领域内建立起一定的显示度,但要成为知名学者还需要具有深厚的内在基础,比如在科学计量学领域中,“大学者”不是在数理上超出同行(如:Wolfgang Glänzel,Ronald Rousseau以及Leo Egghe等),就是在理论上超过同行(如:Robert K. Merton),深厚的数理基础和理论修养是可持续成长的关键,否则只能昙花一现。
致谢
感谢武夷山研究员在论文撰写过程中的研究建议,感谢张琳教授对初稿的审阅与建议。
参考文献
Laudation on the occasion of the presentation of the Derek de Solla Price Award 2021 to Prof. Ludo Waltman at the ISSI conference, Leuven, 2021
[J].
A review of the literature on citation impact indicators
[J].
A systematic empirical comparison of different approaches for normalizing citation impact indicators
[J].
Source normalized indicators of citation impact: an overview of different approaches and an empirical comparison
[J].
The Leiden ranking 2011/2012: Data collection, indicators, and interpretation
[J].
The Inconsistency of the h-index
[J].
Towards a new crown indicator: Some theoretical considerations
[J].
Towards a new crown indicator: an empirical analysis
[J].We present an empirical comparison between two normalization mechanisms for citation-based indicators of research performance. These mechanisms aim to normalize citation counts for the field and the year in which a publication was published. One mechanism is applied in the current so-called crown indicator of our institute. The other mechanism is applied in the new crown indicator that our institute is currently exploring. We find that at high aggregation levels, such as at the level of large research institutions or at the level of countries, the differences between the two mechanisms are very small. At lower aggregation levels, such as at the level of research groups or at the level of journals, the differences between the two mechanisms are somewhat larger. We pay special attention to the way in which recent publications are handled. These publications typically have very low citation counts and should therefore be handled with special care.
From Louvain to Leiden: guaranteeing well-connected communities
[J].Community detection is often used to understand the structure of large and complex networks. One of the most popular algorithms for uncovering community structure is the so-called Louvain algorithm. We show that this algorithm has a major defect that largely went unnoticed until now: the Louvain algorithm may yield arbitrarily badly connected communities. In the worst case, communities may even be disconnected, especially when running the algorithm iteratively. In our experimental analysis, we observe that up to 25% of the communities are badly connected and up to 16% are disconnected. To address this problem, we introduce the Leiden algorithm. We prove that the Leiden algorithm yields communities that are guaranteed to be connected. In addition, we prove that, when the Leiden algorithm is applied iteratively, it converges to a partition in which all subsets of all communities are locally optimally assigned. Furthermore, by relying on a fast local move approach, the Leiden algorithm runs faster than the Louvain algorithm. We demonstrate the performance of the Leiden algorithm for several benchmark and real-world networks. We find that the Leiden algorithm is faster than the Louvain algorithm and uncovers better partitions, in addition to providing explicit guarantees.
A smart local moving algorithm for large-scale modularity-based community detection
[J].
CitNetExplorer: A new software tool for analyzing and visualizing citation networks
[J].
Citation-based clustering of publications using CitNetExplorer and VOSviewer
[J].Clustering scientific publications in an important problem in bibliometric research. We demonstrate how two software tools, CitNetExplorer and VOSviewer, can be used to cluster publications and to analyze the resulting clustering solutions. CitNetExplorer is used to cluster a large set of publications in the field of astronomy and astrophysics. The publications are clustered based on direct citation relations. CitNetExplorer and VOSviewer are used together to analyze the resulting clustering solutions. Both tools use visualizations to support the analysis of the clustering solutions, with CitNetExplorer focusing on the analysis at the level of individual publications and VOSviewer focusing on the analysis at an aggregate level. The demonstration provided in this paper shows how a clustering of publications can be created and analyzed using freely available software tools. Using the approach presented in this paper, bibliometricians are able to carry out sophisticated cluster analyses without the need to have a deep knowledge of clustering techniques and without requiring advanced computer skills.
Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping
[J].We present VOSviewer, a freely available computer program that we have developed for constructing and viewing bibliometric maps. Unlike most computer programs that are used for bibliometric mapping, VOSviewer pays special attention to the graphical representation of bibliometric maps. The functionality of VOSviewer is especially useful for displaying large bibliometric maps in an easy-to-interpret way. The paper consists of three parts. In the first part, an overview of VOSviewer's functionality for displaying bibliometric maps is provided. In the second part, the technical implementation of specific parts of the program is discussed. Finally, in the third part, VOSviewer's ability to handle large maps is demonstrated by using the program to construct and display a co-citation map of 5,000 major scientific journals.
A unified approach to mapping and clustering of bibliometric networks
[J].
How to Normalize Cooccurrence Data? An Analysis of Some Well-Known Similarity Measures
[J].
A comparison of two techniques for bibliometric mapping: Multidimensional scaling and VOS
[J].
Constructing bibliometric networks: A comparison between full and fractional counting
[J].
A new methodology for constructing a publication-level classification system of science
[J].
An index to quantify an individual’s scientific research output
[J].
Citation analysis may severely underestimate the impact of clinical research as compared to basic research
Modifying the journal impact factor by fractional citation weighting: The audience factor
[J].
Lifting the crown—citation z-score
[J].